- Estrogen receptor
-
estrogen receptor 1 (ER-alpha) 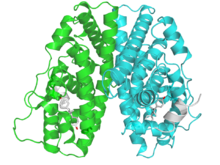
A dimer of the ligand-binding region of ERα (PDB rendering based on 3erd). Identifiers Symbol ESR1 Alt. symbols ER-α, NR3A1 Entrez 2099 HUGO 3467 OMIM 133430 PDB 1ERE RefSeq NM_000125 UniProt P03372 Other data Locus Chr. 6 q24-q27 estrogen receptor 2 (ER-beta) 
A dimer of the ligand-binding region of ERβ (PDB rendering based on 1u3s). Identifiers Symbol ESR2 Alt. symbols ER-β, NR3A2 Entrez 2100 HUGO 3468 OMIM 601663 PDB 1QKM RefSeq NM_001040275 UniProt Q92731 Other data Locus Chr. 14 q21-q22 Estrogen receptor refers to a group of receptors that are activated by the hormone 17β-estradiol[1] (estrogen). Two types of estrogen receptor exist: ER, which is a member of the nuclear hormone family of intracellular receptors, and the estrogen G protein-coupled receptor GPR30 (GPER), which is a G protein-coupled receptor. This article refers to the nuclear hormone receptor ER.
The main function of the estrogen receptor is as a DNA-binding transcription factor that regulates gene expression. However, the estrogen receptor has additional functions independent of DNA binding.[2]
Contents
Proteomics
There are two different forms of the estrogen receptor, usually referred to as α and β, each encoded by a separate gene (ESR1 and ESR2, respectively). Hormone-activated estrogen receptors form dimers, and, since the two forms are coexpressed in many cell types, the receptors may form ERα (αα) or ERβ (ββ) homodimers or ERαβ (αβ) heterodimers.[3] Estrogen receptor alpha and beta show significant overall sequence homology, and both are composed of five domains (listed from the N- to C-terminus; amino acid sequence numbers refer to human ER):(A-F domain)
The N-terminal A/B domain is able to transactivate gene transcription in the absence of bound ligand (e.g., the estrogen hormone). While this region is able to activate gene transcription without ligand, this activation is weak and more selective compared to the activation provided by the E domain. The C domain, also known as the DNA-binding domain, binds to estrogen response elements in DNA. The D domain is a hinge region that connects the C and E domains. The E domain contains the ligand binding cavity as well as binding sites for coactivator and corepressor proteins. The E-domain in the presence of bound ligand is able to activate gene transcription. The C-terminal F domain function is not entirely clear and is variable in length.
Estrogen receptor alpha
N-terminal AF1 domainIdentifiers Symbol Oest_recep Pfam PF02159 InterPro IPR001292 SCOP 1hcp Available protein structures: Pfam structures PDB RCSB PDB; PDBe PDBsum structure summary Estrogen and estrogen related receptor C-terminal domain Identifiers Symbol ESR1_C Pfam PF12743 Available protein structures: Pfam structures PDB RCSB PDB; PDBe PDBsum structure summary Due to alternative RNA splicing, several ER isoforms are known to exist. At least three ERalpha and five ERbeta isoforms have been identified. The ERbeta isoforms receptor subtypes can transactivate transcription only when a heterodimer with the functional ERß1 receptor of 59 kDa is formed. The ERß3 receptor was detected at high levels in the testis. The two other ERalpha isoforms are 36 and 46kDa.[4][5]
Only in fish, but not in humans, an ERgamma receptor has been described.[6]
Genetics
The two forms of the estrogen receptor are encoded by different genes, ESR1 and ESR2 on the sixth and fourteenth chromosome (6q25.1 and 14q23.2), respectively.
Distribution
Both ERs are widely expressed in different tissue types, however there are some notable differences in their expression patterns:[7]
- The ERα is found in endometrium, breast cancer cells, ovarian stroma cells, and the hypothalamus.[8] In males, ERα protein is found in the epithelium of the efferent ducts.[9]
- The expression of the ERβ protein has been documented in kidney, brain, bone, heart,[10] lungs, intestinal mucosa, prostate, and endothelial cells.
The ERs are regarded to be cytoplasmic receptors in their unliganded state, but visualization research has shown that a fraction of the ERs resides in the nucleus.[11] The "ERα" primary transcript gives rise to several alternatively spliced variants of unknown function.[12]
Binding and functional selectivity
The ER's helix 12 domain plays a crucial role in determining interactions with coactivators and corepressors and, therefore, the respective agonist or antagonist effect of the ligand.[13][14]
Different ligands may differ in their affinity for alpha and beta isoforms of the estrogen receptor:
- 17-beta-estradiol binds equally well to both receptors
- estrone, and raloxifene bind preferentially to the alpha receptor
- estriol, and genistein to the beta receptor
Subtype selective estrogen receptor modulators preferentially bind to either the α- or the β-subtype of the receptor. In addition, the different estrogen receptor combinations may respond differently to various ligands, which may translate into tissue selective agonistic and antagonistic effects.[15] The ratio of α- to β- subtype concentration has been proposed to play a role in certain diseases.[16]
The concept of selective estrogen receptor modulators is based on the ability to promote ER interactions with different proteins such as transcriptional coactivator or corepressors. Furthermore, the ratio of coactivator to corepressor protein varies in different tissues.[17] As a consequence, the same ligand may be an agonist in some tissue (where coactivators predominate) while antagonistic in other tissues (where corepressors dominate). Tamoxifen, for example, is an antagonist in breast and is, therefore, used as a breast cancer treatment[18] but an ER agonist in bone (thereby preventing osteoporosis) and a partial agonist in the endometrium (increasing the risk of uterine cancer) .
Signal transduction
Since estrogen is a steroidal hormone, it can pass through the phospholipid membranes of the cell, and receptors therefore do not need to be membrane-bound in order to bind with estrogen.
Genomic
In the absence of hormone, estrogen receptors are largely located in the cytosol. Hormone binding to the receptor triggers a number of events starting with migration of the receptor from the cytosol into the nucleus, dimerization of the receptor, and subsequent binding of the receptor dimer to specific sequences of DNA known as hormone response elements. The DNA/receptor complex then recruits other proteins that are responsible for the transcription of downstream DNA into mRNA and finally protein that results in a change in cell function. Estrogen receptors also occur within the cell nucleus, and both estrogen receptor subtypes have a DNA-binding domain and can function as transcription factors to regulate the production of proteins.
The receptor also interacts with activator protein 1 and Sp-1 to promote transcription, via several coactivators such as PELP-1.[2]
Nongenomic
Some estrogen receptors associate with the cell surface membrane and can be rapidly activated by exposure of cells to estrogen.[19][20]
In addition, some ER may associate with cell membranes by attachment to caveolin-1 and form complexes with G proteins, striatin, receptor tyrosine kinases (e.g., EGFR and IGF-1), and non-receptor tyrosine kinases (e.g., Src).[2][19] Through striatin, some of this membrane bound ER may lead to increased levels of Ca2+ and nitric oxide (NO).[21] Through the receptor tyrosine kinases, signals are sent to the nucleus through the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK/ERK) pathway and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (Pl3K/AKT) pathway.[22] Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK)-3β inhibits transcription by nuclear ER by inhibiting phosphorylation of serine 118 of nuclear ERα. Phosphorylation of GSK-3β removes its inhibitory effect, and this can be achieved by the PI3K/AKT pathway and the MAPK/ERK pathway, via rsk.
17β-Estradiol has been shown to activate the G protein-coupled receptor GPR30.[23] However the subcellular localization and role of this receptor are still object of controversy.[24]
Disease
 Nolvadex (tamoxifen) 20 mg
Nolvadex (tamoxifen) 20 mg
 Arimidex (anastrozole) 1 mg
Arimidex (anastrozole) 1 mg
Cancer
Estrogen receptors are over-expressed in around 70% of breast cancer cases, referred to as "ER-positive". Two hypotheses have been proposed to explain why this causes tumorigenesis, and the available evidence suggests that both mechanisms contribute:
- First, binding of estrogen to the ER stimulates proliferation of mammary cells, with the resulting increase in cell division and DNA replication, leading to mutations.
- Second, estrogen metabolism produces genotoxic waste.
The result of both processes is disruption of cell cycle, apoptosis and DNA repair, and, therefore, tumour formation. ERα is certainly associated with more differentiated tumours, while evidence that ERβ is involved is controversial. Different versions of the ESR1 gene have been identified (with single-nucleotide polymorphisms) and are associated with different risks of developing breast cancer.[18]
Endocrine therapy for breast cancer involves selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMS), such as tamoxifen, which behave as ER antagonists in breast tissue, or aromatase inhibitors, such as anastrozole. ER status is used to determine sensitivity of breast cancer lesions to tamoxifen and aromatase inhibitors.[25] Another SERM, raloxifene, has been used as a preventative chemotherapy for women judged to have a high risk of developing breast cancer.[26] Another chemotherapeutic anti-estrogen, ICI 182,780 (Faslodex), which acts as a complete antagonist, also promotes degradation of the estrogen receptor.
Estrogen and the ERs have also been implicated in breast cancer, ovarian cancer, colon cancer, prostate cancer, and endometrial cancer. Advanced colon cancer is associated with a loss of ERβ, the predominant ER in colon tissue, and colon cancer is treated with ERβ-specific agonists.[27]
Aging
Studies in female mice have shown that estrogen receptor-alpha declines in the pre-optic hypothalamus as they grow old. Female mice that were given a calorically restricted diet during the majority of their lives maintained higher levels of ERα in the pre-optic hypothalamus than their non-calorically restricted counterparts.[8]
Obesity
A dramatic demonstration of the importance of estrogens in the regulation of fat deposition comes from transgenic mice that were genetically engineered to lack a functional aromatase gene. These mice have very low levels of estrogen and are obese.[28] Obesity was also observed in estrogen deficient female mice lacking the follicle-stimulating hormone receptor.[29] The effect of low estrogen on increased obesity has been linked to estrogen receptor alpha.[30]
Research history
Estrogen receptors were first identified by Elwood V. Jensen at the University of Chicago in 1958,[31][32] for which Jensen was awarded the Lasker Award.[33] The gene for a second estrogen receptor (ERβ) was identified in 1996 by Kuiper et al. in rat prostate and ovary using degenerate ERalpha primers.[34]
References
- ^ Dahlman-Wright K, Cavailles V, Fuqua SA, Jordan VC, Katzenellenbogen JA, Korach KS, Maggi A, Muramatsu M, Parker MG, Gustafsson JA (2006). "International Union of Pharmacology. LXIV. Estrogen receptors". Pharmacol. Rev. 58 (4): 773–81. doi:10.1124/pr.58.4.8. PMID 17132854.
- ^ a b c Levin ER (2005). "Integration of the extranuclear and nuclear actions of estrogen". Mol. Endocrinol. 19 (8): 1951–9. doi:10.1210/me.2004-0390. PMC 1249516. PMID 15705661. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1249516.
- ^ Li X, Huang J, Yi P, Bambara RA, Hilf R, Muyan M (2004). "Single-chain estrogen receptors (ERs) reveal that the ERalpha/beta heterodimer emulates functions of the ERalpha dimer in genomic estrogen signaling pathways". Mol. Cell. Biol. 24 (17): 7681–94. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.17.7681-7694.2004. PMC 506997. PMID 15314175. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=506997.
- ^ Nilsson S, Mäkelä S, Treuter E, et al. (October 2001). "Mechanisms of estrogen action". Physiol Rev 81 (4): 1535–65. PMID 11581496. http://physrev.physiology.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=11581496.
- ^ Leung YK, Mak P, Hassan S, Ho SM (August 2006). "Estrogen receptor (ER)-beta isoforms: a key to understanding ER-beta signaling". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103 (35): 13162–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.0605676103. PMC 1552044. PMID 16938840. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1552044.
- ^ Hawkins MB, Thornton JW, Crews D, Skipper JK, Dotte A, Thomas P (September 2000). "Identification of a third distinct estrogen receptor and reclassification of estrogen receptors in teleosts". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97 (20): 10751–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.20.10751. PMC 27095. PMID 11005855. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=27095.
- ^ Couse JF, Lindzey J, Grandien K, Gustafsson JA, Korach KS (November 1997). "Tissue distribution and quantitative analysis of estrogen receptor-alpha (ERalpha) and estrogen receptor-beta (ERbeta) messenger ribonucleic acid in the wild-type and ERalpha-knockout mouse". Endocrinology 138 (11): 4613–21. doi:10.1210/en.138.11.4613. PMID 9348186.
- ^ a b Yaghmaie F, Saeed O, Garan SA, Freitag W, Timiras PS, Sternberg H (2005). "Caloric restriction reduces cell loss and maintains estrogen receptor-alpha immunoreactivity in the pre-optic hypothalamus of female B6D2F1 mice". Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 26 (3): 197–203. PMID 15990721. http://www.nel.edu/pdf_/26_3/260305A01_15990721_Yaghmaie_.pdf.
- ^ Hess, RA (2003). "Estrogen in the adult male reproductive tract: A review". Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology 1 (52): 52. doi:10.1186/1477-7827-1-52. PMC 179885. PMID 12904263. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=179885.
- ^ Babiker FA, De Windt LJ, van Eickels M, Grohe C, Meyer R, Doevendans PA (2002). "Estrogenic hormone action in the heart: regulatory network and function". Cardiovasc. Res. 53 (3): 709–19. doi:10.1016/S0008-6363(01)00526-0. PMID 11861041. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/s0008636301005260.
- ^ Htun H, Holth LT, Walker D, Davie JR, Hager GL (1 February 1999). "Direct visualization of the human estrogen receptor alpha reveals a role for ligand in the nuclear distribution of the receptor". Mol Biol Cell 10 (2): 471–86. PMC 25181. PMID 9950689. http://www.molbiolcell.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=9950689.
- ^ Pfeffer U, Fecarotta E, Vidali G (15 May 1995). "Coexpression of multiple estrogen receptor variant messenger RNAs in normal and neoplastic breast tissues and in MCF-7 cells". Cancer Res 55 (10): 2158–65. PMID 7743517.
- ^ Ascenzi P, Bocedi A, Marino M (August 2006). "Structure-function relationship of estrogen receptor alpha and beta: impact on human health". Mol Aspects Med 27 (4): 299–402. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2006.07.001. PMID 16914190.
- ^ Bourguet W, Germain P, Gronemeyer H (October 2000). "Nuclear receptor ligand-binding domains: three-dimensional structures, molecular interactions and pharmacological implications". Trends Pharmacol Sci 21 (10): 381–8. doi:10.1016/S0165-6147(00)01548-0. PMID 11050318.
- ^ Kansra S, Yamagata S, Sneade L, Foster L, Ben-Jonathan N (2005). "Differential effects of estrogen receptor antagonists on pituitary lactotroph proliferation and prolactin release". Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 239 (1-2): 27–36. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2005.04.008. PMID 15950373.
- ^ Bakas P, Liapis A, Vlahopoulos S, Giner M, Logotheti S, Creatsas G, Meligova AK, Alexis MN, Zoumpourlis V (December 2007). "Estrogen receptor alpha and beta in uterine fibroids: a basis for altered estrogen responsiveness". Fertil. Steril. 90 (5): 1878–85. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2007.09.019. PMID 18166184.
- ^ Shang Y, Brown M (2002). "Molecular determinants for the tissue specificity of SERMs". Science 295 (5564): 2465–8. doi:10.1126/science.1068537. PMID 11923541.
- ^ a b Deroo BJ, Korach KS (2006). "Estrogen receptors and human disease". J. Clin. Invest. 116 (3): 561–7. doi:10.1172/JCI27987. PMC 2373424. PMID 16511588. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2373424.
- ^ a b Zivadinovic D, Gametchu B, Watson CS (2005). "Membrane estrogen receptor-alpha levels in MCF-7 breast cancer cells predict cAMP and proliferation responses". Breast Cancer Res. 7 (1): R101–12. doi:10.1186/bcr958. PMC 1064104. PMID 15642158. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1064104.
- ^ Björnström L, Sjöberg M (2004). "Estrogen receptor-dependent activation of AP-1 via non-genomic signalling". Nucl Recept 2 (1): 3. doi:10.1186/1478-1336-2-3. PMC 434532. PMID 15196329. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=434532.
- ^ Lu Q, Pallas DC, Surks HK, Baur WE, Mendelsohn ME, Karas RH (2004). "Striatin assembles a membrane signaling complex necessary for rapid, nongenomic activation of endothelial NO synthase by estrogen receptor alpha". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (49): 17126–31. doi:10.1073/pnas.0407492101. PMC 534607. PMID 15569929. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=534607.
- ^ Kato S, Endoh H, Masuhiro Y, Kitamoto T, Uchiyama S, Sasaki H, Masushige S, Gotoh Y, Nishida E, Kawashima H, Metzger D, Chambon P (1995). "Activation of the estrogen receptor through phosphorylation by mitogen-activated protein kinase". Science 270 (5241): 1491–4. doi:10.1126/science.270.5241.1491. PMID 7491495.
- ^ Prossnitz ER, Arterburn JB, Sklar LA (2007). "GPR30: A G protein-coupled receptor for estrogen". Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 265-266: 138–42. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2006.12.010. PMC 1847610. PMID 17222505. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1847610.
- ^ Otto C, Rohde-Schulz B, Schwarz G, Fuchs I, Klewer M, Brittain D, Langer G, Bader B, Prelle K, Nubbemeyer R, Fritzemeier KH (2008). "G protein-coupled receptor 30 localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum and is not activated by estradiol.". Endocrinology. 149 (10): 4846–56. doi:10.1210/en.2008-0269. PMID 18566127.
- ^ Clemons M, Danson S, Howell A (2002). "Tamoxifen (Nolvadox): A Review". Cancer Treat. Rev. 28 (4): 165–180. PMID 12363457.
- ^ Fabian CJ, Kimler BF (2005). "Selective estrogen-receptor modulators for primary prevention of breast cancer". J. Clin. Oncol. 23 (8): 1644–55. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.11.005. PMID 15755972.
- ^ Harris HA, Albert LM, Leathurby Y, Malamas MS, Mewshaw RE, Miller CP, Kharode YP, Marzolf J, Komm BS, Winneker RC, Frail DE, Henderson RA, Zhu Y, Keith JC (2003). "Evaluation of an estrogen receptor-beta agonist in animal models of human disease". Endocrinology 144 (10): 4241–9. doi:10.1210/en.2003-0550. PMID 14500559.
- ^ Hewitt KN, Boon WC, Murata Y, Jones ME, Simpson ER (2003). "The aromatase knockout mouse presents with a sexually dimorphic disruption to cholesterol homeostasis". Endocrinology 144 (9): 3895–903. doi:10.1210/en.2003-0244. PMID 12933663.
- ^ Danilovich N, Babu PS, Xing W, Gerdes M, Krishnamurthy H, Sairam MR (2000). "Estrogen deficiency, obesity, and skeletal abnormalities in follicle-stimulating hormone receptor knockout (FORKO) female mice". Endocrinology 141 (11): 4295–308. doi:10.1210/en.141.11.4295. PMID 11089565.
- ^ Ohlsson C, Hellberg N, Parini P, Vidal O, Bohlooly-Y M, Bohlooly M, Rudling M, Lindberg MK, Warner M, Angelin B, Gustafsson JA (2000). "Obesity and disturbed lipoprotein profile in estrogen receptor-alpha-deficient male mice". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 278 (3): 640–5. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2000.3827. PMID 11095962.
- ^ Jensen EV, Jordan VC (1 June 2003). "The estrogen receptor: a model for molecular medicine" (abstract). Clin. Cancer Res. 9 (6): 1980–9. PMID 12796359. http://clincancerres.aacrjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/9/6/1980.
- ^ Moore DD (2011). "A Conversation with Elwood Jensen.". Annu Rev Physiol. doi:10.1146/annurev-physiol-020911-153327. PMID 21888507.
- ^ David Bracey, 2004 "UC Scientist Wins 'American Nobel' Research Award." University of Cincinnati press release.
- ^ Kuiper GG, Enmark E, Pelto-Huikko M, Nilsson S, Gustafsson JA (1996). "Cloning of a novel receptor expressed in rat prostate and ovary". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93 (12): 5925–30. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.12.5925. PMC 39164. PMID 8650195. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=39164.
External links
- MeSH Receptors Estrogen Receptors
- David S. Goodsell (2003-09-01). "Estrogen Receptor". Protein Data Bank, Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics (RCSB). http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/static.do?p=education_discussion/molecule_of_the_month/pdb45_1.html. Retrieved 2008-03-15.
Transcription factors and intracellular receptors (1) Basic domains (1.1) Basic leucine zipper (bZIP)Activating transcription factor (AATF, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) · AP-1 (c-Fos, FOSB, FOSL1, FOSL2, JDP2, c-Jun, JUNB, JUND) · BACH (1, 2) · BATF · BLZF1 · C/EBP (α, β, γ, δ, ε, ζ) · CREB (1, 3, L1) · CREM · DBP · DDIT3 · GABPA · HLF · MAF (B, F, G, K) · NFE (2, L1, L2, L3) · NFIL3 · NRL · NRF (1, 2, 3) · XBP1(1.2) Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)ATOH1 · AhR · AHRR · ARNT · ASCL1 · BHLHB2 · BMAL (ARNTL, ARNTL2) · CLOCK · EPAS1 · FIGLA · HAND (1, 2) · HES (5, 6) · HEY (1, 2, L) · HES1 · HIF (1A, 3A) · ID (1, 2, 3, 4) · LYL1 · MESP2 · MXD4 · MYCL1 · MYCN · Myogenic regulatory factors (MyoD, Myogenin, MYF5, MYF6) · Neurogenins (1, 2, 3) · NeuroD (1, 2) · NPAS (1, 2, 3) · OLIG (1, 2) · Pho4 · Scleraxis · SIM (1, 2) · TAL (1, 2) · Twist · USF1(1.3) bHLH-ZIP(1.4) NF-1(1.5) RF-X(1.6) Basic helix-span-helix (bHSH)(2) Zinc finger DNA-binding domains (2.1) Nuclear receptor (Cys4)subfamily 1 (Thyroid hormone (α, β), CAR, FXR, LXR (α, β), PPAR (α, β/δ, γ), PXR, RAR (α, β, γ), ROR (α, β, γ), Rev-ErbA (α, β), VDR)
subfamily 2 (COUP-TF (I, II), Ear-2, HNF4 (α, γ), PNR, RXR (α, β, γ), Testicular receptor (2, 4), TLX)
subfamily 3 (Steroid hormone (Androgen, Estrogen (α, β), Glucocorticoid, Mineralocorticoid, Progesterone), Estrogen related (α, β, γ))
subfamily 4 NUR (NGFIB, NOR1, NURR1) · subfamily 5 (LRH-1, SF1) · subfamily 6 (GCNF) · subfamily 0 (DAX1, SHP)(2.2) Other Cys4(2.3) Cys2His2General transcription factors (TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE (1, 2), TFIIF (1, 2), TFIIH (1, 2, 4, 2I, 3A, 3C1, 3C2))
ATBF1 · BCL (6, 11A, 11B) · CTCF · E4F1 · EGR (1, 2, 3, 4) · ERV3 · GFI1 · GLI-Krüppel family (1, 2, 3, REST, S2, YY1) · HIC (1, 2) · HIVEP (1, 2, 3) · IKZF (1, 2, 3) · ILF (2, 3) · KLF (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17) · MTF1 · MYT1 · OSR1 · PRDM9 · SALL (1, 2, 3, 4) · SP (1, 2, 4, 7, 8) · TSHZ3 · WT1 · Zbtb7 (7A, 7B) · ZBTB (16, 17, 20, 32, 33, 40) · zinc finger (3, 7, 9, 10, 19, 22, 24, 33B, 34, 35, 41, 43, 44, 51, 74, 143, 146, 148, 165, 202, 217, 219, 238, 239, 259, 267, 268, 281, 295, 300, 318, 330, 346, 350, 365, 366, 384, 423, 451, 452, 471, 593, 638, 644, 649, 655)(2.4) Cys6(2.5) Alternating composition(3) Helix-turn-helix domains (3.1) HomeodomainARX · CDX (1, 2) · CRX · CUTL1 · DBX (1, 2) · DLX (3, 4, 5) · EMX2 · EN (1, 2) · FHL (1, 2, 3) · HESX1 · HHEX · HLX · Homeobox (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A7, A9, A10, A11, A13, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9, B13, C4, C5, C6, C8, C9, C10, C11, C12, C13, D1, D3, D4, D8, D9, D10, D11, D12, D13) · HOPX · IRX (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, MKX) · LMX (1A, 1B) · MEIS (1, 2) · MEOX2 · MNX1 · MSX (1, 2) · NANOG · NKX (2-1, 2-2, 2-3, 2-5, 3-1, 3-2, 6-1, 6-2) · NOBOX · PBX (1, 2, 3) · PHF (1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 16, 17, 20, 21A) · PHOX (2A, 2B) · PITX (1, 2, 3) · POU domain (PIT-1, BRN-3: A, B, C, Octamer transcription factor: 1, 2, 3/4, 6, 7, 11) · OTX (1, 2) · PDX1 · SATB2 · SHOX2 · VAX1 · ZEB (1, 2)(3.2) Paired box(3.3) Fork head / winged helix(3.4) Heat Shock Factors(3.5) Tryptophan clusters(3.6) TEA domain(4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts (4.1) Rel homology region(4.2) STAT(4.3) p53(4.4) MADS box(4.6) TATA binding proteins(4.7) High-mobility group(4.10) Cold-shock domainCSDA, YBX1(4.11) Runt(0) Other transcription factors (0.2) HMGI(Y)(0.3) Pocket domain(0.6) MiscellaneousEstrogens and progestogens (G03C-D, L02) Progestogens/
progestins
(progesterone)AgonistAndrostene (Drospirenone) • 19-norprogesterone (Nomegestrol • Promegestone • Trimegestone) • 19-nortestosterone (Dienogest)Other/
ungroupedPregnenedione (Gestonorone) • Pregnene (Ethisterone) • Pregnadiene (Medrogestone • Melengestrol) • Norpregnane (Norgestrienone) • Lynestrenol • Norethynodrel • Tibolone • Dydrogesterone • Quingestanolantagonist: MifepristoneAsoprisnil • CDB-4124 • Ulipristal acetateEstrogens AgonistDiosgenin • Estradiol (Ethinylestradiol#/Mestranol • Estradiol 17 beta-cypionate# • Polyestradiol phosphate) • Estrone (Estrone sulfate) • Estriol • Promestriene • Equilenin • EquilinAfimoxifene • Arzoxifene • Bazedoxifene • Cyclofenil • Lasofoxifene • Ormeloxifene • Raloxifene • Tamoxifen • Toremifenepure antagonist: FulvestrantCategories:- Genes on chromosome 6
- Genes on chromosome 14
- Intracellular receptors
- Transcription factors
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

