- Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha
-
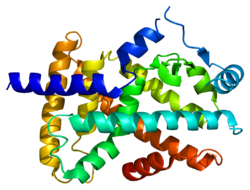
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-alpha), also known as NR1C1 (nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group C, member 1), is a nuclear receptor protein that in humans is encoded by the PPARA gene.[1]
Contents
Function
PPAR-alpha is a transcription factor and a major regulator of lipid metabolism in the liver. PPAR-alpha is activated under nutrient-deficient conditions and is necessary for the process of ketogenesis, a key adaptive response to prolonged fasting [2]. Activation of PPAR-alpha promotes uptake, utilization, and catabolism of fatty acids by upregulation of genes involved in fatty acid transport and peroxisomal and mitochondrial fatty acid β-oxidation. PPAR-alpha is primarily activated through ligand binding. Synthetic ligands include the fibrate drugs, which are used to treat hyperlipidemia. An endogenous ligand has been identified as the phosphatidylcholine species 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphocholine [3]. Endogenous activation of PPAR-alpha is dependent on the presence of fatty acid synthase.
Interactions
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha has been shown to interact with:
See also
References
- ^ Sher T, Yi HF, McBride OW, Gonzalez FJ (June 1993). "cDNA cloning, chromosomal mapping, and functional characterization of the human peroxisome proliferator activated receptor". Biochemistry 32 (21): 5598–604. doi:10.1021/bi00072a015. PMID 7684926.
- ^ Kersten S, Seydoux J, Peters JM, Gonzalez FJ, Desvergne B, Wahli W. (June 1999). "Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha mediates the adaptive response to fasting.". J Clin Invest. 103 (11): 1489–98. doi:10.1172/JCI6223. PMC 408372. PMID 10359558. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=408372.
- ^ Chakravarthy MV, Lodhi IJ, Yin L, Malapaka RR, Xu HE, Turk J, Semenkovich CF. (August 2009). "Identification of a physiologically relevant endogenous ligand for PPARalpha in liver.". Cell. 138 (3): 476–88. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.036. PMC 2725194. PMID 19646743. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2725194.
- ^ a b Sumanasekera WK, Tien ES, Turpey R, Vanden Heuvel JP, Perdew GH (February 2003). "Evidence that peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha is complexed with the 90-kDa heat shock protein and the hepatitis virus B X-associated protein 2". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (7): 4467–73. doi:10.1074/jbc.M211261200. PMID 12482853.
- ^ a b Dowell P, Ishmael JE, Avram D, Peterson VJ, Nevrivy DJ, Leid M (December 1997). "p300 functions as a coactivator for the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (52): 33435–43. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.52.33435. PMID 9407140.
- ^ a b Dowell P, Ishmael JE, Avram D, Peterson VJ, Nevrivy DJ, Leid M (May 1999). "Identification of nuclear receptor corepressor as a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha interacting protein". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (22): 15901–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.22.15901. PMID 10336495.
- ^ Treuter E, Albrektsen T, Johansson L, Leers J, Gustafsson JA (June 1998). "A regulatory role for RIP140 in nuclear receptor activation". Mol. Endocrinol. 12 (6): 864–81. doi:10.1210/me.12.6.864. PMID 9626662.
Further reading
- Bouwens M, Afman LA, Müller M. (2008). "Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells reveals an individual gene expression profile response.". BMC Genomics 9: 262. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-9-262. PMC 2430976. PMID 18518955. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2430976.
- Berger J, Moller DE (2002). "The mechanisms of action of PPARs.". Annu. Rev. Med. 53: 409–35. doi:10.1146/annurev.med.53.082901.104018. PMID 11818483.
- Kuenzli S, Saurat JH (2003). "Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in cutaneous biology.". Br. J. Dermatol. 149 (2): 229–36. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2003.05532.x. PMID 12932225.
- Mandard S, Müller M, Kersten S (2004). "Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha target genes.". Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 61 (4): 393–416. doi:10.1007/s00018-003-3216-3. PMID 14999402.
- van Raalte DH, Li M, Pritchard PH, Wasan KM (2005). "Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-alpha: a pharmacological target with a promising future.". Pharm. Res. 21 (9): 1531–8. doi:10.1023/B:PHAM.0000041444.06122.8d. PMID 15497675.
- Lefebvre P, Chinetti G, Fruchart JC, Staels B (2006). "Sorting out the roles of PPAR alpha in energy metabolism and vascular homeostasis.". J. Clin. Invest. 116 (3): 571–80. doi:10.1172/JCI27989. PMC 1386122. PMID 16511589. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1386122.
- Mukherjee R, Jow L, Noonan D, McDonnell DP (1995). "Human and rat peroxisome proliferator activated receptors (PPARs) demonstrate similar tissue distribution but different responsiveness to PPAR activators.". J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 51 (3-4): 157–66. doi:10.1016/0960-0760(94)90089-2. PMID 7981125.
- Miyata KS, McCaw SE, Patel HV, et al. (1996). "The orphan nuclear hormone receptor LXR alpha interacts with the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor and inhibits peroxisome proliferator signaling.". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (16): 9189–92. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.16.9189. PMID 8621574.
- Chu R, Lin Y, Rao MS, Reddy JK (1996). "Cloning and identification of rat deoxyuridine triphosphatase as an inhibitor of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha.". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (44): 27670–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.44.27670. PMID 8910358.
- Tugwood JD, Aldridge TC, Lambe KG, et al. (1997). "Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: structures and function.". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 804: 252–65. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1996.tb18620.x. PMID 8993548.
- Li H, Gomes PJ, Chen JD (1997). "RAC3, a steroid/nuclear receptor-associated coactivator that is related to SRC-1 and TIF2.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94 (16): 8479–84. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.16.8479. PMC 22964. PMID 9238002. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=22964.
- Dowell P, Ishmael JE, Avram D, et al. (1998). "p300 functions as a coactivator for the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha.". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (52): 33435–43. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.52.33435. PMID 9407140.
- Inoue I, Shino K, Noji S, et al. (1998). "Expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR alpha) in primary cultures of human vascular endothelial cells.". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 246 (2): 370–4. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1998.8622. PMID 9610365.
- Treuter E, Albrektsen T, Johansson L, et al. (1998). "A regulatory role for RIP140 in nuclear receptor activation.". Mol. Endocrinol. 12 (6): 864–81. doi:10.1210/me.12.6.864. PMID 9626662.
- Rubino D, Driggers P, Arbit D, et al. (1998). "Characterization of Brx, a novel Dbl family member that modulates estrogen receptor action.". Oncogene 16 (19): 2513–26. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1201783. PMID 9627117.
- Yuan CX, Ito M, Fondell JD, et al. (1998). "The TRAP220 component of a thyroid hormone receptor- associated protein (TRAP) coactivator complex interacts directly with nuclear receptors in a ligand-dependent fashion.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95 (14): 7939–44. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.14.7939. PMC 20908. PMID 9653119. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=20908.
- Chinetti G, Griglio S, Antonucci M, et al. (1998). "Activation of proliferator-activated receptors alpha and gamma induces apoptosis of human monocyte-derived macrophages.". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (40): 25573–80. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.40.25573. PMID 9748221.
- Costet P, Legendre C, Moré J, et al. (1998). "Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha-isoform deficiency leads to progressive dyslipidemia with sexually dimorphic obesity and steatosis.". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (45): 29577–85. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.45.29577. PMID 9792666.
- Masuda N, Yasumo H, Furusawa T, et al. (1998). "Nuclear receptor binding factor-1 (NRBF-1), a protein interacting with a wide spectrum of nuclear hormone receptors.". Gene 221 (2): 225–33. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(98)00461-2. PMID 9795230.
- Ellinghaus P, Wolfrum C, Assmann G, et al. (1999). "Phytanic acid activates the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) in sterol carrier protein 2-/ sterol carrier protein x-deficient mice.". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (5): 2766–72. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.5.2766. PMID 9915808.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
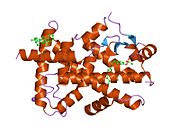
PDB gallery 1i7g: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE LIGAND BINDING DOMAIN FROM HUMAN PPAR-ALPHA IN COMPLEX WITH THE AGONIST AZ 2421k7l: The 2.5 Angstrom resolution crystal structure of the human PPARalpha ligand binding domain bound with GW409544 and a co-activator peptide.1kkq: Crystal structure of the human PPAR-alpha ligand-binding domain in complex with an antagonist GW6471 and a SMRT corepressor motif2p54: a crystal structure of PPAR alpha bound with SRC1 peptide and GW735Transcription factors and intracellular receptors (1) Basic domains (1.1) Basic leucine zipper (bZIP)Activating transcription factor (AATF, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) · AP-1 (c-Fos, FOSB, FOSL1, FOSL2, JDP2, c-Jun, JUNB, JUND) · BACH (1, 2) · BATF · BLZF1 · C/EBP (α, β, γ, δ, ε, ζ) · CREB (1, 3, L1) · CREM · DBP · DDIT3 · GABPA · HLF · MAF (B, F, G, K) · NFE (2, L1, L2, L3) · NFIL3 · NRL · NRF (1, 2, 3) · XBP1(1.2) Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)ATOH1 · AhR · AHRR · ARNT · ASCL1 · BHLHB2 · BMAL (ARNTL, ARNTL2) · CLOCK · EPAS1 · FIGLA · HAND (1, 2) · HES (5, 6) · HEY (1, 2, L) · HES1 · HIF (1A, 3A) · ID (1, 2, 3, 4) · LYL1 · MESP2 · MXD4 · MYCL1 · MYCN · Myogenic regulatory factors (MyoD, Myogenin, MYF5, MYF6) · Neurogenins (1, 2, 3) · NeuroD (1, 2) · NPAS (1, 2, 3) · OLIG (1, 2) · Pho4 · Scleraxis · SIM (1, 2) · TAL (1, 2) · Twist · USF1(1.3) bHLH-ZIP(1.4) NF-1(1.5) RF-X(1.6) Basic helix-span-helix (bHSH)(2) Zinc finger DNA-binding domains (2.1) Nuclear receptor (Cys4)subfamily 1 (Thyroid hormone (α, β), CAR, FXR, LXR (α, β), PPAR (α, β/δ, γ), PXR, RAR (α, β, γ), ROR (α, β, γ), Rev-ErbA (α, β), VDR)
subfamily 2 (COUP-TF (I, II), Ear-2, HNF4 (α, γ), PNR, RXR (α, β, γ), Testicular receptor (2, 4), TLX)
subfamily 3 (Steroid hormone (Androgen, Estrogen (α, β), Glucocorticoid, Mineralocorticoid, Progesterone), Estrogen related (α, β, γ))
subfamily 4 NUR (NGFIB, NOR1, NURR1) · subfamily 5 (LRH-1, SF1) · subfamily 6 (GCNF) · subfamily 0 (DAX1, SHP)(2.2) Other Cys4(2.3) Cys2His2General transcription factors (TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE (1, 2), TFIIF (1, 2), TFIIH (1, 2, 4, 2I, 3A, 3C1, 3C2))
ATBF1 · BCL (6, 11A, 11B) · CTCF · E4F1 · EGR (1, 2, 3, 4) · ERV3 · GFI1 · GLI-Krüppel family (1, 2, 3, REST, S2, YY1) · HIC (1, 2) · HIVEP (1, 2, 3) · IKZF (1, 2, 3) · ILF (2, 3) · KLF (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17) · MTF1 · MYT1 · OSR1 · PRDM9 · SALL (1, 2, 3, 4) · SP (1, 2, 4, 7, 8) · TSHZ3 · WT1 · Zbtb7 (7A, 7B) · ZBTB (16, 17, 20, 32, 33, 40) · zinc finger (3, 7, 9, 10, 19, 22, 24, 33B, 34, 35, 41, 43, 44, 51, 74, 143, 146, 148, 165, 202, 217, 219, 238, 239, 259, 267, 268, 281, 295, 300, 318, 330, 346, 350, 365, 366, 384, 423, 451, 452, 471, 593, 638, 644, 649, 655)(2.4) Cys6(2.5) Alternating composition(3) Helix-turn-helix domains (3.1) HomeodomainARX · CDX (1, 2) · CRX · CUTL1 · DBX (1, 2) · DLX (3, 4, 5) · EMX2 · EN (1, 2) · FHL (1, 2, 3) · HESX1 · HHEX · HLX · Homeobox (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A7, A9, A10, A11, A13, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9, B13, C4, C5, C6, C8, C9, C10, C11, C12, C13, D1, D3, D4, D8, D9, D10, D11, D12, D13) · HOPX · IRX (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, MKX) · LMX (1A, 1B) · MEIS (1, 2) · MEOX2 · MNX1 · MSX (1, 2) · NANOG · NKX (2-1, 2-2, 2-3, 2-5, 3-1, 3-2, 6-1, 6-2) · NOBOX · PBX (1, 2, 3) · PHF (1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 16, 17, 20, 21A) · PHOX (2A, 2B) · PITX (1, 2, 3) · POU domain (PIT-1, BRN-3: A, B, C, Octamer transcription factor: 1, 2, 3/4, 6, 7, 11) · OTX (1, 2) · PDX1 · SATB2 · SHOX2 · VAX1 · ZEB (1, 2)(3.2) Paired box(3.3) Fork head / winged helix(3.4) Heat Shock Factors(3.5) Tryptophan clusters(3.6) TEA domain(4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts (4.1) Rel homology region(4.2) STAT(4.3) p53(4.4) MADS box(4.6) TATA binding proteins(4.7) High-mobility group(4.10) Cold-shock domainCSDA, YBX1(4.11) Runt(0) Other transcription factors (0.2) HMGI(Y)(0.3) Pocket domain(0.6) MiscellaneousCategories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 22 gene stubs
- Intracellular receptors
- Transcription factors
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.