- Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2A
-
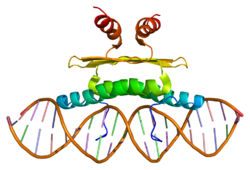
Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MEF2A gene.[1][2] MEF2A is a transcription factor in the Mef2 family. In humans it is located on chromosome 15q26. Certain mutations in MEF2A cause an autosomal dominant form of coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction.
The process of differentiation from mesodermal precursor cells to myoblasts has led to the discovery of a variety of tissue-specific factors that regulate muscle gene expression. The myogenic basic helix-loop-helix proteins, including myoD (MIM 159970), myogenin (MIM 159980), MYF5 (MIM 159990), and MRF4 (MIM 159991) are 1 class of identified factors. A second family of DNA binding regulatory proteins is the myocyte-specific enhancer factor-2 (MEF2) family. Each of these proteins binds to the MEF2 target DNA sequence present in the regulatory regions of many, if not all, muscle-specific genes. The MEF2 genes are members of the MADS gene family (named for the yeast mating type-specific transcription factor MCM1, the plant homeotic genes 'agamous' and 'deficiens' and the human serum response factor SRF (MIM 600589)), a family that also includes several homeotic genes and other transcription factors, all of which share a conserved DNA-binding domain.[supplied by OMIM][2]
Contents
Interactions
Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2A has been shown to interact with HDAC9,[3][4] MEF2D,[5] MAPK14,[6][7] Histone deacetylase 5,[4] EP300,[8] ASCL1,[9] HDAC4,[3][4] Thyroid hormone receptor alpha[8] and Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2.[10]
References
- ^ Yu YT, Breitbart RE, Smoot LB, Lee Y, Mahdavi V, Nadal-Ginard B (Oct 1992). "Human myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2 comprises a group of tissue-restricted MADS box transcription factors". Genes Dev 6 (9): 1783–98. doi:10.1101/gad.6.9.1783. PMID 1516833.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: MEF2A MADS box transcription enhancer factor 2, polypeptide A (myocyte enhancer factor 2A)". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=4205.
- ^ a b Miska, E A; Karlsson C, Langley E, Nielsen S J, Pines J, Kouzarides T (Sep. 1999). "HDAC4 deacetylase associates with and represses the MEF2 transcription factor". EMBO J. (ENGLAND) 18 (18): 5099–107. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.18.5099. ISSN 0261-4189. PMC 1171580. PMID 10487761. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1171580.
- ^ a b c Lemercier, C; Verdel A, Galloo B, Curtet S, Brocard M P, Khochbin S (May. 2000). "mHDA1/HDAC5 histone deacetylase interacts with and represses MEF2A transcriptional activity". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 275 (20): 15594–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M908437199. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 10748098.
- ^ Ornatsky, O I; McDermott J C (Oct. 1996). "MEF2 protein expression, DNA binding specificity and complex composition, and transcriptional activity in muscle and non-muscle cells". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 271 (40): 24927–33. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.40.24927. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 8798771.
- ^ Zhao, M; New L, Kravchenko V V, Kato Y, Gram H, di Padova F, Olson E N, Ulevitch R J, Han J (Jan. 1999). "Regulation of the MEF2 Family of Transcription Factors by p38". Mol. Cell. Biol. (UNITED STATES) 19 (1): 21–30. ISSN 0270-7306. PMC 83862. PMID 9858528. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=83862.
- ^ Yang, S H; Galanis A, Sharrocks A D (Jun. 1999). "Targeting of p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases to MEF2 Transcription Factors". Mol. Cell. Biol. (UNITED STATES) 19 (6): 4028–38. ISSN 0270-7306. PMC 104362. PMID 10330143. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=104362.
- ^ a b De Luca, Antonio; Severino Anna, De Paolis Paola, Cottone Giuliano, De Luca Luca, De Falco Maria, Porcellini Antonio, Volpe Massimo, Condorelli Gianluigi (Feb. 2003). "p300/cAMP-response-element-binding-protein ('CREB')-binding protein (CBP) modulates co-operation between myocyte enhancer factor 2A (MEF2A) and thyroid hormone receptor-retinoid X receptor". Biochem. J. (England) 369 (Pt 3): 477–84. doi:10.1042/BJ20020057. ISSN 0264-6021. PMC 1223100. PMID 12371907. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1223100.
- ^ Mao, Z; Nadal-Ginard B (Jun. 1996). "Functional and physical interactions between mammalian achaete-scute homolog 1 and myocyte enhancer factor 2A". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 271 (24): 14371–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.24.14371. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 8662987.
- ^ Quinn, Z A; Yang C C, Wrana J L, McDermott J C (Feb. 2001). "Smad proteins function as co-modulators for MEF2 transcriptional regulatory proteins". Nucleic Acids Res. (England) 29 (3): 732–42. doi:10.1093/nar/29.3.732. PMC 30396. PMID 11160896. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=30396.
Further reading
- Wang Q (2005). "Advances in the Genetic Basis of Coronary Artery Disease". Current atherosclerosis reports 7 (3): 235–41. doi:10.1007/s11883-005-0012-6. PMC 1783687. PMID 15811259. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1783687.
- Wang Q (2005). "Molecular genetics of coronary artery disease". Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 20 (3): 182–8. doi:10.1097/01.hco.0000160373.77190.f1. PMC 1579824. PMID 15861005. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1579824.
- Funk WD, Wright WE (1992). "Cyclic amplification and selection of targets for multicomponent complexes: myogenin interacts with factors recognizing binding sites for basic helix-loop-helix, nuclear factor 1, myocyte-specific enhancer-binding factor 2, and COMP1 factor". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89 (20): 9484–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.20.9484. PMC 50156. PMID 1329097. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=50156.
- Pollock R, Treisman R (1992). "Human SRF-related proteins: DNA-binding properties and potential regulatory targets". Genes Dev. 5 (12A): 2327–41. doi:10.1101/gad.5.12a.2327. PMID 1748287.
- Molkentin JD, Black BL, Martin JF, Olson EN (1996). "Cooperative activation of muscle gene expression by MEF2 and myogenic bHLH proteins". Cell 83 (7): 1125–36. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90139-6. PMID 8548800.
- Hobson GM, Krahe R, Garcia E, et al. (1996). "Regional chromosomal assignments for four members of the MADS domain transcription enhancer factor 2 (MEF2) gene family to human chromosomes 15q26, 19p12, 5q14, and 1q12-q23". Genomics 29 (3): 704–11. doi:10.1006/geno.1995.9007. PMID 8575763.
- Mao Z, Nadal-Ginard B (1996). "Functional and physical interactions between mammalian achaete-scute homolog 1 and myocyte enhancer factor 2A". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (24): 14371–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.24.14371. PMID 8662987.
- Suzuki E, Lowry J, Sonoda G, et al. (1996). "Structures and chromosome locations of the human MEF2A gene and a pseudogene MEF2AP". Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 73 (3): 244–9. doi:10.1159/000134348. PMID 8697817.
- Ornatsky OI, McDermott JC (1996). "MEF2 protein expression, DNA binding specificity and complex composition, and transcriptional activity in muscle and non-muscle cells". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (40): 24927–33. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.40.24927. PMID 8798771.
- Black BL, Molkentin JD, Olson EN (1998). "Multiple Roles for the MyoD Basic Region in Transmission of Transcriptional Activation Signals and Interaction with MEF2". Mol. Cell. Biol. 18 (1): 69–77. PMC 121453. PMID 9418854. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=121453.
- Yang CC, Ornatsky OI, McDermott JC, et al. (1998). "Interaction of myocyte enhancer factor 2 (MEF2) with a mitogen-activated protein kinase, ERK5/BMK1". Nucleic Acids Res. 26 (20): 4771–7. doi:10.1093/nar/26.20.4771. PMC 147902. PMID 9753748. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=147902.
- Zhao M, New L, Kravchenko VV, et al. (1999). "Regulation of the MEF2 Family of Transcription Factors by p38". Mol. Cell. Biol. 19 (1): 21–30. PMC 83862. PMID 9858528. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=83862.
- Yang SH, Galanis A, Sharrocks AD (1999). "Targeting of p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases to MEF2 Transcription Factors". Mol. Cell. Biol. 19 (6): 4028–38. PMC 104362. PMID 10330143. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=104362.
- Iida K, Hidaka K, Takeuchi M, et al. (1999). "Expression of MEF2 genes during human cardiac development". Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 187 (1): 15–23. doi:10.1620/tjem.187.15. PMID 10458488.
- Miska EA, Karlsson C, Langley E, et al. (1999). "HDAC4 deacetylase associates with and represses the MEF2 transcription factor". EMBO J. 18 (18): 5099–107. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.18.5099. PMC 1171580. PMID 10487761. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1171580.
- Mao Z, Bonni A, Xia F, et al. (1999). "Neuronal activity-dependent cell survival mediated by transcription factor MEF2". Science 286 (5440): 785–90. doi:10.1126/science.286.5440.785. PMID 10531066.
- Lu J, McKinsey TA, Nicol RL, Olson EN (2000). "Signal-dependent activation of the MEF2 transcription factor by dissociation from histone deacetylases". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (8): 4070–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.080064097. PMC 18151. PMID 10737771. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=18151.
- Lemercier C, Verdel A, Galloo B, et al. (2000). "mHDA1/HDAC5 histone deacetylase interacts with and represses MEF2A transcriptional activity". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (20): 15594–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M908437199. PMID 10748098.
- Youn HD, Grozinger CM, Liu JO (2000). "Calcium regulates transcriptional repression of myocyte enhancer factor 2 by histone deacetylase 4". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (29): 22563–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.C000304200. PMID 10825153.
External links
PDB gallery Transcription factors and intracellular receptors (1) Basic domains (1.1) Basic leucine zipper (bZIP)Activating transcription factor (AATF, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) · AP-1 (c-Fos, FOSB, FOSL1, FOSL2, JDP2, c-Jun, JUNB, JUND) · BACH (1, 2) · BATF · BLZF1 · C/EBP (α, β, γ, δ, ε, ζ) · CREB (1, 3, L1) · CREM · DBP · DDIT3 · GABPA · HLF · MAF (B, F, G, K) · NFE (2, L1, L2, L3) · NFIL3 · NRL · NRF (1, 2, 3) · XBP1(1.2) Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)ATOH1 · AhR · AHRR · ARNT · ASCL1 · BHLHB2 · BMAL (ARNTL, ARNTL2) · CLOCK · EPAS1 · FIGLA · HAND (1, 2) · HES (5, 6) · HEY (1, 2, L) · HES1 · HIF (1A, 3A) · ID (1, 2, 3, 4) · LYL1 · MESP2 · MXD4 · MYCL1 · MYCN · Myogenic regulatory factors (MyoD, Myogenin, MYF5, MYF6) · Neurogenins (1, 2, 3) · NeuroD (1, 2) · NPAS (1, 2, 3) · OLIG (1, 2) · Pho4 · Scleraxis · SIM (1, 2) · TAL (1, 2) · Twist · USF1(1.3) bHLH-ZIP(1.4) NF-1(1.5) RF-X(1.6) Basic helix-span-helix (bHSH)(2) Zinc finger DNA-binding domains (2.1) Nuclear receptor (Cys4)subfamily 1 (Thyroid hormone (α, β), CAR, FXR, LXR (α, β), PPAR (α, β/δ, γ), PXR, RAR (α, β, γ), ROR (α, β, γ), Rev-ErbA (α, β), VDR)
subfamily 2 (COUP-TF (I, II), Ear-2, HNF4 (α, γ), PNR, RXR (α, β, γ), Testicular receptor (2, 4), TLX)
subfamily 3 (Steroid hormone (Androgen, Estrogen (α, β), Glucocorticoid, Mineralocorticoid, Progesterone), Estrogen related (α, β, γ))
subfamily 4 NUR (NGFIB, NOR1, NURR1) · subfamily 5 (LRH-1, SF1) · subfamily 6 (GCNF) · subfamily 0 (DAX1, SHP)(2.2) Other Cys4(2.3) Cys2His2General transcription factors (TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE (1, 2), TFIIF (1, 2), TFIIH (1, 2, 4, 2I, 3A, 3C1, 3C2))
ATBF1 · BCL (6, 11A, 11B) · CTCF · E4F1 · EGR (1, 2, 3, 4) · ERV3 · GFI1 · GLI-Krüppel family (1, 2, 3, REST, S2, YY1) · HIC (1, 2) · HIVEP (1, 2, 3) · IKZF (1, 2, 3) · ILF (2, 3) · KLF (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17) · MTF1 · MYT1 · OSR1 · PRDM9 · SALL (1, 2, 3, 4) · SP (1, 2, 4, 7, 8) · TSHZ3 · WT1 · Zbtb7 (7A, 7B) · ZBTB (16, 17, 20, 32, 33, 40) · zinc finger (3, 7, 9, 10, 19, 22, 24, 33B, 34, 35, 41, 43, 44, 51, 74, 143, 146, 148, 165, 202, 217, 219, 238, 239, 259, 267, 268, 281, 295, 300, 318, 330, 346, 350, 365, 366, 384, 423, 451, 452, 471, 593, 638, 644, 649, 655)(2.4) Cys6(2.5) Alternating composition(3) Helix-turn-helix domains (3.1) HomeodomainARX · CDX (1, 2) · CRX · CUTL1 · DBX (1, 2) · DLX (3, 4, 5) · EMX2 · EN (1, 2) · FHL (1, 2, 3) · HESX1 · HHEX · HLX · Homeobox (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A7, A9, A10, A11, A13, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9, B13, C4, C5, C6, C8, C9, C10, C11, C13, D1, D3, D4, D8, D9, D10, D11, D12, D13) · HOPX · IRX (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, MKX) · LMX (1A, 1B) · MEIS (1, 2) · MEOX2 · MNX1 · MSX (1, 2) · NANOG · NKX (2-1, 2-2, 2-3, 2-5, 3-1, 3-2, 6-1, 6-2) · NOBOX · PBX (1, 2, 3) · PHF (1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 16, 17, 20, 21A) · PHOX (2A, 2B) · PITX (1, 2, 3) · POU domain (PIT-1, BRN-3: A, B, C, Octamer transcription factor: 1, 2, 3/4, 6, 7, 11) · OTX (1, 2) · PDX1 · SATB2 · SHOX2 · VAX1 · ZEB (1, 2)(3.2) Paired box(3.3) Fork head / winged helix(3.4) Heat Shock Factors(3.5) Tryptophan clusters(3.6) TEA domain(4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts (4.1) Rel homology region(4.2) STAT(4.3) p53(4.4) MADS box(4.6) TATA binding proteins(4.7) High-mobility group(4.10) Cold-shock domainCSDA, YBX1(4.11) Runt(0) Other transcription factors (0.2) HMGI(Y)(0.3) Pocket domain(0.6) Miscellaneoussee also transcription factor/coregulator deficiencies
B bsyn: dna (repl, cycl, reco, repr) · tscr (fact, tcrg, nucl, rnat, rept, ptts) · tltn (risu, pttl, nexn) · dnab, rnab/runp · stru (domn, 1°, 2°, 3°, 4°)Categories:- Human proteins
- Genes
- Transcription factors
- Chromosome 15 gene stubs
- Genetics stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.