- EGR1
-
EGR-1 (Early growth response protein 1) also known as Zif268 (zinc finger protein 225) or NGFI-A (nerve growth factor-induced protein A) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EGR1 gene.
EGR-1 is a mammalian transcription factor. It was also named Krox-24, TIS8, and ZENK. It was originally discovered in mice.
Contents
Function
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the EGR family of C2H2-type zinc-finger proteins. It is a nuclear protein and functions as a transcriptional regulator. The products of target genes it activates are required for differentiation and mitogenesis. Studies suggest this is a tumor suppressor gene.[1]
Structure
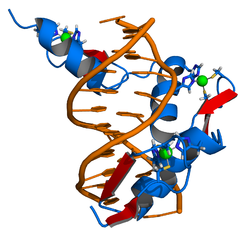
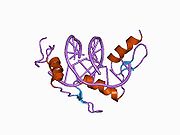
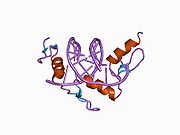
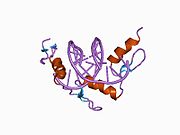
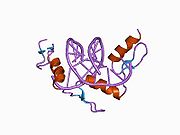
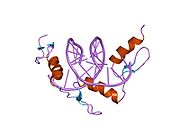
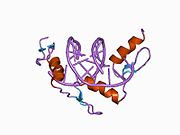
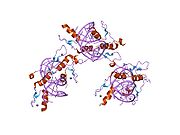
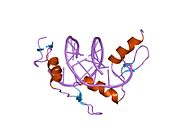
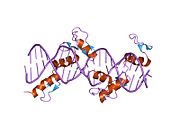
The DNA-binding domain of Zif268 consists of three zinc finger domains of the Cys2His2 type. The amino acid structure of the Zif268 zinc finger domain is given in this table, using the single letter amino acid code. The fingers 1 to 3 are indicated by f1 - f3. The numbers are in reference to the residues (amino acids) of alpha helix (there is no '0'). The residues marked 'x' are not part of the zinc fingers, but rather serve to connect them all together.
-1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 x x x x x f1 M A E E R P Y A C P V E S C D R R F S R S D E L T R H I R I H T G Q K P f2 F O C A I ? ? C M R N F S R S D H L T T H I A T H T G E K P f3 F A C D I ? ? C G R K F A R S D E R K R H T K I H L R Q K D The crystal structure of DNA bound by the zinc finger domain of Zif268 was solved in 1991, which greatly aided early research in zinc finger DNA-binding domains.[2]
The human Zif268/EGR1 protein contains (in its unprocessed form) 543 amino acids with a molecular weight of 57.5 kDa, and the gene is located on the chromosome 5.
Function
Zif268 binds the DNA sequence 5'-GCG[G/T]GGGCG-3'.[3][4]
It has a distinct pattern of expression in the brain, and its induction has been shown to be associated with neuronal activity. Several studies suggest it has a role in neuronal plasticity.[5]
Zif268 has also been found to regulate the expression of synaptobrevin II (a protein important for synaptic exocytosis).[6]
Interactions
Zif268 has been shown to interact with NAB1,[7] CEBPB,[8] EP300,[9] CREB-binding protein,[9] PSMA3[10] and P53.[11]
See also
References
- ^ "Entrez Gene: EGR1 early growth response 1". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=1958.
- ^ Pavletich, N. P. and C. O. Pabo (1991). "Zinc finger-DNA recognition: crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A." Science 252(5007): 809-17.
- ^ Christy B, Nathans D (1989). "DNA binding site of the growth factor-inducible protein Zif268". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86 (22): 8737–41. doi:10.1073/pnas.86.22.8737. PMC 298363. PMID 2510170. http://www.pnas.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=2510170.
- ^ Swirnoff AH, Milbrandt J (1995). "DNA-binding specificity of NGFI-A and related zinc finger transcription factors". Mol. Cell. Biol. 15 (4): 2275–87. PMC 230455. PMID 7891721. http://mcb.asm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=7891721.
- ^ Knapska, E and Kaczmarek, L (2004) "A gene for Neuronal Plasticity in the Mammalian Brain: Zif286/Egr1/NGFI-A/Krox-24/TIS-8/ZENK?" Progress in Neurobiology 74, 2004
- ^ Petersohn,D and Thiel. G (1996)"Role of zinc-finger proteins Sp1 and zif268/egr-1 in transcriptional regulation of the human synaptobrevin II gene" European Journal of Biochemistry, 239, 1996
- ^ Russo, M W; Sevetson B R, Milbrandt J (Jul. 1995). "Identification of NAB1, a repressor of NGFI-A- and Krox20-mediated transcription". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (UNITED STATES) 92 (15): 6873–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.15.6873. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 41432. PMID 7624335. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=41432.
- ^ Zhang, Fang; Lin Meihong, Abidi Parveen, Thiel Gerald, Liu Jingwen (Nov. 2003). "Specific interaction of Egr1 and c/EBPbeta leads to the transcriptional activation of the human low density lipoprotein receptor gene". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 278 (45): 44246–54. doi:10.1074/jbc.M305564200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 12947119.
- ^ a b Silverman, E S; Du J, Williams A J, Wadgaonkar R, Drazen J M, Collins T (Nov. 1998). "cAMP-response-element-binding-protein-binding protein (CBP) and p300 are transcriptional co-activators of early growth response factor-1 (Egr-1)". Biochem. J. (ENGLAND) 336 ( Pt 1): 183–9. ISSN 0264-6021. PMC 1219856. PMID 9806899. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1219856.
- ^ Bae, Myung-Ho; Jeong Chul-Ho, Kim Se-Hee, Bae Moon-Kyoung, Jeong Joo-Won, Ahn Mee-Young, Bae Soo-Kyung, Kim Nam Deuk, Kim Chul Woo, Kim Kwang-Rok, Kim Kyu-Won (Oct. 2002). "Regulation of Egr-1 by association with the proteasome component C8". Biochim. Biophys. Acta (Netherlands) 1592 (2): 163–7. ISSN 0006-3002. PMID 12379479.
- ^ Liu, J; Grogan L, Nau M M, Allegra C J, Chu E, Wright J J (Apr. 2001). "Physical interaction between p53 and primary response gene Egr-1". Int. J. Oncol. (Greece) 18 (4): 863–70. ISSN 1019-6439. PMID 11251186.
Further reading
- Heath RG (1975). "Brain function and behavior. I. Emotion and sensory phenomena in psychotic patients and in experimental animals". J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 160 (3): 159–75. doi:10.1097/00005053-197503000-00002. PMID 1090709.
- Silverman ES, Collins T (1999). "Pathways of Egr-1-mediated gene transcription in vascular biology". Am. J. Pathol. 154 (3): 665–70. PMC 1866415. PMID 10079243. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1866415.
- Adamson ED, Mercola D (2002). "Egr1 transcription factor: multiple roles in prostate tumor cell growth and survival". Tumour Biol. 23 (2): 93–102. doi:10.1159/000059711. PMID 12065847.
- Blaschke F, Bruemmer D, Law RE (2004). "Egr-1 is a major vascular pathogenic transcription factor in atherosclerosis and restenosis". Reviews in endocrine & metabolic disorders 5 (3): 249–54. doi:10.1023/B:REMD.0000032413.88756.ee. PMID 15211096.
- Abdulkadir SA (2006). "Mechanisms of prostate tumorigenesis: roles for transcription factors Nkx3.1 and Egr1". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1059: 33–40. doi:10.1196/annals.1339.018. PMID 16382041.
- Khachigian LM (2006). "Early growth response-1 in cardiovascular pathobiology.". Circ Res. 98 (2): 186–191. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000200177.53882.c3. PMID 16456111.
External links
PDB gallery 1a1f: DSNR (ZIF268 VARIANT) ZINC FINGER-DNA COMPLEX (GACC SITE)1a1g: DSNR (ZIF268 VARIANT) ZINC FINGER-DNA COMPLEX (GCGT SITE)1a1h: QGSR (ZIF268 VARIANT) ZINC FINGER-DNA COMPLEX (GCAC SITE)1a1i: RADR (ZIF268 VARIANT) ZINC FINGER-DNA COMPLEX (GCAC SITE)1a1j: RADR (ZIF268 VARIANT) ZINC FINGER-DNA COMPLEX (GCGT SITE)1a1k: RADR (ZIF268 VARIANT) ZINC FINGER-DNA COMPLEX (GACC SITE)1a1l: ZIF268 ZINC FINGER-DNA COMPLEX (GCAC SITE)1aay: ZIF268 ZINC FINGER-DNA COMPLEX1f2i: COCRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF SELECTED ZINC FINGER DIMER BOUND TO DNA1jk1: Zif268 D20A Mutant Bound to WT DNA Site1jk2: Zif268 D20A mutant bound to the GCT DNA site1p47: Crystal Structure of tandem Zif268 molecules complexed to DNA1zaa: ZINC FINGER-DNA RECOGNITION: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A ZIF268-DNA COMPLEX AT 2.1 ANGSTROMSTranscription factors and intracellular receptors (1) Basic domains (1.1) Basic leucine zipper (bZIP)Activating transcription factor (AATF, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) · AP-1 (c-Fos, FOSB, FOSL1, FOSL2, JDP2, c-Jun, JUNB, JUND) · BACH (1, 2) · BATF · BLZF1 · C/EBP (α, β, γ, δ, ε, ζ) · CREB (1, 3, L1) · CREM · DBP · DDIT3 · GABPA · HLF · MAF (B, F, G, K) · NFE (2, L1, L2, L3) · NFIL3 · NRL · NRF (1, 2, 3) · XBP1(1.2) Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)ATOH1 · AhR · AHRR · ARNT · ASCL1 · BHLHB2 · BMAL (ARNTL, ARNTL2) · CLOCK · EPAS1 · FIGLA · HAND (1, 2) · HES (5, 6) · HEY (1, 2, L) · HES1 · HIF (1A, 3A) · ID (1, 2, 3, 4) · LYL1 · MESP2 · MXD4 · MYCL1 · MYCN · Myogenic regulatory factors (MyoD, Myogenin, MYF5, MYF6) · Neurogenins (1, 2, 3) · NeuroD (1, 2) · NPAS (1, 2, 3) · OLIG (1, 2) · Pho4 · Scleraxis · SIM (1, 2) · TAL (1, 2) · Twist · USF1(1.3) bHLH-ZIP(1.4) NF-1(1.5) RF-X(1.6) Basic helix-span-helix (bHSH)(2) Zinc finger DNA-binding domains (2.1) Nuclear receptor (Cys4)subfamily 1 (Thyroid hormone (α, β), CAR, FXR, LXR (α, β), PPAR (α, β/δ, γ), PXR, RAR (α, β, γ), ROR (α, β, γ), Rev-ErbA (α, β), VDR)
subfamily 2 (COUP-TF (I, II), Ear-2, HNF4 (α, γ), PNR, RXR (α, β, γ), Testicular receptor (2, 4), TLX)
subfamily 3 (Steroid hormone (Androgen, Estrogen (α, β), Glucocorticoid, Mineralocorticoid, Progesterone), Estrogen related (α, β, γ))
subfamily 4 NUR (NGFIB, NOR1, NURR1) · subfamily 5 (LRH-1, SF1) · subfamily 6 (GCNF) · subfamily 0 (DAX1, SHP)(2.2) Other Cys4(2.3) Cys2His2General transcription factors (TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE (1, 2), TFIIF (1, 2), TFIIH (1, 2, 4, 2I, 3A, 3C1, 3C2))
ATBF1 · BCL (6, 11A, 11B) · CTCF · E4F1 · EGR (1, 2, 3, 4) · ERV3 · GFI1 · GLI-Krüppel family (1, 2, 3, REST, S2, YY1) · HIC (1, 2) · HIVEP (1, 2, 3) · IKZF (1, 2, 3) · ILF (2, 3) · KLF (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17) · MTF1 · MYT1 · OSR1 · PRDM9 · SALL (1, 2, 3, 4) · SP (1, 2, 4, 7, 8) · TSHZ3 · WT1 · Zbtb7 (7A, 7B) · ZBTB (16, 17, 20, 32, 33, 40) · zinc finger (3, 7, 9, 10, 19, 22, 24, 33B, 34, 35, 41, 43, 44, 51, 74, 143, 146, 148, 165, 202, 217, 219, 238, 239, 259, 267, 268, 281, 295, 300, 318, 330, 346, 350, 365, 366, 384, 423, 451, 452, 471, 593, 638, 644, 649, 655)(2.4) Cys6(2.5) Alternating composition(3) Helix-turn-helix domains (3.1) HomeodomainARX · CDX (1, 2) · CRX · CUTL1 · DBX (1, 2) · DLX (3, 4, 5) · EMX2 · EN (1, 2) · FHL (1, 2, 3) · HESX1 · HHEX · HLX · Homeobox (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A7, A9, A10, A11, A13, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9, B13, C4, C5, C6, C8, C9, C10, C11, C12, C13, D1, D3, D4, D8, D9, D10, D11, D12, D13) · HOPX · IRX (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, MKX) · LMX (1A, 1B) · MEIS (1, 2) · MEOX2 · MNX1 · MSX (1, 2) · NANOG · NKX (2-1, 2-2, 2-3, 2-5, 3-1, 3-2, 6-1, 6-2) · NOBOX · PBX (1, 2, 3) · PHF (1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 16, 17, 20, 21A) · PHOX (2A, 2B) · PITX (1, 2, 3) · POU domain (PIT-1, BRN-3: A, B, C, Octamer transcription factor: 1, 2, 3/4, 6, 7, 11) · OTX (1, 2) · PDX1 · SATB2 · SHOX2 · VAX1 · ZEB (1, 2)(3.2) Paired box(3.3) Fork head / winged helix(3.4) Heat Shock Factors(3.5) Tryptophan clusters(3.6) TEA domain(4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts (4.1) Rel homology region(4.2) STAT(4.3) p53(4.4) MADS box(4.6) TATA binding proteins(4.7) High-mobility group(4.10) Cold-shock domainCSDA, YBX1(4.11) Runt(0) Other transcription factors (0.2) HMGI(Y)(0.3) Pocket domain(0.6) MiscellaneousCategories:- Human proteins
- Molecular neuroscience
- Transcription factors
- Zinc proteins
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.