- Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor beta or delta (PPAR-β or PPAR-δ), also known as NR1C2 (nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group C, member 2) is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the PPARD gene.[1]
This gene encodes a member of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) family. It was first identified in Xenopus in 1993.[2]
Contents
Function
PPARs are nuclear hormone receptors that bind peroxisome proliferators and control the size and number of peroxisomes produced by cells. PPARs mediate a variety of biological processes, and may be involved in the development of several chronic diseases, including diabetes, obesity, atherosclerosis, and cancer.[3][4]
This protein is a potent inhibitor of ligand-induced transcription activity of PPAR-α and PPAR-γ. It may function as an integrator of transcription repression and nuclear receptor signaling. The expression of this gene is found to be elevated in colorectal cancer cells.[5] The elevated expression can be repressed by adenomatosis polyposis coli (APC), a tumor suppressor protein involved in the APC/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Knockout studies in mice suggested the role of this protein in myelination of the corpus callosum, epidermal cell proliferation, and glucose[6] and lipid metabolism.[7]
This protein has been shown to be involved in differentiation, lipid accumulation,[8] directional sensing, polarization, and migration in keratinocytes.[9]
Clinical significance
In one study, polymorphisms of PPARD were found to be associated with bipolar disorder.[10]
Pharmacology
Several high affinity ligands for PPAR-δ/β have been developed, including GW 501516 and GW 0742, which play an important role in research. In one study utilizing such a ligand, it has been shown that agonism of PPAR-δ changes the body's fuel preference from glucose to lipids.[11]
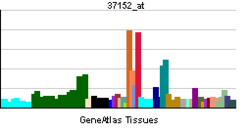
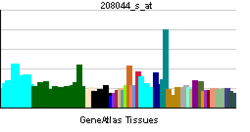
Tissue distribution
PPAR-δ/β is highly expressed in colon, small intestine, liver and keratinocytes. In contrast, heart, spleen, skeletal muscle, lung, brain and thymus show low expression.[12]
Knockout studies
Knockout mice lacking the ligand binding domain of PPAR-δ/β are viable. However these mice are smaller than the wild type both neo and postnatally. In addition, fat stores in the gonads of the mutants are smaller. The mutants also display increased epidermal hyperplasia upon induction with TPA.[13]
Ligands
Several selective ligands for PPARδ are now available.
Agonists
- GW-501,516
- GW-610,742[14]
Interactions
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta has been shown to interact with HDAC3[15][16] and NCOR2.[16]
References
- ^ Schmidt A, Endo N, Rutledge SJ, Vogel R, Shinar D, Rodan GA (1992). "Identification of a new member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily that is activated by a peroxisome proliferator and fatty acids". Mol. Endocrinol. 6 (10): 1634–41. doi:10.1210/me.6.10.1634. PMID 1333051.
- ^ Krey G, Keller H, Mahfoudi A, Medin J, Ozato K, Dreyer C, Wahli W (1993). "Xenopus peroxisome proliferator activated receptors: genomic organization, response element recognition, heterodimer formation with retinoid X receptor and activation by fatty acids". J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 47 (1–6): 65–73. doi:10.1016/0960-0760(93)90058-5. PMID 8274443.
- ^ Berger J, Moller DE (2002). "The mechanisms of action of PPARs". Annu. Rev. Med. 53: 409–35. doi:10.1146/annurev.med.53.082901.104018. PMID 11818483.
- ^ Feige JN, Gelman L, Michalik L, Desvergne B, Wahli W (2006). "From molecular action to physiological outputs: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors are nuclear receptors at the crossroads of key cellular functions". Prog. Lipid Res. 45 (2): 120–59. doi:10.1016/j.plipres.2005.12.002. PMID 16476485.
- ^ Takayama O, Yamamoto H, Damdinsuren B, Sugita Y, Ngan CY, Xu X, Tsujino T, Takemasa I, Ikeda M, Sekimoto M, Matsuura N, Monden M (2006). "Expression of PPARδ in multistage carcinogenesis of the colorectum: implications of malignant cancer morphology". Br. J. Cancer 95 (7): 889–95. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6603343. PMC 2360534. PMID 16969348. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2360534.
- ^ Lee CH, Olson P, Hevener A, Mehl I, Chong LW, Olefsky JM, Gonzalez FJ, Ham J, Kang H, Peters JM, Evans RM (2006). "PPARδ regulates glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103 (9): 3444–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.0511253103. PMC 1413918. PMID 16492734. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1413918.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: PPARD peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=5467.
- ^ Schmuth M, Haqq CM, Cairns WJ, Holder JC, Dorsam S, Chang S, Lau P, Fowler AJ, Chuang G, Moser AH, Brown BE, Mao-Qiang M, Uchida Y, Schoonjans K, Auwerx J, Chambon P, Willson TM, Elias PM, Feingold KR (April 2004). "Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-beta/delta stimulates differentiation and lipid accumulation in keratinocytes". J. Invest. Dermatol. 122 (4): 971–83. doi:10.1111/j.0022-202X.2004.22412.x. PMID 15102088.
- ^ Tan NS, Icre G, Montagner A, Bordier-ten-Heggeler B, Wahli W, Michalik L (October 2007). "The Nuclear Hormone Receptor Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor β/δ Potentiates Cell Chemotactism, Polarization, and Migration". Mol. Cell. Biol. 27 (20): 7161–75. doi:10.1128/MCB.00436-07. PMC 2168901. PMID 17682064. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2168901.
- ^ Zandi PP, Belmonte PL, Willour VL, Goes FS, Badner JA, Simpson SG, Gershon ES, McMahon FJ, DePaulo JR Jr, Potash JB; Bipolar Disorder Phenome Group; National Institute of Mental Health Genetics Initiative Bipolar Disorder Consortium (July 2008). "Association Study of Wnt Signaling Pathway Genes in Bipolar Disorder". Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 65 (7): 785–93. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.65.7.785. PMC 3170992. PMID 18606951. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=3170992.
- ^ Brunmair B, Staniek K, Dörig J, Szöcs Z, Stadlbauer K, Marian V, Gras F, Anderwald C, Nohl H, Waldhäusl W, Fürnsinn C (November 2006). "Activation of PPAR-δ in isolated rat skeletal muscle switches fuel preference from glucose to fatty acids". Diabetologia 49 (11): 2713–22. doi:10.1007/s00125-006-0357-6. PMID 16960684.
- ^ Girroir EE, Hollingshead HE, He P, Zhu B, Perdew GH, Peters JM (July 2008). "Quantitative expression patterns of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-β/δ (PPARβ/δ) protein in mice". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 371 (3): 456–61. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.04.086. PMC 2586836. PMID 18442472. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2586836.
- ^ Peters JM, Lee SS, Li W, Ward JM, Gavrilova O, Everett C, Reitman ML, Hudson LD, Gonzalez FJ. (1993). "Growth, Adipose, Brain, and Skin Alterations Resulting from Targeted Disruption of the Mouse Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor β(δ)". Mol Cell Biol. 20 (14): 5119–28. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.14.5119-5128.2000. PMC 85961. PMID 10866668. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=85961.
- ^ van der Veen JN, Kruit JK, Havinga R, Baller JF, Chimini G, Lestavel S, Staels B, Groot PH, Groen AK, Kuipers F (March 2005). "Reduced cholesterol absorption upon PPAR-δ activation coincides with decreased intestinal expression of NPC1L1". J. Lipid Res. 46 (3): 526–34. doi:10.1194/jlr.M400400-JLR200. PMID 15604518.
- ^ Franco PJ, Li G, Wei LN (August 2003). "Interaction of nuclear receptor zinc finger DNA binding domains with histone deacetylase". Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 206 (1–2): 1–12. doi:10.1016/S0303-7207(03)00254-5. PMID 12943985.
- ^ a b Shi Y, Hon M, Evans RM (March 2002). "The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor δ, an integrator of transcriptional repression and nuclear receptor signaling". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (5): 2613–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.052707099. PMC 122396. PMID 11867749. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=122396.
Further reading
- Chong HC et al. (2009). "Regulation of epithelial–mesenchymal IL-1 signaling by PPARβ/δ is essential for skin homeostasis and wound healing". J. Cell Biol. 184 (6): 817–831. doi:10.1083/jcb.200809028. PMC 2699156. PMID 19307598. http://jcb.rupress.org/content/184/6/817.long.
- Tan NS et al. (2005). "Genetic- or transforming growth factor-beta 1-induced changes in epidermal peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor beta/delta expression dictate wound repair kinetics". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (18): 18163–18170. doi:10.1074/jbc.M412829200. PMID 15708854. http://www.jbc.org/content/280/18/18163.long.
- Tan NS et al. (2004). "Essential role of Smad3 in the inhibition of inflammation-induced PPARβ/δ expression". EMBO J. 23 (21): 4211–4221. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600437. PMC 524401. PMID 15470497. http://www.nature.com/emboj/journal/v23/n21/full/7600437a.html.
- Di-Poï N et al. (2002). "Antiapoptotic role of PPARbeta in keratinocytes via transcriptional control of the Akt1 signaling pathway". Mol. Cell 10 (4): 721–733. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00646-9. PMID 12419217. http://www.cell.com/molecular-cell/retrieve/pii/S1097276502006469.
- Tan NS et al. (2001). "Critical roles of PPARβ/δ in keratinocyte response to inflammation". Genes Dev. 15 (24): 3263–3277. doi:10.1101/gad.207501. PMC 312855. PMID 11751632. http://genesdev.cshlp.org/content/15/24/3263.long.
- Michalik L et al. (2001). "Impaired skin wound healing in peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor (PPAR)α and PPARβ mutant mice". J. Cell Biol. 154 (4): 799–814. doi:10.1083/jcb.200011148. PMC 2196455. PMID 11514592. http://jcb.rupress.org/content/154/4/799.long.
External links
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
PDB gallery 1gwx: MOLECULAR RECOGNITION OF FATTY ACIDS BY PEROXISOME PROLIFERATOR-ACTIVATED RECEPTORS1y0s: Crystal structure of PPAR delta complexed with GW23312awh: Human Nuclear Receptor-Ligand Complex 12b50: Human Nuclear Receptor-Ligand Complex 22baw: Human Nuclear Receptor-Ligand Complex 12gwx: MOLECULAR RECOGNITION OF FATTY ACIDS BY PEROXISOME PROLIFERATOR-ACTIVATED RECEPTORS2j14: 3,4,5-TRISUBSTITUTED ISOXAZOLES AS NOVEL PPARDELTA AGONISTS: PART23gwx: MOLECULAR RECOGNITION OF FATTY ACIDS BY PEROXISOME PROLIFERATOR-ACTIVATED RECEPTORSTranscription factors and intracellular receptors (1) Basic domains Activating transcription factor (AATF, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) · AP-1 (c-Fos, FOSB, FOSL1, FOSL2, JDP2, c-Jun, JUNB, JUND) · BACH (1, 2) · BATF · BLZF1 · C/EBP (α, β, γ, δ, ε, ζ) · CREB (1, 3, L1) · CREM · DBP · DDIT3 · GABPA · HLF · MAF (B, F, G, K) · NFE (2, L1, L2, L3) · NFIL3 · NRL · NRF (1, 2, 3) · XBP1ATOH1 · AhR · AHRR · ARNT · ASCL1 · BHLHB2 · BMAL (ARNTL, ARNTL2) · CLOCK · EPAS1 · FIGLA · HAND (1, 2) · HES (5, 6) · HEY (1, 2, L) · HES1 · HIF (1A, 3A) · ID (1, 2, 3, 4) · LYL1 · MESP2 · MXD4 · MYCL1 · MYCN · Myogenic regulatory factors (MyoD, Myogenin, MYF5, MYF6) · Neurogenins (1, 2, 3) · NeuroD (1, 2) · NPAS (1, 2, 3) · OLIG (1, 2) · Pho4 · Scleraxis · SIM (1, 2) · TAL (1, 2) · Twist · USF1(1.4) NF-1(1.5) RF-X(1.6) Basic helix-span-helix (bHSH)(2) Zinc finger DNA-binding domains subfamily 1 (Thyroid hormone (α, β), CAR, FXR, LXR (α, β), PPAR (α, β/δ, γ), PXR, RAR (α, β, γ), ROR (α, β, γ), Rev-ErbA (α, β), VDR)
subfamily 2 (COUP-TF (I, II), Ear-2, HNF4 (α, γ), PNR, RXR (α, β, γ), Testicular receptor (2, 4), TLX)
subfamily 3 (Steroid hormone (Androgen, Estrogen (α, β), Glucocorticoid, Mineralocorticoid, Progesterone), Estrogen related (α, β, γ))
subfamily 4 NUR (NGFIB, NOR1, NURR1) · subfamily 5 (LRH-1, SF1) · subfamily 6 (GCNF) · subfamily 0 (DAX1, SHP)(2.2) Other Cys4(2.3) Cys2His2General transcription factors (TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE (1, 2), TFIIF (1, 2), TFIIH (1, 2, 4, 2I, 3A, 3C1, 3C2))
ATBF1 · BCL (6, 11A, 11B) · CTCF · E4F1 · EGR (1, 2, 3, 4) · ERV3 · GFI1 · GLI-Krüppel family (1, 2, 3, REST, S2, YY1) · HIC (1, 2) · HIVEP (1, 2, 3) · IKZF (1, 2, 3) · ILF (2, 3) · KLF (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17) · MTF1 · MYT1 · OSR1 · PRDM9 · SALL (1, 2, 3, 4) · SP (1, 2, 4, 7, 8) · TSHZ3 · WT1 · Zbtb7 (7A, 7B) · ZBTB (16, 17, 20, 32, 33, 40) · zinc finger (3, 7, 9, 10, 19, 22, 24, 33B, 34, 35, 41, 43, 44, 51, 74, 143, 146, 148, 165, 202, 217, 219, 238, 239, 259, 267, 268, 281, 295, 300, 318, 330, 346, 350, 365, 366, 384, 423, 451, 452, 471, 593, 638, 644, 649, 655)(2.4) Cys6(2.5) Alternating composition(3) Helix-turn-helix domains ARX · CDX (1, 2) · CRX · CUTL1 · DBX (1, 2) · DLX (3, 4, 5) · EMX2 · EN (1, 2) · FHL (1, 2, 3) · HESX1 · HHEX · HLX · Homeobox (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A7, A9, A10, A11, A13, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9, B13, C4, C5, C6, C8, C9, C10, C11, C12, C13, D1, D3, D4, D8, D9, D10, D11, D12, D13) · HOPX · IRX (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, MKX) · LMX (1A, 1B) · MEIS (1, 2) · MEOX2 · MNX1 · MSX (1, 2) · NANOG · NKX (2-1, 2-2, 2-3, 2-5, 3-1, 3-2, 6-1, 6-2) · NOBOX · PBX (1, 2, 3) · PHF (1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 16, 17, 20, 21A) · PHOX (2A, 2B) · PITX (1, 2, 3) · POU domain (PIT-1, BRN-3: A, B, C, Octamer transcription factor: 1, 2, 3/4, 6, 7, 11) · OTX (1, 2) · PDX1 · SATB2 · SHOX2 · VAX1 · ZEB (1, 2)(3.2) Paired box(3.5) Tryptophan clusters(3.6) TEA domain(4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts (4.1) Rel homology region(4.3) p53(4.7) High-mobility group(4.10) Cold-shock domainCSDA, YBX1(4.11) Runt(0) Other transcription factors (0.2) HMGI(Y)(0.6) MiscellaneousCategories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 6 gene stubs
- Intracellular receptors
- Transcription factors
- Biology of bipolar disorder
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.