- CEBPB
-
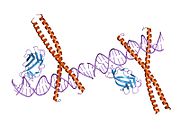
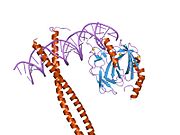
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEBPB gene.[1][2]
Contents
Function
The protein encoded by this intronless gene is a bZIP transcription factor that can bind as a homodimer to certain DNA regulatory regions. It can also form heterodimers with the related proteins CEBP-alpha, CEBP-delta, and CEBP-gamma. The encoded protein is important in the regulation of genes involved in immune and inflammatory responses and has been shown to bind to the IL-1 response element in the IL-6 gene, as well as to regulatory regions of several acute-phase and cytokine genes. In addition, the encoded protein can bind the promoter and upstream element and stimulate the expression of the collagen type I gene.[3]
Target genes
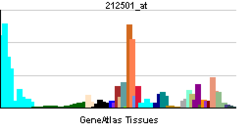
CEBPB is capable of increasing the expression of several target genes. Among them, some have specific role in the nervous system such as the preprotachykinin gene, giving rise to substance P and neurokinin A[4] and the choline acetyltransferase responsible for the biosynthesis of the important neurotransmitter acetylcholine.[5] Other targets include genes coding for cytokines such as IL-6,[6] IL-4,[7] IL-5,[8] and TNF-alpha.[9] Genes coding for transporter proteins that confer multidrug resistance to the cells have also been found to be activated by CEBPB. Such genes include ABCC2[10] and ABCB1.[11]
Interactions
CEBPB has been shown to interact with:
See also
References
- ^ Szpirer C, Riviere M, Cortese R, Nakamura T, Islam MQ, Levan G, Szpirer J (Jul 1992). "Chromosomal localization in man and rat of the genes encoding the liver-enriched transcription factors C/EBP, DBP, and HNF1/LFB-1 (CEBP, DBP, and transcription factor 1, TCF1, respectively) and of the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor gene (HGF)". Genomics 13 (2): 293–300. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(92)90245-N. PMID 1535333.
- ^ Cao Z, Umek RM, McKnight SL (Oct 1991). "Regulated expression of three C/EBP isoforms during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells". Genes Dev 5 (9): 1538–52. doi:10.1101/gad.5.9.1538. PMID 1840554.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: CEBPB CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), beta". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=1051.
- ^ Kovács KA, Steinmann M, Magistretti PJ, Halfon O, Cardinaux JR (September 2006). "C/EBPbeta couples dopamine signalling to substance P precursor gene expression in striatal neurones". J. Neurochem. 98 (5): 1390–9. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03957.x. PMID 16771829.
- ^ Robert I, Sutter A, Quirin-Stricker C (October 2002). "Synergistic activation of the human choline acetyltransferase gene by c-Myb and C/EBPbeta". Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 106 (1–2): 124–35. doi:10.1016/S0169-328X(02)00419-9. PMID 12393272.
- ^ Natsuka S, Akira S, Nishio Y, Hashimoto S, Sugita T, Isshiki H, Kishimoto T (January 1992). "Macrophage differentiation-specific expression of NF-IL6, a transcription factor for interleukin-6". Blood 79 (2): 460–6. PMID 1730090.
- ^ Davydov IV, Krammer PH, Li-Weber M (December 1995). "Nuclear factor-IL6 activates the human IL-4 promoter in T cells". J. Immunol. 155 (11): 5273–9. PMID 7594540.
- ^ van Dijk TB, Baltus B, Raaijmakers JA, Lammers JW, Koenderman L, de Groot RP (September 1999). "A composite C/EBP binding site is essential for the activity of the promoter of the IL-3/IL-5/granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor beta c gene". J. Immunol. 163 (5): 2674–80. PMID 10453008.
- ^ Greenwel P, Tanaka S, Penkov D, Zhang W, Olive M, Moll J, Vinson C, Di Liberto M, Ramirez F (February 2000). "Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Inhibits Type I Collagen Synthesis through Repressive CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Proteins". Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (3): 912–8. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.3.912-918.2000. PMC 85208. PMID 10629048. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=85208.
- ^ Tanaka T, Uchiumi T, Hinoshita E, Inokuchi A, Toh S, Wada M, Takano H, Kohno K, Kuwano M (December 1999). "The human multidrug resistance protein 2 gene: functional characterization of the 5'-flanking region and expression in hepatic cells". Hepatology 30 (6): 1507–12. doi:10.1002/hep.510300617. PMID 10573531.
- ^ Chen GK, Sale S, Tan T, Ermoian RP, Sikic BI (April 2004). "CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta (nuclear factor for interleukin 6) transactivates the human MDR1 gene by interaction with an inverted CCAAT box in human cancer cells". Mol. Pharmacol. 65 (4): 906–16. doi:10.1124/mol.65.4.906. PMID 15044620.
- ^ Chen, Yongchang; Zhuang Shunhui, Cassenaer Stijn, Casteel Darren E, Gudi Tanima, Boss Gerry R, Pilz Renate B (Jun. 2003). "Synergism between Calcium and Cyclic GMP in Cyclic AMP Response Element-Dependent Transcriptional Regulation Requires Cooperation between CREB and C/EBP-β". Mol. Cell. Biol. 23 (12): 4066–82. doi:10.1128/MCB.23.12.4066-4082.2003. PMC 156132. PMID 12773552. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=156132.
- ^ Mo, Xianming; Kowenz-Leutz Elisabeth, Xu Hong, Leutz Achim (Jan. 2004). "Ras induces mediator complex exchange on C/EBP beta". Mol. Cell 13 (2): 241–50. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(03)00521-5. PMID 14759369.
- ^ Hattori, Takayuki; Ohoka Nobumichi, Hayashi Hidetoshi, Onozaki Kikuo (Apr. 2003). "C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) up-regulates IL-6 transcription by trapping negative regulating NF-IL6 isoform". FEBS Lett. 541 (1–3): 33–9. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(03)00283-7. PMID 12706815.
- ^ Fawcett, T W; Eastman H B, Martindale J L, Holbrook N J (Jun. 1996). "Physical and functional association between GADD153 and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta during cellular stress". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (24): 14285–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.24.14285. PMID 8662954.
- ^ Mink, S; Haenig B, Klempnauer K H (Nov. 1997). "Interaction and functional collaboration of p300 and C/EBPbeta". Mol. Cell. Biol. 17 (11): 6609–17. PMC 232514. PMID 9343424. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=232514.
- ^ a b Boruk, M; Savory J G, Haché R J (Nov. 1998). "AF-2-dependent potentiation of CCAAT enhancer binding protein beta-mediated transcriptional activation by glucocorticoid receptor". Mol. Endocrinol. 12 (11): 1749–63. doi:10.1210/me.12.11.1749. PMID 9817600.
- ^ Stein, B; Yang M X (Sep. 1995). "Repression of the interleukin-6 promoter by estrogen receptor is mediated by NF-kappa B and C/EBP beta". Mol. Cell. Biol. 15 (9): 4971–9. PMC 230744. PMID 7651415. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=230744.
- ^ a b Foti, Daniela; Iuliano Rodolfo, Chiefari Eusebio, Brunetti Antonio (Apr. 2003). "A Nucleoprotein Complex Containing Sp1, C/EBPβ, and HMGI-Y Controls Human Insulin Receptor Gene Transcription". Mol. Cell. Biol. 23 (8): 2720–32. doi:10.1128/MCB.23.8.2720-2732.2003. PMC 152545. PMID 12665574. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=152545.
- ^ Xie, Yue; Chen Changmin, Stevenson Mary Ann, Auron Philip E, Calderwood Stuart K (Apr. 2002). "Heat shock factor 1 represses transcription of the IL-1beta gene through physical interaction with the nuclear factor of interleukin 6". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (14): 11802–10. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109296200. PMID 11801594.
- ^ Miau, L H; Chang C J, Shen B J, Tsai W H, Lee S C (Apr. 1998). "Identification of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP K) as a repressor of C/EBPbeta-mediated gene activation". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (17): 10784–91. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.17.10784. PMID 9553145.
- ^ Weber, Marion; Sydlik Carmen, Quirling Martina, Nothdurfter Caroline, Zwergal Andreas, Heiss Peter, Bell Susanne, Neumeier Dieter, Ziegler-Heitbrock H W Loms, Brand Korbinian (Jun. 2003). "Transcriptional inhibition of interleukin-8 expression in tumor necrosis factor-tolerant cells: evidence for involvement of C/EBP beta". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (26): 23586–93. doi:10.1074/jbc.M211646200. PMID 12707271.
- ^ Xia, C; Cheshire J K, Patel H, Woo P (Dec. 1997). "Cross-talk between transcription factors NF-kappa B and C/EBP in the transcriptional regulation of genes". Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 29 (12): 1525–39. doi:10.1016/S1357-2725(97)00083-6. PMID 9570146.
- ^ Hanlon, M; Sealy L (May. 1999). "Ras regulates the association of serum response factor and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (20): 14224–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.20.14224. PMID 10318842.
- ^ Sealy, L; Malone D, Pawlak M (Mar. 1997). "Regulation of the cfos serum response element by C/EBPbeta". Mol. Cell. Biol. 17 (3): 1744–55. PMC 231899. PMID 9032301. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=231899.
- ^ Kowenz-Leutz, E; Leutz A (Nov. 1999). "A C/EBP beta isoform recruits the SWI/SNF complex to activate myeloid genes". Mol. Cell 4 (5): 735–43. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80384-6. PMID 10619021.
- ^ Liu, Yi-Wen; Tseng Hui-Ping, Chen Lei-Chin, Chen Ben-Kuen, Chang Wen-Chang (Jul. 2003). "Functional cooperation of simian virus 40 promoter factor 1 and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta and delta in lipopolysaccharide-induced gene activation of IL-10 in mouse macrophages". J. Immunol. 171 (2): 821–8. PMID 12847250.
- ^ Rooney, J W; Calame K L (Nov. 2001). "TIF1β functions as a coactivator for C/EBPβ and is required for induced differentiation in the myelomonocytic cell line U937". Genes Dev. 15 (22): 3023–38. doi:10.1101/gad.937201. PMC 312827. PMID 11711437. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=312827.
- ^ Chang, C J; Chen Y L, Lee S C (Oct. 1998). "Coactivator TIF1β Interacts with Transcription Factor C/EBPβ and Glucocorticoid Receptor To Induce α1-Acid Glycoprotein Gene Expression". Mol. Cell. Biol. 18 (10): 5880–7. PMC 109174. PMID 9742105. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=109174.
- ^ Zhang, Fang; Lin Meihong, Abidi Parveen, Thiel Gerald, Liu Jingwen (Nov. 2003). "Specific interaction of Egr1 and c/EBPbeta leads to the transcriptional activation of the human low density lipoprotein receptor gene". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (45): 44246–54. doi:10.1074/jbc.M305564200. PMID 12947119.
Further reading
- Sladek FM, Darnell JE (1992). "Mechanisms of liver-specific gene expression". Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2 (2): 256–9. doi:10.1016/S0959-437X(05)80282-5. PMID 1638120.
- Maytin EV, Habener JF (1998). "Transcription factors C/EBP alpha, C/EBP beta, and CHOP (Gadd153) expressed during the differentiation program of keratinocytes in vitro and in vivo". J. Invest. Dermatol. 110 (3): 238–46. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.1998.00123.x. PMID 9506442.
- Cornwall GA, Hsia N (2003). "[Cres (cystatin-related epididymal spermatogenic) gene regulation and function]". Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue 8 (5): 313–8. PMID 12479114.
External links
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
PDB gallery 1ci6: TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR ATF4-C/EBP BETA BZIP HETERODIMER1gtw: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF C/EBPBETA BZIP DIMERIC BOUND TO A DNA FRAGMENT FROM THE TOM-1A PROMOTER1gu4: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF C/EBPBETA BZIP DIMERIC BOUND TO A HIGH AFFINITY DNA FRAGMENT1gu5: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF C/EBPBETA BZIP DIMERIC BOUND TO A DNA FRAGMENT FROM THE MIM-1 PROMOTER1h88: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF TERNARY PROTEIN-DNA COMPLEX11h89: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF TERNARY PROTEIN-DNA COMPLEX21h8a: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF TERNARY PROTEIN-DNA COMPLEX31hjb: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF RUNX-1/AML1/CBFALPHA RUNT DOMAIN AND C/EBPBETA BZIP DIMERIC BOUND TO A DNA FRAGMENT FROM THE CSF-1R PROMOTER1io4: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF RUNX-1/AML1/CBFALPHA RUNT DOMAIN-CBFBETA CORE DOMAIN HETERODIMER AND C/EBPBETA BZIP HOMODIMER BOUND TO A DNA FRAGMENT FROM THE CSF-1R PROMOTERTranscription factors and intracellular receptors (1) Basic domains (1.1) Basic leucine zipper (bZIP)Activating transcription factor (AATF, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) · AP-1 (c-Fos, FOSB, FOSL1, FOSL2, JDP2, c-Jun, JUNB, JUND) · BACH (1, 2) · BATF · BLZF1 · C/EBP (α, β, γ, δ, ε, ζ) · CREB (1, 3, L1) · CREM · DBP · DDIT3 · GABPA · HLF · MAF (B, F, G, K) · NFE (2, L1, L2, L3) · NFIL3 · NRL · NRF (1, 2, 3) · XBP1(1.2) Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)ATOH1 · AhR · AHRR · ARNT · ASCL1 · BHLHB2 · BMAL (ARNTL, ARNTL2) · CLOCK · EPAS1 · FIGLA · HAND (1, 2) · HES (5, 6) · HEY (1, 2, L) · HES1 · HIF (1A, 3A) · ID (1, 2, 3, 4) · LYL1 · MESP2 · MXD4 · MYCL1 · MYCN · Myogenic regulatory factors (MyoD, Myogenin, MYF5, MYF6) · Neurogenins (1, 2, 3) · NeuroD (1, 2) · NPAS (1, 2, 3) · OLIG (1, 2) · Pho4 · Scleraxis · SIM (1, 2) · TAL (1, 2) · Twist · USF1(1.3) bHLH-ZIP(1.4) NF-1(1.5) RF-X(1.6) Basic helix-span-helix (bHSH)(2) Zinc finger DNA-binding domains (2.1) Nuclear receptor (Cys4)subfamily 1 (Thyroid hormone (α, β), CAR, FXR, LXR (α, β), PPAR (α, β/δ, γ), PXR, RAR (α, β, γ), ROR (α, β, γ), Rev-ErbA (α, β), VDR)
subfamily 2 (COUP-TF (I, II), Ear-2, HNF4 (α, γ), PNR, RXR (α, β, γ), Testicular receptor (2, 4), TLX)
subfamily 3 (Steroid hormone (Androgen, Estrogen (α, β), Glucocorticoid, Mineralocorticoid, Progesterone), Estrogen related (α, β, γ))
subfamily 4 NUR (NGFIB, NOR1, NURR1) · subfamily 5 (LRH-1, SF1) · subfamily 6 (GCNF) · subfamily 0 (DAX1, SHP)(2.2) Other Cys4(2.3) Cys2His2General transcription factors (TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE (1, 2), TFIIF (1, 2), TFIIH (1, 2, 4, 2I, 3A, 3C1, 3C2))
ATBF1 · BCL (6, 11A, 11B) · CTCF · E4F1 · EGR (1, 2, 3, 4) · ERV3 · GFI1 · GLI-Krüppel family (1, 2, 3, REST, S2, YY1) · HIC (1, 2) · HIVEP (1, 2, 3) · IKZF (1, 2, 3) · ILF (2, 3) · KLF (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17) · MTF1 · MYT1 · OSR1 · PRDM9 · SALL (1, 2, 3, 4) · SP (1, 2, 4, 7, 8) · TSHZ3 · WT1 · Zbtb7 (7A, 7B) · ZBTB (16, 17, 20, 32, 33, 40) · zinc finger (3, 7, 9, 10, 19, 22, 24, 33B, 34, 35, 41, 43, 44, 51, 74, 143, 146, 148, 165, 202, 217, 219, 238, 239, 259, 267, 268, 281, 295, 300, 318, 330, 346, 350, 365, 366, 384, 423, 451, 452, 471, 593, 638, 644, 649, 655)(2.4) Cys6(2.5) Alternating composition(3) Helix-turn-helix domains (3.1) HomeodomainARX · CDX (1, 2) · CRX · CUTL1 · DBX (1, 2) · DLX (3, 4, 5) · EMX2 · EN (1, 2) · FHL (1, 2, 3) · HESX1 · HHEX · HLX · Homeobox (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A7, A9, A10, A11, A13, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9, B13, C4, C5, C6, C8, C9, C10, C11, C12, C13, D1, D3, D4, D8, D9, D10, D11, D12, D13) · HOPX · IRX (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, MKX) · LMX (1A, 1B) · MEIS (1, 2) · MEOX2 · MNX1 · MSX (1, 2) · NANOG · NKX (2-1, 2-2, 2-3, 2-5, 3-1, 3-2, 6-1, 6-2) · NOBOX · PBX (1, 2, 3) · PHF (1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 16, 17, 20, 21A) · PHOX (2A, 2B) · PITX (1, 2, 3) · POU domain (PIT-1, BRN-3: A, B, C, Octamer transcription factor: 1, 2, 3/4, 6, 7, 11) · OTX (1, 2) · PDX1 · SATB2 · SHOX2 · VAX1 · ZEB (1, 2)(3.2) Paired box(3.3) Fork head / winged helix(3.4) Heat Shock Factors(3.5) Tryptophan clusters(3.6) TEA domain(4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts (4.1) Rel homology region(4.2) STAT(4.3) p53(4.4) MADS box(4.6) TATA binding proteins(4.7) High-mobility group(4.10) Cold-shock domainCSDA, YBX1(4.11) Runt(0) Other transcription factors (0.2) HMGI(Y)(0.3) Pocket domain(0.6) MiscellaneousCategories:- Human proteins
- Transcription factors
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.