- NFATC4
-
Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic, calcineurin-dependent 4 Identifiers Symbols NFATC4; NF-ATc4; NFAT3 External IDs OMIM: 602699 MGI: 1920431 HomoloGene: 3349 GeneCards: NFATC4 Gene Gene Ontology Molecular function • DNA binding
• sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factor activity
• transcription coactivator activityCellular component • nucleus
• cytoplasm
• intermediate filament cytoskeletonBiological process • transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
• inflammatory response
• cell differentiationSources: Amigo / QuickGO RNA expression pattern 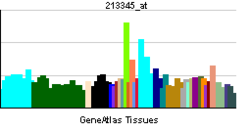
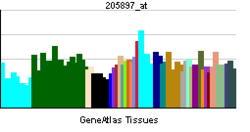
More reference expression data Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 4776 73181 Ensembl ENSG00000100968 ENSMUSG00000023411 UniProt Q14934 n/a RefSeq (mRNA) NM_001136022.1 NM_023699 RefSeq (protein) NP_001129494.1 NP_076188 Location (UCSC) Chr 14:
24.83 – 24.85 MbChr 14:
56.44 – 56.45 MbPubMed search [1] [2] Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NFATC4 gene.[1][2]
The product of this gene is a member of the nuclear factors of activated T cells DNA-binding transcription complex. This complex consists of at least two components: a preexisting cytosolic component that translocates to the nucleus upon T cell receptor (TCR) stimulation and an inducible nuclear component. Other members of this family of nuclear factors of activated T cells also participate in the formation of this complex. The product of this gene plays a role in the inducible expression of cytokine genes in T cells, especially in the induction of the IL-2 and IL-4.[2]
NFAT transcription factors are implicated in breast cancer, more specifically in the process of cell motility at the basis of metastasis formation. Indeed NFAT3 (NFATc4) is an inhibitor of cell motility by blocking the expression of LCN2 [3].Contents
Interactions
NFATC4 has been shown to interact with CREB-binding protein.[4]
See also
References
- ^ Hoey T, Sun YL, Williamson K, Xu X (Jun 1995). "Isolation of two new members of the NF-AT gene family and functional characterization of the NF-AT proteins". Immunity 2 (5): 461–72. doi:10.1016/1074-7613(95)90027-6. PMID 7749981.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: NFATC4 nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic, calcineurin-dependent 4". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=4776.
- ^ Fougère, M; Gaudineau, B, Barbier, J, Guaddachi, F, Feugeas, JP, Auboeuf, D, Jauliac, S (2010 Apr 15). "NFAT3 transcription factor inhibits breast cancer cell motility by targeting the Lipocalin 2 gene.". Oncogene 29 (15): 2292–301. PMID 20101218.
- ^ Yang, T; Davis R J, Chow C W (Oct. 2001). "Requirement of two NFATc4 transactivation domains for CBP potentiation". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 276 (43): 39569–76. doi:10.1074/jbc.M102961200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 11514544.
Further reading
- Rao A, Luo C, Hogan PG (1997). "Transcription factors of the NFAT family: regulation and function.". Annu. Rev. Immunol. 15: 707–47. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.15.1.707. PMID 9143705.
- Crabtree GR (1999). "Generic signals and specific outcomes: signaling through Ca2+, calcineurin, and NF-AT.". Cell 96 (5): 611–4. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80571-1. PMID 10089876.
- Horsley V, Pavlath GK (2002). "NFAT: ubiquitous regulator of cell differentiation and adaptation.". J. Cell Biol. 156 (5): 771–4. doi:10.1083/jcb.200111073. PMC 2173310. PMID 11877454. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2173310.
- Jabado N, Le Deist F, Fisher A, Hivroz C (1994). "Interaction of HIV gp120 and anti-CD4 antibodies with the CD4 molecule on human CD4+ T cells inhibits the binding activity of NF-AT, NF-kappa B and AP-1, three nuclear factors regulating interleukin-2 gene enhancer activity.". Eur. J. Immunol. 24 (11): 2646–52. doi:10.1002/eji.1830241112. PMID 7957556.
- Vacca A, Farina M, Maroder M, et al. (1995). "Human immunodeficiency virus type-1 tat enhances interleukin-2 promoter activity through synergism with phorbol ester and calcium-mediated activation of the NF-AT cis-regulatory motif.". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 205 (1): 467–74. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1994.2689. PMID 7999066.
- Di Somma MM, Majolini MB, Burastero SE, et al. (1996). "Cyclosporin A sensitivity of the HIV-1 long terminal repeat identifies distinct p56lck-dependent pathways activated by CD4 triggering.". Eur. J. Immunol. 26 (9): 2181–8. doi:10.1002/eji.1830260933. PMID 8814265.
- Molkentin JD, Lu JR, Antos CL, et al. (1998). "A calcineurin-dependent transcriptional pathway for cardiac hypertrophy.". Cell 93 (2): 215–28. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81573-1. PMID 9568714.
- Aramburu J, Garcia-Cózar F, Raghavan A, et al. (1998). "Selective inhibition of NFAT activation by a peptide spanning the calcineurin targeting site of NFAT.". Mol. Cell 1 (5): 627–37. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80063-5. PMID 9660947.
- Chow CW, Davis RJ (2000). "Integration of calcium and cyclic AMP signaling pathways by 14-3-3.". Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (2): 702–12. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.2.702-712.2000. PMC 85175. PMID 10611249. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=85175.
- Graef IA, Chen F, Chen L, et al. (2001). "Signals transduced by Ca(2+)/calcineurin and NFATc3/c4 pattern the developing vasculature.". Cell 105 (7): 863–75. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00396-8. PMID 11439183.
- Yang T, Davis RJ, Chow CW (2001). "Requirement of two NFATc4 transactivation domains for CBP potentiation.". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (43): 39569–76. doi:10.1074/jbc.M102961200. PMID 11514544.
- Yang TT, Xiong Q, Enslen H, et al. (2002). "Phosphorylation of NFATc4 by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases.". Mol. Cell. Biol. 22 (11): 3892–904. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.11.3892-3904.2002. PMC 133816. PMID 11997522. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=133816.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139241.
- Bennasser Y, Badou A, Tkaczuk J, Bahraoui E (2003). "Signaling pathways triggered by HIV-1 Tat in human monocytes to induce TNF-alpha.". Virology 303 (1): 174–80. doi:10.1006/viro.2002.1676. PMID 12482669.
- Graef IA, Wang F, Charron F, et al. (2003). "Neurotrophins and netrins require calcineurin/NFAT signaling to stimulate outgrowth of embryonic axons.". Cell 113 (5): 657–70. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00390-8. PMID 12787506.
- Lahti AL, Manninen A, Saksela K (2003). "Regulation of T cell activation by HIV-1 accessory proteins: Vpr acts via distinct mechanisms to cooperate with Nef in NFAT-directed gene expression and to promote transactivation by CREB.". Virology 310 (1): 190–6. doi:10.1016/S0042-6822(03)00164-8. PMID 12788643.
External links
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
Transcription factors and intracellular receptors (1) Basic domains Activating transcription factor (AATF, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) · AP-1 (c-Fos, FOSB, FOSL1, FOSL2, JDP2, c-Jun, JUNB, JUND) · BACH (1, 2) · BATF · BLZF1 · C/EBP (α, β, γ, δ, ε, ζ) · CREB (1, 3, L1) · CREM · DBP · DDIT3 · GABPA · HLF · MAF (B, F, G, K) · NFE (2, L1, L2, L3) · NFIL3 · NRL · NRF (1, 2, 3) · XBP1ATOH1 · AhR · AHRR · ARNT · ASCL1 · BHLHB2 · BMAL (ARNTL, ARNTL2) · CLOCK · EPAS1 · FIGLA · HAND (1, 2) · HES (5, 6) · HEY (1, 2, L) · HES1 · HIF (1A, 3A) · ID (1, 2, 3, 4) · LYL1 · MESP2 · MXD4 · MYCL1 · MYCN · Myogenic regulatory factors (MyoD, Myogenin, MYF5, MYF6) · Neurogenins (1, 2, 3) · NeuroD (1, 2) · NPAS (1, 2, 3) · OLIG (1, 2) · Pho4 · Scleraxis · SIM (1, 2) · TAL (1, 2) · Twist · USF1(1.4) NF-1(1.5) RF-X(1.6) Basic helix-span-helix (bHSH)(2) Zinc finger DNA-binding domains subfamily 1 (Thyroid hormone (α, β), CAR, FXR, LXR (α, β), PPAR (α, β/δ, γ), PXR, RAR (α, β, γ), ROR (α, β, γ), Rev-ErbA (α, β), VDR)
subfamily 2 (COUP-TF (I, II), Ear-2, HNF4 (α, γ), PNR, RXR (α, β, γ), Testicular receptor (2, 4), TLX)
subfamily 3 (Steroid hormone (Androgen, Estrogen (α, β), Glucocorticoid, Mineralocorticoid, Progesterone), Estrogen related (α, β, γ))
subfamily 4 NUR (NGFIB, NOR1, NURR1) · subfamily 5 (LRH-1, SF1) · subfamily 6 (GCNF) · subfamily 0 (DAX1, SHP)(2.2) Other Cys4(2.3) Cys2His2General transcription factors (TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE (1, 2), TFIIF (1, 2), TFIIH (1, 2, 4, 2I, 3A, 3C1, 3C2))
ATBF1 · BCL (6, 11A, 11B) · CTCF · E4F1 · EGR (1, 2, 3, 4) · ERV3 · GFI1 · GLI-Krüppel family (1, 2, 3, REST, S2, YY1) · HIC (1, 2) · HIVEP (1, 2, 3) · IKZF (1, 2, 3) · ILF (2, 3) · KLF (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17) · MTF1 · MYT1 · OSR1 · PRDM9 · SALL (1, 2, 3, 4) · SP (1, 2, 4, 7, 8) · TSHZ3 · WT1 · Zbtb7 (7A, 7B) · ZBTB (16, 17, 20, 32, 33, 40) · zinc finger (3, 7, 9, 10, 19, 22, 24, 33B, 34, 35, 41, 43, 44, 51, 74, 143, 146, 148, 165, 202, 217, 219, 238, 239, 259, 267, 268, 281, 295, 300, 318, 330, 346, 350, 365, 366, 384, 423, 451, 452, 471, 593, 638, 644, 649, 655)(2.4) Cys6(2.5) Alternating composition(3) Helix-turn-helix domains ARX · CDX (1, 2) · CRX · CUTL1 · DBX (1, 2) · DLX (3, 4, 5) · EMX2 · EN (1, 2) · FHL (1, 2, 3) · HESX1 · HHEX · HLX · Homeobox (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A7, A9, A10, A11, A13, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9, B13, C4, C5, C6, C8, C9, C10, C11, C12, C13, D1, D3, D4, D8, D9, D10, D11, D12, D13) · HOPX · IRX (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, MKX) · LMX (1A, 1B) · MEIS (1, 2) · MEOX2 · MNX1 · MSX (1, 2) · NANOG · NKX (2-1, 2-2, 2-3, 2-5, 3-1, 3-2, 6-1, 6-2) · NOBOX · PBX (1, 2, 3) · PHF (1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 16, 17, 20, 21A) · PHOX (2A, 2B) · PITX (1, 2, 3) · POU domain (PIT-1, BRN-3: A, B, C, Octamer transcription factor: 1, 2, 3/4, 6, 7, 11) · OTX (1, 2) · PDX1 · SATB2 · SHOX2 · VAX1 · ZEB (1, 2)(3.2) Paired box(3.5) Tryptophan clusters(3.6) TEA domain(4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts (4.1) Rel homology region(4.3) p53(4.7) High-mobility group(4.10) Cold-shock domainCSDA, YBX1(4.11) Runt(0) Other transcription factors (0.2) HMGI(Y)(0.6) MiscellaneousCategories:- Human proteins
- Transcription factors
- Chromosome 14 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
