- Estrogen-related receptor gamma
-
Estrogen-related receptor gamma (ERR-gamma), also known as NR3B3 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group B, member 3), is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the ESRRG (EStrogen Related Receptor Gamma) gene.[1][2][3] It behaves as a constitutive activator of transcription.[4]
This protein is a member of nuclear hormone receptor family of steroid hormone receptors. No physiological activating ligand is known for this orphan receptor, but 4-hydroxytamoxifen and diethylstilbestrol act as inverse agonists and deactivate ESRRG.[5] It also seems to be the target of bisphenol A (see below).
Bisphenol A binding
Further information: Bisphenol AThere is evidence that bisphenol A functions as an endocrine disruptor by binding strongly to ERR-γ.[4] BPA seems to binds strongly to ERR-γ (dissociation constant = 5.5 nM), but not to the estrogen receptor (ER).[4] BPA binding to ERR-γ preserves its basal constitutive activity.[4] It can also protect it from deactivation from the selective estrogen receptor modulator 4-hydroxytamoxifen.[4]
Different expression of ERR-γ in different parts of the body may account for variations in bisphenol A effects. For instance, ERR-γ has been found in high concentration in the placenta, explaining reports of high bisphenol A accumulation there.[6]
References
- ^ "Entrez Gene: ESRRG estrogen-related receptor gamma". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=2104.
- ^ Eudy JD, Yao S, Weston MD, Ma-Edmonds M, Talmadge CB, Cheng JJ, Kimberling WJ, Sumegi J (June 1998). "Isolation of a gene encoding a novel member of the nuclear receptor superfamily from the critical region of Usher syndrome type IIa at 1q41". Genomics 50 (3): 382–4. doi:10.1006/geno.1998.5345. PMID 9676434.
- ^ Chen F, Zhang Q, McDonald T, Davidoff MJ, Bailey W, Bai C, Liu Q, Caskey CT (March 1999). "Identification of two hERR2-related novel nuclear receptors utilizing bioinformatics and inverse PCR". Gene 228 (1–2): 101–9. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(98)00619-2. PMID 10072763.
- ^ a b c d e Matsushima A, Kakuta Y, Teramoto T, Koshiba T, Liu X, Okada H, Tokunaga T, Kawabata S, Kimura M, Shimohigashi Y (October 2007). "Structural evidence for endocrine disruptor bisphenol A binding to human nuclear receptor ERR gamma". J. Biochem. 142 (4): 517–24. doi:10.1093/jb/mvm158. PMID 17761695.
- ^ Huppunen J, Aarnisalo P (February 2004). "Dimerization modulates the activity of the orphan nuclear receptor ERRgamma". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 314 (4): 964–70. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.12.194. PMID 14751226.
- ^ Takeda Y, Liu X, Sumiyoshi M, Matsushima A, Shimohigashi M, Shimohigashi Y (July 2009). "Placenta expressing the greatest quantity of bisphenol A receptor ER-γ among the human reproductive tissues: Predominant expression of type-1 ERRgamma isoform". J. Biochem. 146 (1): 113–22. doi:10.1093/jb/mvp049. PMID 19304792.
Further reading
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (1997). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery". Genome Res. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.
- Nagase T, Ishikawa K, Suyama M, et al. (1999). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. XII. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Res. 5 (6): 355–64. doi:10.1093/dnares/5.6.355. PMID 10048485.
- Hong H, Yang L, Stallcup MR (1999). "Hormone-independent transcriptional activation and coactivator binding by novel orphan nuclear receptor ERR3". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (32): 22618–26. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.32.22618. PMID 10428842.
- Heard DJ, Norby PL, Holloway J, Vissing H (2000). "Human ERRgamma, a third member of the estrogen receptor-related receptor (ERR) subfamily of orphan nuclear receptors: tissue-specific isoforms are expressed during development and in the adult". Mol. Endocrinol. 14 (3): 382–92. doi:10.1210/me.14.3.382. PMID 10707956.
- Greschik H, Wurtz JM, Sanglier S, et al. (2002). "Structural and functional evidence for ligand-independent transcriptional activation by the estrogen-related receptor 3". Mol. Cell 9 (2): 303–13. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00444-6. PMID 11864604.
- Wistow G, Bernstein SL, Wyatt MK, et al. (2002). "Expressed sequence tag analysis of human RPE/choroid for the NEIBank Project: over 6000 non-redundant transcripts, novel genes and splice variants". Mol. Vis. 8: 205–20. PMID 12107410.
- Hentschke M, Süsens U, Borgmeyer U (2002). "Domains of ERRgamma that mediate homodimerization and interaction with factors stimulating DNA binding". Eur. J. Biochem. 269 (16): 4086–97. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.03102.x. PMID 12180985.
- Hentschke M, Süsens U, Borgmeyer U (2003). "PGC-1 and PERC, coactivators of the estrogen receptor-related receptor gamma". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 299 (5): 872–9. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(02)02753-5. PMID 12470660.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139241.
- Hentschke M, Schulze C, Süsens U, Borgmeyer U (2003). "Characterization of calmodulin binding to the orphan nuclear receptor Errgamma". Biol. Chem. 384 (3): 473–82. doi:10.1515/BC.2003.053. PMID 12715898.
- Hentschke M, Borgmeyer U (2004). "Identification of PNRC2 and TLE1 as activation function-1 cofactors of the orphan nuclear receptor ERRgamma". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 312 (4): 975–82. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.11.025. PMID 14651967.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=528928.
- Cheung CP, Yu S, Wong KB, et al. (2005). "Expression and functional study of estrogen receptor-related receptors in human prostatic cells and tissues". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 90 (3): 1830–44. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-1421. PMID 15598686.
- Liu D, Zhang Z, Teng CT (2005). "Estrogen-related receptor-gamma and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1alpha regulate estrogen-related receptor-alpha gene expression via a conserved multi-hormone response element". J. Mol. Endocrinol. 34 (2): 473–87. doi:10.1677/jme.1.01586. PMID 15821111.
- Gao M, Sun P, Wang J, et al. (2006). "Expression of estrogen receptor-related receptor isoforms and clinical significance in endometrial adenocarcinoma". Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 16 (2): 827–33. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1438.2006.00527.x. PMID 16681769.
- Gregory SG, Barlow KF, McLay KE, et al. (2006). "The DNA sequence and biological annotation of human chromosome 1". Nature 441 (7091): 315–21. doi:10.1038/nature04727. PMID 16710414.
- Wang L, Zuercher WJ, Consler TG, et al. (2007). "X-ray crystal structures of the estrogen-related receptor-gamma ligand binding domain in three functional states reveal the molecular basis of small molecule regulation". J. Biol. Chem. 281 (49): 37773–81. doi:10.1074/jbc.M608410200. PMID 16990259.
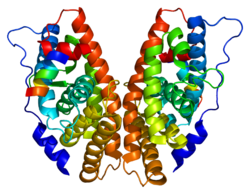
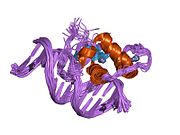
PDB gallery 1kv6: X-ray structure of the orphan nuclear receptor ERR3 ligand-binding domain in the constitutively active conformation1lo1: ESTROGEN RELATED RECEPTOR 2 DNA BINDING DOMAIN IN COMPLEX WITH DNA1s9p: crystal structure of the ligand-binding domain of the estrogen-related receptor gamma in complex with diethylstilbestrol1s9q: crystal structure of the ligand-binding domain of the estrogen-related receptor gamma in complex with 4-hydroxytamoxifen1tfc: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE LIGAND-BINDING DOMAIN OF THE ESTROGEN-RELATED RECEPTOR GAMMA IN COMPLEX WITH A STEROID RECEPTOR COACTIVATOR-1 PEPTIDE1vjb: crystal structure of the ligand-binding domain of the estrogen-related receptor gamma in complex with 4-hydroxytamoxifen2ewp: Crystal structure of Estrogen Related Reecptor-3 (ERR-gamma) ligand binding domaind with tamoxifen analog GSK51822gp7: Estrogen Related Receptor-gamma ligand binding domain2gpo: Estrogen Related Receptor-gamma ligand binding domain complexed with a synthetic peptide from RIP1402gpp: Estrogen Related Receptor-gamma ligand binding domain complexed with a RIP140 peptide and synthetic ligand GSK47162gpu: Estrogen Related Receptor-gamma ligand binding domain complexed with 4-hydroxy-tamoxifen2gpv: Estrogen Related Receptor-gamma ligand binding domain complexed with 4-hydroxy-tamoxifen and a SMRT peptideTranscription factors and intracellular receptors (1) Basic domains (1.1) Basic leucine zipper (bZIP)Activating transcription factor (AATF, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) · AP-1 (c-Fos, FOSB, FOSL1, FOSL2, JDP2, c-Jun, JUNB, JUND) · BACH (1, 2) · BATF · BLZF1 · C/EBP (α, β, γ, δ, ε, ζ) · CREB (1, 3, L1) · CREM · DBP · DDIT3 · GABPA · HLF · MAF (B, F, G, K) · NFE (2, L1, L2, L3) · NFIL3 · NRL · NRF (1, 2, 3) · XBP1(1.2) Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)ATOH1 · AhR · AHRR · ARNT · ASCL1 · BHLHB2 · BMAL (ARNTL, ARNTL2) · CLOCK · EPAS1 · FIGLA · HAND (1, 2) · HES (5, 6) · HEY (1, 2, L) · HES1 · HIF (1A, 3A) · ID (1, 2, 3, 4) · LYL1 · MESP2 · MXD4 · MYCL1 · MYCN · Myogenic regulatory factors (MyoD, Myogenin, MYF5, MYF6) · Neurogenins (1, 2, 3) · NeuroD (1, 2) · NPAS (1, 2, 3) · OLIG (1, 2) · Pho4 · Scleraxis · SIM (1, 2) · TAL (1, 2) · Twist · USF1(1.3) bHLH-ZIP(1.4) NF-1(1.5) RF-X(1.6) Basic helix-span-helix (bHSH)(2) Zinc finger DNA-binding domains (2.1) Nuclear receptor (Cys4)subfamily 1 (Thyroid hormone (α, β), CAR, FXR, LXR (α, β), PPAR (α, β/δ, γ), PXR, RAR (α, β, γ), ROR (α, β, γ), Rev-ErbA (α, β), VDR)
subfamily 2 (COUP-TF (I, II), Ear-2, HNF4 (α, γ), PNR, RXR (α, β, γ), Testicular receptor (2, 4), TLX)
subfamily 3 (Steroid hormone (Androgen, Estrogen (α, β), Glucocorticoid, Mineralocorticoid, Progesterone), Estrogen related (α, β, γ))
subfamily 4 NUR (NGFIB, NOR1, NURR1) · subfamily 5 (LRH-1, SF1) · subfamily 6 (GCNF) · subfamily 0 (DAX1, SHP)(2.2) Other Cys4(2.3) Cys2His2General transcription factors (TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE (1, 2), TFIIF (1, 2), TFIIH (1, 2, 4, 2I, 3A, 3C1, 3C2))
ATBF1 · BCL (6, 11A, 11B) · CTCF · E4F1 · EGR (1, 2, 3, 4) · ERV3 · GFI1 · GLI-Krüppel family (1, 2, 3, REST, S2, YY1) · HIC (1, 2) · HIVEP (1, 2, 3) · IKZF (1, 2, 3) · ILF (2, 3) · KLF (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17) · MTF1 · MYT1 · OSR1 · PRDM9 · SALL (1, 2, 3, 4) · SP (1, 2, 4, 7, 8) · TSHZ3 · WT1 · Zbtb7 (7A, 7B) · ZBTB (16, 17, 20, 32, 33, 40) · zinc finger (3, 7, 9, 10, 19, 22, 24, 33B, 34, 35, 41, 43, 44, 51, 74, 143, 146, 148, 165, 202, 217, 219, 238, 239, 259, 267, 268, 281, 295, 300, 318, 330, 346, 350, 365, 366, 384, 423, 451, 452, 471, 593, 638, 644, 649, 655)(2.4) Cys6(2.5) Alternating composition(3) Helix-turn-helix domains (3.1) HomeodomainARX · CDX (1, 2) · CRX · CUTL1 · DBX (1, 2) · DLX (3, 4, 5) · EMX2 · EN (1, 2) · FHL (1, 2, 3) · HESX1 · HHEX · HLX · Homeobox (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A7, A9, A10, A11, A13, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9, B13, C4, C5, C6, C8, C9, C10, C11, C12, C13, D1, D3, D4, D8, D9, D10, D11, D12, D13) · HOPX · IRX (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, MKX) · LMX (1A, 1B) · MEIS (1, 2) · MEOX2 · MNX1 · MSX (1, 2) · NANOG · NKX (2-1, 2-2, 2-3, 2-5, 3-1, 3-2, 6-1, 6-2) · NOBOX · PBX (1, 2, 3) · PHF (1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 16, 17, 20, 21A) · PHOX (2A, 2B) · PITX (1, 2, 3) · POU domain (PIT-1, BRN-3: A, B, C, Octamer transcription factor: 1, 2, 3/4, 6, 7, 11) · OTX (1, 2) · PDX1 · SATB2 · SHOX2 · VAX1 · ZEB (1, 2)(3.2) Paired box(3.3) Fork head / winged helix(3.4) Heat Shock Factors(3.5) Tryptophan clusters(3.6) TEA domain(4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts (4.1) Rel homology region(4.2) STAT(4.3) p53(4.4) MADS box(4.6) TATA binding proteins(4.7) High-mobility group(4.10) Cold-shock domainCSDA, YBX1(4.11) Runt(0) Other transcription factors (0.2) HMGI(Y)(0.3) Pocket domain(0.6) MiscellaneousCategories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 1 gene stubs
- Intracellular receptors
- Transcription factors
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.