- NK2 homeobox 1
-
Not to be confused with transcription termination factor, RNA polymerase I or TTF1.
NK2 homeobox 1 (NKX2-1), also known as thyroid transcription factor 1 (TTF-1), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the NKX2-1 gene.[1][2]
Contents
Function
Thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF-1) is a protein that regulates transcription of genes specific for the thyroid, lung, and diencephalon. It is also known as thyroid specific enhancer binding protein. It is used in anatomic pathology as a marker to determine if a tumor arises from the lung or thyroid.
Clinical significance
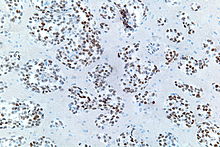 Micrograph of a metastatic lung adenocarcinoma (found in the brain) that exhibits nuclear staining (brown) for TTF-1.
Micrograph of a metastatic lung adenocarcinoma (found in the brain) that exhibits nuclear staining (brown) for TTF-1.
TTF-1 positive cells are found in the lung as type II pneumocytes and Clara cells. In the thyroid, follicular and parafollicular cells are also positive for TTF-1.
For lung cancers, adenocarcinomas are usually positive, while squamous cell carcinomas and large cell carcinomas are rarely positive. Small cell carcinomas (of any primary site) are usually positive. TTF1 is more than merely a clinical marker of lung adenocarcinoma. It plays an active role in sustaining lung cancer cells in view of the experimental observation that it is mutated in lung cancer.[3][4][5][6]
However others have found that TTF-1 staining is often positive in pulmonary adenocarcinomas, large cell carcinomas, small-cell lung carcinomas, neuroendocrine tumors other than small-cell lung carcinomas and extrapulmonary small-cell carcinomas.[7]
It is also positive in thyroid cancers and is used for monitoring for metastasis and recurrence.[8]
Interactions
NK2 homeobox 1 has been shown to interact with Calreticulin[9] and PAX8.[10]
References
- ^ "Entrez Gene: NKX2-1". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=7080.
- ^ Guazzi S, Price M, De Felice M, Damante G, Mattei MG, Di Lauro R (November 1990). "Thyroid nuclear factor 1 (TTF-1) contains a homeodomain and displays a novel DNA binding specificity". EMBO J. 9 (11): 3631–9. PMC 552115. PMID 1976511. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=552115.
- ^ Kendall J, Liu Q, Bakleh A, Krasnitz A, Nguyen KC, Lakshmi B, Gerald WL, Powers S, Mu D (October 2007). "Oncogenic cooperation and coamplification of developmental transcription factor genes in lung cancer". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104 (42): 16663–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.0708286104. PMC 2034240. PMID 17925434. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2034240.
- ^ Tanaka H, Yanagisawa K, Shinjo K, Taguchi A, Maeno K, Tomida S, Shimada Y, Osada H, Kosaka T, Matsubara H, Mitsudomi T, Sekido Y, Tanimoto M, Yatabe Y, Takahashi T. (July 2007). "Lineage-specific dependency of lung adenocarcinomas on the lung development regulator TTF-1". Cancer Research 67 (13): 6007–11. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4774. PMID 17616654.
- ^ Weir BA, Woo MS, Getz G, Perner S, Ding L, Beroukhim R, Lin WM, Province MA, Kraja A, Johnson LA, Shah K, Sato M, Thomas RK, Barletta JA, Borecki IB, Broderick S, Chang AC, Chiang DY, Chirieac LR, Cho J, Fujii Y, Gazdar AF, Giordano T, Greulich H, Hanna M, Johnson BE, Kris MG, Lash A, Lin L, Lindeman N, Mardis ER, McPherson JD, Minna JD, Morgan MB, Nadel M, Orringer MB, Osborne JR, Ozenberger B, Ramos AH, Robinson J, Roth JA, Rusch V, Sasaki H, Shepherd F, Sougnez C, Spitz MR, Tsao MS, Twomey D, Verhaak RG, Weinstock GM, Wheeler DA, Winckler W, Yoshizawa A, Yu S, Zakowski MF, Zhang Q, Beer DG, Wistuba II, Watson MA, Garraway LA, Ladanyi M, Travis WD, Pao W, Rubin MA, Gabriel SB, Gibbs RA, Varmus HE, Wilson RK, Lander ES, Meyerson M. (December 2007). "Characterizing the cancer genome in lung adenocarcinoma". Nature 450 (7171): 893–8. doi:10.1038/nature06358. PMC 2538683. PMID 17982442. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2538683.
- ^ Kwei KA, Kim YH, Girard L, Kao J, Pacyna-Gengelbach M, Salari K, Lee J, Choi YL, Sato M, Wang P, Hernandez-Boussard T, Gazdar AF, Petersen I, Minna JD, Pollack JR. (June 2008). "Genomic profiling identifies TITF1 as a lineage-specific oncogene amplified in lung cancer.". Oncogene 27 (25): 3635–40. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1211012. PMC 2903002. PMID 18212743. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2903002.
- ^ Kalhor N, Zander DS, Liu J (August 2006). "TTF-1 and p63 for distinguishing pulmonary small-cell carcinoma from poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma in previously pap-stained cytologic material". Mod. Pathol. 19 (8): 1117–23. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800629. PMID 16680154.
- ^ Espinoza CR, Schmitt TL, Loos U (August 2001). "Thyroid transcription factor 1 and Pax8 synergistically activate the promoter of the human thyroglobulin gene". J. Mol. Endocrinol. 27 (1): 59–67. doi:10.1677/jme.0.0270059. PMID 11463576.
- ^ Perrone, L; Tell G, Di Lauro R (Feb. 1999). "Calreticulin enhances the transcriptional activity of thyroid transcription factor-1 by binding to its homeodomain". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 274 (8): 4640–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.8.4640. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 9988700.
- ^ Di Palma, Tina; Nitsch Roberto, Mascia Anna, Nitsch Lucio, Di Lauro Roberto, Zannini Mariastella (Jan. 2003). "The paired domain-containing factor Pax8 and the homeodomain-containing factor TTF-1 directly interact and synergistically activate transcription". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 278 (5): 3395–402. doi:10.1074/jbc.M205977200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 12441357.
Further reading
- Lau SK, Luthringer DJ, Eisen RN (2002). "Thyroid transcription factor-1: a review.". Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 10 (2): 97–102. doi:10.1097/00022744-200206000-00001. PMID 12051643.
- Guazzi S, Price M, De Felice M, et al. (1990). "Thyroid nuclear factor 1 (TTF-1) contains a homeodomain and displays a novel DNA binding specificity.". EMBO J. 9 (11): 3631–9. PMC 552115. PMID 1976511. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=552115.
- Oguchi H, Pan YT, Kimura S (1995). "The complete nucleotide sequence of the mouse thyroid-specific enhancer-binding protein (T/EBP) gene: extensive identity of the deduced amino acid sequence with the human protein.". Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1261 (2): 304–6. doi:10.1016/0167-4781(95)00033-D. PMID 7711079.
- Saiardi A, Tassi V, De Filippis V, Civitareale D (1995). "Cloning and sequence analysis of human thyroid transcription factor 1.". Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1261 (2): 307–10. doi:10.1016/0167-4781(95)00034-E. PMID 7711080.
- Ikeda K, Clark JC, Shaw-White JR, et al. (1995). "Gene structure and expression of human thyroid transcription factor-1 in respiratory epithelial cells.". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (14): 8108–14. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.44.26460. PMID 7713914.
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (1997). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery.". Genome Res. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.
- Ghaffari M, Zeng X, Whitsett JA, Yan C (1998). "Nuclear localization domain of thyroid transcription factor-1 in respiratory epithelial cells.". Biochem. J. 328 ( Pt 3): 757–61. PMC 1218983. PMID 9396717. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1218983.
- Hamdan H, Liu H, Li C, et al. (1998). "Structure of the human Nkx2.1 gene.". Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1396 (3): 336–48. doi:10.1016/S0167-4781(97)00210-8. PMID 9545595.
- Perrone L, Tell G, Di Lauro R (1999). "Calreticulin enhances the transcriptional activity of thyroid transcription factor-1 by binding to its homeodomain.". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (8): 4640–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.8.4640. PMID 9988700.
- Naltner A, Ghaffari M, Whitsett JA, Yan C (2000). "Retinoic acid stimulation of the human surfactant protein B promoter is thyroid transcription factor 1 site-dependent.". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (1): 56–62. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.1.56. PMID 10617585.
- Missero C, Pirro MT, Di Lauro R (2000). "Multiple ras downstream pathways mediate functional repression of the homeobox gene product TTF-1.". Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (8): 2783–93. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.8.2783-2793.2000. PMC 85494. PMID 10733581. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=85494.
- Naltner A, Wert S, Whitsett JA, Yan C (2000). "Temporal/spatial expression of nuclear receptor coactivators in the mouse lung.". Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 279 (6): L1066–74. PMID 11076796.
- Yan C, Naltner A, Conkright J, Ghaffari M (2001). "Protein-protein interaction of retinoic acid receptor alpha and thyroid transcription factor-1 in respiratory epithelial cells.". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (24): 21686–91. doi:10.1074/jbc.M011378200. PMID 11274148.
- Missero C, Pirro MT, Simeone S, et al. (2001). "The DNA glycosylase T:G mismatch-specific thymine DNA glycosylase represses thyroid transcription factor-1-activated transcription.". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (36): 33569–75. doi:10.1074/jbc.M104963200. PMID 11438542.
- Yi M, Tong GX, Murry B, Mendelson CR (2002). "Role of CBP/p300 and SRC-1 in transcriptional regulation of the pulmonary surfactant protein-A (SP-A) gene by thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF-1).". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (4): 2997–3005. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109793200. PMID 11713256.
- Liu C, Glasser SW, Wan H, Whitsett JA (2002). "GATA-6 and thyroid transcription factor-1 directly interact and regulate surfactant protein-C gene expression.". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (6): 4519–25. doi:10.1074/jbc.M107585200. PMID 11733512.
- Ng WK, Chow JC, Ng PK (2002). "Thyroid transcription factor-1 is highly sensitive and specific in differentiating metastatic pulmonary from extrapulmonary adenocarcinoma in effusion fluid cytology specimens.". Cancer 96 (1): 43–8. doi:10.1002/cncr.10310. PMID 11836702.
- Pohlenz J, Dumitrescu A, Zundel D, et al. (2002). "Partial deficiency of thyroid transcription factor 1 produces predominantly neurological defects in humans and mice.". J. Clin. Invest. 109 (4): 469–73. doi:10.1172/JCI14192. PMC 150877. PMID 11854318. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=150877.
- Krude H, Schütz B, Biebermann H, et al. (2002). "Choreoathetosis, hypothyroidism, and pulmonary alterations due to human NKX2-1 haploinsufficiency.". J. Clin. Invest. 109 (4): 475–80. doi:10.1172/JCI14341. PMC 150790. PMID 11854319. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=150790.
- Miccadei S, De Leo R, Zammarchi E, et al. (2002). "The synergistic activity of thyroid transcription factor 1 and Pax 8 relies on the promoter/enhancer interplay.". Mol. Endocrinol. 16 (4): 837–46. doi:10.1210/me.16.4.837. PMID 11923479.
PDB gallery External links
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
Transcription factors and intracellular receptors (1) Basic domains (1.1) Basic leucine zipper (bZIP)Activating transcription factor (AATF, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) · AP-1 (c-Fos, FOSB, FOSL1, FOSL2, JDP2, c-Jun, JUNB, JUND) · BACH (1, 2) · BATF · BLZF1 · C/EBP (α, β, γ, δ, ε, ζ) · CREB (1, 3, L1) · CREM · DBP · DDIT3 · GABPA · HLF · MAF (B, F, G, K) · NFE (2, L1, L2, L3) · NFIL3 · NRL · NRF (1, 2, 3) · XBP1(1.2) Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)ATOH1 · AhR · AHRR · ARNT · ASCL1 · BHLHB2 · BMAL (ARNTL, ARNTL2) · CLOCK · EPAS1 · FIGLA · HAND (1, 2) · HES (5, 6) · HEY (1, 2, L) · HES1 · HIF (1A, 3A) · ID (1, 2, 3, 4) · LYL1 · MESP2 · MXD4 · MYCL1 · MYCN · Myogenic regulatory factors (MyoD, Myogenin, MYF5, MYF6) · Neurogenins (1, 2, 3) · NeuroD (1, 2) · NPAS (1, 2, 3) · OLIG (1, 2) · Pho4 · Scleraxis · SIM (1, 2) · TAL (1, 2) · Twist · USF1(1.3) bHLH-ZIP(1.4) NF-1(1.5) RF-X(1.6) Basic helix-span-helix (bHSH)(2) Zinc finger DNA-binding domains (2.1) Nuclear receptor (Cys4)subfamily 1 (Thyroid hormone (α, β), CAR, FXR, LXR (α, β), PPAR (α, β/δ, γ), PXR, RAR (α, β, γ), ROR (α, β, γ), Rev-ErbA (α, β), VDR)
subfamily 2 (COUP-TF (I, II), Ear-2, HNF4 (α, γ), PNR, RXR (α, β, γ), Testicular receptor (2, 4), TLX)
subfamily 3 (Steroid hormone (Androgen, Estrogen (α, β), Glucocorticoid, Mineralocorticoid, Progesterone), Estrogen related (α, β, γ))
subfamily 4 NUR (NGFIB, NOR1, NURR1) · subfamily 5 (LRH-1, SF1) · subfamily 6 (GCNF) · subfamily 0 (DAX1, SHP)(2.2) Other Cys4(2.3) Cys2His2General transcription factors (TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE (1, 2), TFIIF (1, 2), TFIIH (1, 2, 4, 2I, 3A, 3C1, 3C2))
ATBF1 · BCL (6, 11A, 11B) · CTCF · E4F1 · EGR (1, 2, 3, 4) · ERV3 · GFI1 · GLI-Krüppel family (1, 2, 3, REST, S2, YY1) · HIC (1, 2) · HIVEP (1, 2, 3) · IKZF (1, 2, 3) · ILF (2, 3) · KLF (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17) · MTF1 · MYT1 · OSR1 · PRDM9 · SALL (1, 2, 3, 4) · SP (1, 2, 4, 7, 8) · TSHZ3 · WT1 · Zbtb7 (7A, 7B) · ZBTB (16, 17, 20, 32, 33, 40) · zinc finger (3, 7, 9, 10, 19, 22, 24, 33B, 34, 35, 41, 43, 44, 51, 74, 143, 146, 148, 165, 202, 217, 219, 238, 239, 259, 267, 268, 281, 295, 300, 318, 330, 346, 350, 365, 366, 384, 423, 451, 452, 471, 593, 638, 644, 649, 655)(2.4) Cys6(2.5) Alternating composition(3) Helix-turn-helix domains (3.1) HomeodomainARX · CDX (1, 2) · CRX · CUTL1 · DBX (1, 2) · DLX (3, 4, 5) · EMX2 · EN (1, 2) · FHL (1, 2, 3) · HESX1 · HHEX · HLX · Homeobox (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A7, A9, A10, A11, A13, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9, B13, C4, C5, C6, C8, C9, C10, C11, C12, C13, D1, D3, D4, D8, D9, D10, D11, D12, D13) · HOPX · IRX (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, MKX) · LMX (1A, 1B) · MEIS (1, 2) · MEOX2 · MNX1 · MSX (1, 2) · NANOG · NKX (2-1, 2-2, 2-3, 2-5, 3-1, 3-2, 6-1, 6-2) · NOBOX · PBX (1, 2, 3) · PHF (1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 16, 17, 20, 21A) · PHOX (2A, 2B) · PITX (1, 2, 3) · POU domain (PIT-1, BRN-3: A, B, C, Octamer transcription factor: 1, 2, 3/4, 6, 7, 11) · OTX (1, 2) · PDX1 · SATB2 · SHOX2 · VAX1 · ZEB (1, 2)(3.2) Paired box(3.3) Fork head / winged helix(3.4) Heat Shock Factors(3.5) Tryptophan clusters(3.6) TEA domain(4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts (4.1) Rel homology region(4.2) STAT(4.3) p53(4.4) MADS box(4.6) TATA binding proteins(4.7) High-mobility group(4.10) Cold-shock domainCSDA, YBX1(4.11) Runt(0) Other transcription factors (0.2) HMGI(Y)(0.3) Pocket domain(0.6) Miscellaneoussee also transcription factor/coregulator deficiencies
B bsyn: dna (repl, cycl, reco, repr) · tscr (fact, tcrg, nucl, rnat, rept, ptts) · tltn (risu, pttl, nexn) · dnab, rnab/runp · stru (domn, 1°, 2°, 3°, 4°)Categories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 14 gene stubs
- Transcription factors
- Anatomical pathology
- Proteins
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.