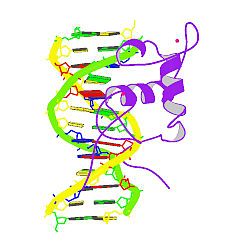
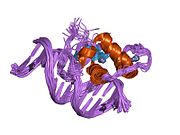
- Estrogen-related receptor beta
-
Estrogen-related receptor beta (ERR-β), also known as NR3B2 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group B, member 2), is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the ESRRB (EStrogen Related Receptor Beta) gene .[1]
Function
This gene encodes a protein with sequence similarity to the estrogen receptor, a member of nuclear hormone receptor family of steroid hormone receptors. Its function is unknown; however, a similar protein in mouse plays an essential role in placental development.[1]
References
Further reading
- Giguère V, Yang N, Segui P, Evans RM (1988). "Identification of a new class of steroid hormone receptors.". Nature 331 (6151): 91–4. doi:10.1038/331091a0. PMID 3267207.
- Sladek R, Beatty B, Squire J, et al. (1998). "Chromosomal mapping of the human and murine orphan receptors ERRalpha (ESRRA) and ERRbeta (ESRRB) and identification of a novel human ERRalpha-related pseudogene.". Genomics 45 (2): 320–6. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.4939. PMID 9344655.
- Enmark E, Pelto-Huikko M, Grandien K, et al. (1998). "Human estrogen receptor beta-gene structure, chromosomal localization, and expression pattern.". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 82 (12): 4258–65. doi:10.1210/jc.82.12.4258. PMID 9398750.
- Chen F, Zhang Q, McDonald T, et al. (1999). "Identification of two hERR2-related novel nuclear receptors utilizing bioinformatics and inverse PCR.". Gene 228 (1–2): 101–9. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(98)00619-2. PMID 10072763.
- Xie W, Hong H, Yang NN, et al. (2000). "Constitutive activation of transcription and binding of coactivator by estrogen-related receptors 1 and 2". Mol. Endocrinol. 13 (12): 2151–62. doi:10.1210/me.13.12.2151. PMID 10598588.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139241.
- Heilig R, Eckenberg R, Petit JL, et al. (2003). "The DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 14". Nature 421 (6923): 601–7. doi:10.1038/nature01348. PMID 12508121.
- Gearhart MD, Holmbeck SM, Evans RM, et al. (2003). "Monomeric complex of human orphan estrogen related receptor-2 with DNA: a pseudo-dimer interface mediates extended half-site recognition". J. Mol. Biol. 327 (4): 819–32. doi:10.1016/S0022-2836(03)00183-9. PMID 12654265.
- Kruijver FP, Balesar R, Espila AM, et al. (2003). "Estrogen-receptor-beta distribution in the human hypothalamus: similarities and differences with ER alpha distribution". J. Comp. Neurol. 466 (2): 251–77. doi:10.1002/cne.10899. PMID 14528452.
- Stossi F, Barnett DH, Frasor J, et al. (2004). "Transcriptional profiling of estrogen-regulated gene expression via estrogen receptor (ER) alpha or ERbeta in human osteosarcoma cells: distinct and common target genes for these receptors". Endocrinology 145 (7): 3473–86. doi:10.1210/en.2003-1682. PMID 15033914.
- Verdier-Sevrain S, Yaar M, Cantatore J, et al. (2005). "Estradiol induces proliferation of keratinocytes via a receptor mediated mechanism". FASEB J. 18 (11): 1252–4. doi:10.1096/fj.03-1088fje. PMID 15208259.
- Smith LH, Coats SR, Qin H, et al. (2005). "Differential and opposing regulation of PAI-1 promoter activity by estrogen receptor alpha and estrogen receptor beta in endothelial cells". Circ. Res. 95 (3): 269–75. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000136521.70093.f1. PMID 15217907.
- Liu PY, Christian RC, Ruan M, et al. (2005). "Correlating androgen and estrogen steroid receptor expression with coronary calcification and atherosclerosis in men without known coronary artery disease". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 90 (2): 1041–6. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-1211. PMID 15536156.
- Cheung CP, Yu S, Wong KB, et al. (2005). "Expression and functional study of estrogen receptor-related receptors in human prostatic cells and tissues". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 90 (3): 1830–44. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-1421. PMID 15598686.
- Zhou W, Liu Z, Wu J, et al. (2006). "Identification and characterization of two novel splicing isoforms of human estrogen-related receptor beta". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 91 (2): 569–79. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-1957. PMID 16332939.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
PDB gallery Transcription factors and intracellular receptors (1) Basic domains (1.1) Basic leucine zipper (bZIP)Activating transcription factor (AATF, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) · AP-1 (c-Fos, FOSB, FOSL1, FOSL2, JDP2, c-Jun, JUNB, JUND) · BACH (1, 2) · BATF · BLZF1 · C/EBP (α, β, γ, δ, ε, ζ) · CREB (1, 3, L1) · CREM · DBP · DDIT3 · GABPA · HLF · MAF (B, F, G, K) · NFE (2, L1, L2, L3) · NFIL3 · NRL · NRF (1, 2, 3) · XBP1(1.2) Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)ATOH1 · AhR · AHRR · ARNT · ASCL1 · BHLHB2 · BMAL (ARNTL, ARNTL2) · CLOCK · EPAS1 · FIGLA · HAND (1, 2) · HES (5, 6) · HEY (1, 2, L) · HES1 · HIF (1A, 3A) · ID (1, 2, 3, 4) · LYL1 · MESP2 · MXD4 · MYCL1 · MYCN · Myogenic regulatory factors (MyoD, Myogenin, MYF5, MYF6) · Neurogenins (1, 2, 3) · NeuroD (1, 2) · NPAS (1, 2, 3) · OLIG (1, 2) · Pho4 · Scleraxis · SIM (1, 2) · TAL (1, 2) · Twist · USF1(1.3) bHLH-ZIP(1.4) NF-1(1.5) RF-X(1.6) Basic helix-span-helix (bHSH)(2) Zinc finger DNA-binding domains (2.1) Nuclear receptor (Cys4)subfamily 1 (Thyroid hormone (α, β), CAR, FXR, LXR (α, β), PPAR (α, β/δ, γ), PXR, RAR (α, β, γ), ROR (α, β, γ), Rev-ErbA (α, β), VDR)
subfamily 2 (COUP-TF (I, II), Ear-2, HNF4 (α, γ), PNR, RXR (α, β, γ), Testicular receptor (2, 4), TLX)
subfamily 3 (Steroid hormone (Androgen, Estrogen (α, β), Glucocorticoid, Mineralocorticoid, Progesterone), Estrogen related (α, β, γ))
subfamily 4 NUR (NGFIB, NOR1, NURR1) · subfamily 5 (LRH-1, SF1) · subfamily 6 (GCNF) · subfamily 0 (DAX1, SHP)(2.2) Other Cys4(2.3) Cys2His2General transcription factors (TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE (1, 2), TFIIF (1, 2), TFIIH (1, 2, 4, 2I, 3A, 3C1, 3C2))
ATBF1 · BCL (6, 11A, 11B) · CTCF · E4F1 · EGR (1, 2, 3, 4) · ERV3 · GFI1 · GLI-Krüppel family (1, 2, 3, REST, S2, YY1) · HIC (1, 2) · HIVEP (1, 2, 3) · IKZF (1, 2, 3) · ILF (2, 3) · KLF (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17) · MTF1 · MYT1 · OSR1 · PRDM9 · SALL (1, 2, 3, 4) · SP (1, 2, 4, 7, 8) · TSHZ3 · WT1 · Zbtb7 (7A, 7B) · ZBTB (16, 17, 20, 32, 33, 40) · zinc finger (3, 7, 9, 10, 19, 22, 24, 33B, 34, 35, 41, 43, 44, 51, 74, 143, 146, 148, 165, 202, 217, 219, 238, 239, 259, 267, 268, 281, 295, 300, 318, 330, 346, 350, 365, 366, 384, 423, 451, 452, 471, 593, 638, 644, 649, 655)(2.4) Cys6(2.5) Alternating composition(3) Helix-turn-helix domains (3.1) HomeodomainARX · CDX (1, 2) · CRX · CUTL1 · DBX (1, 2) · DLX (3, 4, 5) · EMX2 · EN (1, 2) · FHL (1, 2, 3) · HESX1 · HHEX · HLX · Homeobox (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A7, A9, A10, A11, A13, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9, B13, C4, C5, C6, C8, C9, C10, C11, C12, C13, D1, D3, D4, D8, D9, D10, D11, D12, D13) · HOPX · IRX (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, MKX) · LMX (1A, 1B) · MEIS (1, 2) · MEOX2 · MNX1 · MSX (1, 2) · NANOG · NKX (2-1, 2-2, 2-3, 2-5, 3-1, 3-2, 6-1, 6-2) · NOBOX · PBX (1, 2, 3) · PHF (1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 16, 17, 20, 21A) · PHOX (2A, 2B) · PITX (1, 2, 3) · POU domain (PIT-1, BRN-3: A, B, C, Octamer transcription factor: 1, 2, 3/4, 6, 7, 11) · OTX (1, 2) · PDX1 · SATB2 · SHOX2 · VAX1 · ZEB (1, 2)(3.2) Paired box(3.3) Fork head / winged helix(3.4) Heat Shock Factors(3.5) Tryptophan clusters(3.6) TEA domain(4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts (4.1) Rel homology region(4.2) STAT(4.3) p53(4.4) MADS box(4.6) TATA binding proteins(4.7) High-mobility group(4.10) Cold-shock domainCSDA, YBX1(4.11) Runt(0) Other transcription factors (0.2) HMGI(Y)(0.3) Pocket domain(0.6) MiscellaneousCategories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 14 gene stubs
- Intracellular receptors
- Transcription factors
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.