- Calcitriol receptor
-
The calcitriol receptor, also known as the vitamin D receptor (VDR) and also known as NR1I1 (nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group I, member 1), is a member of the nuclear receptor family of transcription factors.[1] Upon activation by vitamin D, the VDR forms a heterodimer with the retinoid-X receptor and binds to hormone response elements on DNA resulting in expression or transrepression of specific geneproducts. In humans, the vitamin D receptor is encoded by the VDR gene.[2]
Glucocorticoids are known to decrease expression of VDR, which is expressed in most tissues of the body and regulate intestinal transport of calcium.
Contents
Function
This gene encodes the nuclear hormone receptor for vitamin D3. This receptor also functions as a receptor for the secondary bile acid lithocholic acid. The receptor belongs to the family of trans-acting transcriptional regulatory factors and shows similarity of sequence to the steroid and thyroid hormone receptors.[3]
Downstream targets of this nuclear hormone receptor are involved principally in mineral metabolism though the receptor regulates a variety of other metabolic pathways, such as those involved in the immune response and cancer.[4]
Mutations in this gene are associated with type II vitamin D-resistant rickets. A single nucleotide polymorphism in the initiation codon results in an alternate translation start site three codons downstream. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding the same protein.[5]
The vitamin D receptor plays an important role in regulating the hair cycle. Loss of VDR is associated with hair loss in experimental animals.[6]
Interactions
Calcitriol receptor has been shown to interact with
References
- ^ Moore DD, Kato S, Xie W, Mangelsdorf DJ, Schmidt DR, Xiao R, Kliewer SA (December 2006). "International Union of Pharmacology. LXII. The NR1H and NR1I receptors: constitutive androstane receptor, pregnene X receptor, farnesoid X receptor alpha, farnesoid X receptor beta, liver X receptor alpha, liver X receptor beta, and vitamin D receptor". Pharmacol. Rev. 58 (4): 742–59. doi:10.1124/pr.58.4.6. PMID 17132852.
- ^ Szpirer J, Szpirer C, Riviere M, Levan G, Marynen P, Cassiman JJ, Wiese R, DeLuca HF (September 1991). "The Sp1 transcription factor gene (SP1) and the 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor gene (VDR) are colocalized on human chromosome arm 12q and rat chromosome 7". Genomics 11 (1): 168–73. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(91)90114-T. PMID 1662663. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/0888-7543(91)90114-T.
- ^ Germain P, Staels B, Dacquet C, Spedding M, Laudet V (December 2006). "Overview of nomenclature of nuclear receptors". Pharmacol. Rev. 58 (4): 685–704. doi:10.1124/pr.58.4.2. PMID 17132848.
- ^ Adorini L, Daniel KC, Penna G (2006). "Vitamin D receptor agonists, cancer and the immune system: an intricate relationship". Curr Top Med Chem 6 (12): 1297–301. doi:10.2174/156802606777864890. PMID 16848743.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: VDR vitamin D (1,25- dihydroxyvitamin D3) receptor". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=7421.
- ^ Luderer HF, Demay MB (July 2010). "The vitamin D receptor, the skin and stem cells". J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 121 (1–2): 314–6. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2010.01.015. PMID 20138991.
- ^ Guzey M, Takayama S, Reed JC (December 2000). "BAG1L enhances trans-activation function of the vitamin D receptor". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (52): 40749–56. doi:10.1074/jbc.M004977200. PMID 10967105.
- ^ a b c d e Kitagawa H, Fujiki R, Yoshimura K, Mezaki Y, Uematsu Y, Matsui D, Ogawa S, Unno K, Okubo M, Tokita A, Nakagawa T, Ito T, Ishimi Y, Nagasawa H, Matsumoto T, Yanagisawa J, Kato S (June 2003). "The chromatin-remodeling complex WINAC targets a nuclear receptor to promoters and is impaired in Williams syndrome". Cell 113 (7): 905–17. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00436-7. PMID 12837248.
- ^ Zhao G, Simpson RU (2010). "Membrane Localization, Caveolin-3 Association and Rapid Actions of Vitamin D Receptor in Cardiac Myocytes". Steroids 75 (8–9): 555–9. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2009.12.001. PMC 2885558. PMID 20015453. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2885558.
- ^ a b Ito M, Yuan CX, Malik S, Gu W, Fondell JD, Yamamura S, Fu ZY, Zhang X, Qin J, Roeder RG (March 1999). "Identity between TRAP and SMCC complexes indicates novel pathways for the function of nuclear receptors and diverse mammalian activators". Mol. Cell 3 (3): 361–70. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80463-3. PMID 10198638.
- ^ a b Tagami T, Lutz WH, Kumar R, Jameson JL (December 1998). "The interaction of the vitamin D receptor with nuclear receptor corepressors and coactivators". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 253 (2): 358–63. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1998.9799. PMID 9878542.
- ^ a b c d Puccetti E, Obradovic D, Beissert T, Bianchini A, Washburn B, Chiaradonna F, Boehrer S, Hoelzer D, Ottmann OG, Pelicci PG, Nervi C, Ruthardt M (December 2002). "AML-associated translocation products block vitamin D(3)-induced differentiation by sequestering the vitamin D(3) receptor". Cancer Res. 62 (23): 7050–8. PMID 12460926.
- ^ Herdick M, Steinmeyer A, Carlberg C (June 2000). "Antagonistic action of a 25-carboxylic ester analogue of 1alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is mediated by a lack of ligand-induced vitamin D receptor interaction with coactivators". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (22): 16506–12. doi:10.1074/jbc.M910000199. PMID 10748178.
- ^ a b c Zhang C, Baudino TA, Dowd DR, Tokumaru H, Wang W, MacDonald PN (November 2001). "Ternary complexes and cooperative interplay between NCoA-62/Ski-interacting protein and steroid receptor coactivators in vitamin D receptor-mediated transcription". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (44): 40614–20. doi:10.1074/jbc.M106263200. PMID 11514567.
- ^ He B, Wilson EM (March 2003). "Electrostatic Modulation in Steroid Receptor Recruitment of LXXLL and FXXLF Motifs". Mol. Cell. Biol. 23 (6): 2135–50. doi:10.1128/MCB.23.6.2135-2150.2003. PMC 149467. PMID 12612084. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=149467.
- ^ a b Baudino TA, Kraichely DM, Jefcoat SC, Winchester SK, Partridge NC, MacDonald PN (June 1998). "Isolation and characterization of a novel coactivator protein, NCoA-62, involved in vitamin D-mediated transcription". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (26): 16434–41. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.26.16434. PMID 9632709.
- ^ Vidal M, Ramana CV, Dusso AS (April 2002). "Stat1-Vitamin D Receptor Interactions Antagonize 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D Transcriptional Activity and Enhance Stat1-Mediated Transcription". Mol. Cell. Biol. 22 (8): 2777–87. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.8.2777-2787.2002. PMC 133712. PMID 11909970. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=133712.
- ^ Ward JO, McConnell MJ, Carlile GW, Pandolfi PP, Licht JD, Freedman LP (December 2001). "The acute promyelocytic leukemia-associated protein, promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger, regulates 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3)-induced monocytic differentiation of U937 cells through a physical interaction with vitamin D(3) receptor". Blood 98 (12): 3290–300. doi:10.1182/blood.V98.12.3290. PMID 11719366.
Further reading
- Hosoi T (2002). "[Polymorphisms of vitamin D receptor gene]". Nippon Rinsho 60 Suppl 3: 106–10. PMID 11979895.
- Uitterlinden AG, Fang Y, Van Meurs JB et al. (2004). "Genetics and biology of vitamin D receptor polymorphisms". Gene 338 (2): 143–56. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2004.05.014. PMID 15315818.
- Norman AW (2007). "Minireview: vitamin D receptor: new assignments for an already busy receptor". Endocrinology 147 (12): 5542–8. doi:10.1210/en.2006-0946. PMID 16946007.
- Bollag WB (2007). "Differentiation of human keratinocytes requires the vitamin d receptor and its coactivators". J. Invest. Dermatol. 127 (4): 748–50. doi:10.1038/sj.jid.5700692. PMID 17363957.
- Bugge TH, Pohl J, Lonnoy O, Stunnenberg HG (1992). "RXR alpha, a promiscuous partner of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptors". EMBO J. 11 (4): 1409–18. PMC 556590. PMID 1314167. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=556590.
- Goto H, Chen KS, Prahl JM, DeLuca HF (1992). "A single receptor identical with that from intestine/T47D cells mediates the action of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-3 in HL-60 cells". Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1132 (1): 103–8. PMID 1324736.
- Saijo T, Ito M, Takeda E et al. (1991). "A unique mutation in the vitamin D receptor gene in three Japanese patients with vitamin D-dependent rickets type II: utility of single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis for heterozygous carrier detection". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 49 (3): 668–73. PMC 1683124. PMID 1652893. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1683124.
- Szpirer J, Szpirer C, Riviere M et al. (1992). "The Sp1 transcription factor gene (SP1) and the 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor gene (VDR) are colocalized on human chromosome arm 12q and rat chromosome 7". Genomics 11 (1): 168–73. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(91)90114-T. PMID 1662663.
- Yu XP, Mocharla H, Hustmyer FG, Manolagas SC (1991). "Vitamin D receptor expression in human lymphocytes. Signal requirements and characterization by western blots and DNA sequencing". J. Biol. Chem. 266 (12): 7588–95. PMID 1850412.
- Malloy PJ, Hochberg Z, Tiosano D et al. (1991). "The molecular basis of hereditary 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 resistant rickets in seven related families". J. Clin. Invest. 86 (6): 2071–9. doi:10.1172/JCI114944. PMC 329846. PMID 2174914. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=329846.
- Sone T, Marx SJ, Liberman UA, Pike JW (1991). "A unique point mutation in the human vitamin D receptor chromosomal gene confers hereditary resistance to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3". Mol. Endocrinol. 4 (4): 623–31. doi:10.1210/mend-4-4-623. PMID 2177843.
- Baker AR, McDonnell DP, Hughes M et al. (1988). "Cloning and expression of full-length cDNA encoding human vitamin D receptor". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85 (10): 3294–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.85.10.3294. PMC 280195. PMID 2835767. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=280195.
- Hughes MR, Malloy PJ, Kieback DG et al. (1989). "Point mutations in the human vitamin D receptor gene associated with hypocalcemic rickets". Science 242 (4886): 1702–5. doi:10.1126/science.2849209. PMID 2849209.
- Rut AR, Hewison M, Kristjansson K et al. (1995). "Two mutations causing vitamin D resistant rickets: modelling on the basis of steroid hormone receptor DNA-binding domain crystal structures". Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf) 41 (5): 581–90. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.1994.tb01822.x. PMID 7828346.
- Malloy PJ, Weisman Y, Feldman D (1994). "Hereditary 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-resistant rickets resulting from a mutation in the vitamin D receptor deoxyribonucleic acid-binding domain". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 78 (2): 313–6. doi:10.1210/jc.78.2.313. PMID 8106618.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Yagi H, Ozono K, Miyake H et al. (1993). "A new point mutation in the deoxyribonucleic acid-binding domain of the vitamin D receptor in a kindred with hereditary 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-resistant rickets". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 76 (2): 509–12. doi:10.1210/jc.76.2.509. PMID 8381803.
- Kristjansson K, Rut AR, Hewison M et al. (1993). "Two mutations in the hormone binding domain of the vitamin D receptor cause tissue resistance to 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3". J. Clin. Invest. 92 (1): 12–6. doi:10.1172/JCI116539. PMC 293517. PMID 8392085. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=293517.
- Jurutka PW, Hsieh JC, Nakajima S et al. (1996). "Human vitamin D receptor phosphorylation by casein kinase II at Ser-208 potentiates transcriptional activation". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93 (8): 3519–24. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.8.3519. PMC 39642. PMID 8622969. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=39642.
- Lin NU, Malloy PJ, Sakati N et al. (1996). "A novel mutation in the deoxyribonucleic acid-binding domain of the vitamin D receptor causes hereditary 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-resistant rickets". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 81 (7): 2564–9. doi:10.1210/jc.81.7.2564. PMID 8675579.
External links
- MeSH Calcitriol+Receptors
- [3] (Nuclear Receptor Resource).
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
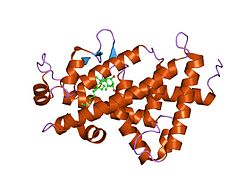
PDB gallery 2hb8: Crystal structure of VDR LBD in complex with 2alpha-methyl calcitriol1ynw: Crystal Structure of Vitmain D Receptor and 9-cis Retinoic Acid Receptor DNA-Binding Domains Bound to a DR3 Response Element1kb2: Crystal Structure of VDR DNA-binding Domain Bound to Mouse Osteopontin (SPP) Response Element1db1: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE NUCLEAR RECEPTOR FOR VITAMIN D COMPLEXED TO VITAMIN D1s0z: Crystal structure of the VDR LBD complexed to seocalcitol.2ham: Crystal structure of VDR LBD complexed to 2alpha-propyl-calcitriol2har: Crystal structure of VDR LBD in complex with 2 alpha-(3-hydroxy-1-propoxy) calcitriol1kb6: Crystal Structure of VDR DNA-binding Domain Bound to Rat Osteocalcin (OC) Response Element1ie9: Crystal Structure Of The Nuclear Receptor For Vitamin D Ligand Binding Domain Bound to MC12881s19: Crystal structure of VDR ligand binding domain complexed to calcipotriol.2has: Crystal structure of VDR LBD in complex with 2alpha-(1-propoxy) calcitriol1ie8: Crystal Structure Of The Nuclear Receptor For Vitamin D Ligand Binding Domain Bound to KH10601txi: Crystal structure of the vdr ligand binding domain complexed to TX5222hb7: Crystal structure of VDR LBD in complex with 2alpha(3-hydroxy-1-propyl) calcitriol1kb4: Crystal Structure of VDR DNA-binding Domain Bound to a Canonical Direct Repeat with Three Base Pair Spacer (DR3) Response ElementTranscription factors and intracellular receptors (1) Basic domains (1.1) Basic leucine zipper (bZIP)Activating transcription factor (AATF, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) · AP-1 (c-Fos, FOSB, FOSL1, FOSL2, JDP2, c-Jun, JUNB, JUND) · BACH (1, 2) · BATF · BLZF1 · C/EBP (α, β, γ, δ, ε, ζ) · CREB (1, 3, L1) · CREM · DBP · DDIT3 · GABPA · HLF · MAF (B, F, G, K) · NFE (2, L1, L2, L3) · NFIL3 · NRL · NRF (1, 2, 3) · XBP1(1.2) Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)ATOH1 · AhR · AHRR · ARNT · ASCL1 · BHLHB2 · BMAL (ARNTL, ARNTL2) · CLOCK · EPAS1 · FIGLA · HAND (1, 2) · HES (5, 6) · HEY (1, 2, L) · HES1 · HIF (1A, 3A) · ID (1, 2, 3, 4) · LYL1 · MESP2 · MXD4 · MYCL1 · MYCN · Myogenic regulatory factors (MyoD, Myogenin, MYF5, MYF6) · Neurogenins (1, 2, 3) · NeuroD (1, 2) · NPAS (1, 2, 3) · OLIG (1, 2) · Pho4 · Scleraxis · SIM (1, 2) · TAL (1, 2) · Twist · USF1(1.3) bHLH-ZIP(1.4) NF-1(1.5) RF-X(1.6) Basic helix-span-helix (bHSH)(2) Zinc finger DNA-binding domains (2.1) Nuclear receptor (Cys4)subfamily 1 (Thyroid hormone (α, β), CAR, FXR, LXR (α, β), PPAR (α, β/δ, γ), PXR, RAR (α, β, γ), ROR (α, β, γ), Rev-ErbA (α, β), VDR)
subfamily 2 (COUP-TF (I, II), Ear-2, HNF4 (α, γ), PNR, RXR (α, β, γ), Testicular receptor (2, 4), TLX)
subfamily 3 (Steroid hormone (Androgen, Estrogen (α, β), Glucocorticoid, Mineralocorticoid, Progesterone), Estrogen related (α, β, γ))
subfamily 4 NUR (NGFIB, NOR1, NURR1) · subfamily 5 (LRH-1, SF1) · subfamily 6 (GCNF) · subfamily 0 (DAX1, SHP)(2.2) Other Cys4(2.3) Cys2His2General transcription factors (TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE (1, 2), TFIIF (1, 2), TFIIH (1, 2, 4, 2I, 3A, 3C1, 3C2))
ATBF1 · BCL (6, 11A, 11B) · CTCF · E4F1 · EGR (1, 2, 3, 4) · ERV3 · GFI1 · GLI-Krüppel family (1, 2, 3, REST, S2, YY1) · HIC (1, 2) · HIVEP (1, 2, 3) · IKZF (1, 2, 3) · ILF (2, 3) · KLF (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17) · MTF1 · MYT1 · OSR1 · PRDM9 · SALL (1, 2, 3, 4) · SP (1, 2, 4, 7, 8) · TSHZ3 · WT1 · Zbtb7 (7A, 7B) · ZBTB (16, 17, 20, 32, 33, 40) · zinc finger (3, 7, 9, 10, 19, 22, 24, 33B, 34, 35, 41, 43, 44, 51, 74, 143, 146, 148, 165, 202, 217, 219, 238, 239, 259, 267, 268, 281, 295, 300, 318, 330, 346, 350, 365, 366, 384, 423, 451, 452, 471, 593, 638, 644, 649, 655)(2.4) Cys6(2.5) Alternating composition(3) Helix-turn-helix domains (3.1) HomeodomainARX · CDX (1, 2) · CRX · CUTL1 · DBX (1, 2) · DLX (3, 4, 5) · EMX2 · EN (1, 2) · FHL (1, 2, 3) · HESX1 · HHEX · HLX · Homeobox (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A7, A9, A10, A11, A13, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9, B13, C4, C5, C6, C8, C9, C10, C11, C12, C13, D1, D3, D4, D8, D9, D10, D11, D12, D13) · HOPX · IRX (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, MKX) · LMX (1A, 1B) · MEIS (1, 2) · MEOX2 · MNX1 · MSX (1, 2) · NANOG · NKX (2-1, 2-2, 2-3, 2-5, 3-1, 3-2, 6-1, 6-2) · NOBOX · PBX (1, 2, 3) · PHF (1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 16, 17, 20, 21A) · PHOX (2A, 2B) · PITX (1, 2, 3) · POU domain (PIT-1, BRN-3: A, B, C, Octamer transcription factor: 1, 2, 3/4, 6, 7, 11) · OTX (1, 2) · PDX1 · SATB2 · SHOX2 · VAX1 · ZEB (1, 2)(3.2) Paired box(3.3) Fork head / winged helix(3.4) Heat Shock Factors(3.5) Tryptophan clusters(3.6) TEA domain(4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts (4.1) Rel homology region(4.2) STAT(4.3) p53(4.4) MADS box(4.6) TATA binding proteins(4.7) High-mobility group(4.10) Cold-shock domainCSDA, YBX1(4.11) Runt(0) Other transcription factors (0.2) HMGI(Y)(0.3) Pocket domain(0.6) MiscellaneousCategories:- Human proteins
- Genetics stubs
- Vitamin D
- Intracellular receptors
- Transcription factors
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.