- NPAS2
-
Neuronal PAS domain protein 2 Identifiers Symbols NPAS2; FLJ23138; MGC71151; MOP4; PASD4; bHLHe9 External IDs OMIM: 603347 MGI: 109232 HomoloGene: 1887 GeneCards: NPAS2 Gene Gene Ontology Molecular function • DNA binding
• sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factor activity
• signal transducer activity
• Hsp90 protein bindingCellular component • nucleus
• transcription factor complexBiological process • transcription, DNA-dependent
• regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
• central nervous system development
• positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
• rhythmic processSources: Amigo / QuickGO RNA expression pattern 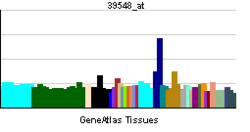
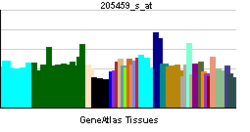
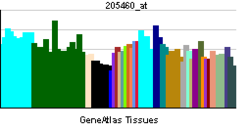
More reference expression data Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 4862 18143 Ensembl ENSG00000170485 ENSMUSG00000026077 UniProt Q99743 Q32ME6 RefSeq (mRNA) NM_002518.3 NM_008719.2 RefSeq (protein) NP_002509.2 NP_032745.2 Location (UCSC) Chr 2:
101.44 – 101.61 MbChr 1:
39.25 – 39.42 MbPubMed search [1] [2] Neuronal PAS domain-containing protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NPAS2 gene.[1][2]
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)-PAS family of transcription factors. A similar mouse protein may play a regulatory role in the acquisition of specific types of memory. It also may function as a part of a molecular clock operative in the mammalian forebrain.[3]
Contents
Interactions
NPAS2 has been shown to interact with Retinoic acid receptor alpha,[4] EP300,[5] ARNTL[4][6] and Retinoid X receptor alpha.[4]
References
- ^ Zhou YD, Barnard M, Tian H, Li X, Ring HZ, Francke U, Shelton J, Richardson J, Russell DW, McKnight SL (Mar 1997). "Molecular characterization of two mammalian bHLH-PAS domain proteins selectively expressed in the central nervous system". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94 (2): 713–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.2.713. PMC 19579. PMID 9012850. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=19579.
- ^ Hogenesch JB, Chan WK, Jackiw VH, Brown RC, Gu YZ, Pray-Grant M, Perdew GH, Bradfield CA (May 1997). "Characterization of a subset of the basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS superfamily that interacts with components of the dioxin signaling pathway". J Biol Chem 272 (13): 8581–93. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.13.8581. PMID 9079689.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: NPAS2 neuronal PAS domain protein 2". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=4862.
- ^ a b c McNamara, P; Seo S B, Rudic R D, Sehgal A, Chakravarti D, FitzGerald G A (Jun. 2001). "Regulation of CLOCK and MOP4 by nuclear hormone receptors in the vasculature: a humoral mechanism to reset a peripheral clock". Cell (United States) 105 (7): 877–89. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00401-9. ISSN 0092-8674. PMID 11439184.
- ^ Curtis, Anne M; Seo Sang-beom, Westgate Elizabeth J, Rudic Radu Daniel, Smyth Emer M, Chakravarti Debabrata, FitzGerald Garret A, McNamara Peter (Feb. 2004). "Histone acetyltransferase-dependent chromatin remodeling and the vascular clock". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 279 (8): 7091–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M311973200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 14645221.
- ^ Hogenesch, J B; Gu Y Z, Jain S, Bradfield C A (May. 1998). "The basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS orphan MOP3 forms transcriptionally active complexes with circadian and hypoxia factors". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (UNITED STATES) 95 (10): 5474–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.10.5474. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 20401. PMID 9576906. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=20401.
Further reading
External links
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
Transcription factors and intracellular receptors (1) Basic domains (1.1) Basic leucine zipper (bZIP)Activating transcription factor (AATF, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) · AP-1 (c-Fos, FOSB, FOSL1, FOSL2, JDP2, c-Jun, JUNB, JUND) · BACH (1, 2) · BATF · BLZF1 · C/EBP (α, β, γ, δ, ε, ζ) · CREB (1, 3, L1) · CREM · DBP · DDIT3 · GABPA · HLF · MAF (B, F, G, K) · NFE (2, L1, L2, L3) · NFIL3 · NRL · NRF (1, 2, 3) · XBP1(1.2) Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)ATOH1 · AhR · AHRR · ARNT · ASCL1 · BHLHB2 · BMAL (ARNTL, ARNTL2) · CLOCK · EPAS1 · FIGLA · HAND (1, 2) · HES (5, 6) · HEY (1, 2, L) · HES1 · HIF (1A, 3A) · ID (1, 2, 3, 4) · LYL1 · MESP2 · MXD4 · MYCL1 · MYCN · Myogenic regulatory factors (MyoD, Myogenin, MYF5, MYF6) · Neurogenins (1, 2, 3) · NeuroD (1, 2) · NPAS (1, 2, 3) · OLIG (1, 2) · Pho4 · Scleraxis · SIM (1, 2) · TAL (1, 2) · Twist · USF1(1.3) bHLH-ZIP(1.4) NF-1(1.5) RF-X(1.6) Basic helix-span-helix (bHSH)(2) Zinc finger DNA-binding domains (2.1) Nuclear receptor (Cys4)subfamily 1 (Thyroid hormone (α, β), CAR, FXR, LXR (α, β), PPAR (α, β/δ, γ), PXR, RAR (α, β, γ), ROR (α, β, γ), Rev-ErbA (α, β), VDR)
subfamily 2 (COUP-TF (I, II), Ear-2, HNF4 (α, γ), PNR, RXR (α, β, γ), Testicular receptor (2, 4), TLX)
subfamily 3 (Steroid hormone (Androgen, Estrogen (α, β), Glucocorticoid, Mineralocorticoid, Progesterone), Estrogen related (α, β, γ))
subfamily 4 NUR (NGFIB, NOR1, NURR1) · subfamily 5 (LRH-1, SF1) · subfamily 6 (GCNF) · subfamily 0 (DAX1, SHP)(2.2) Other Cys4(2.3) Cys2His2General transcription factors (TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE (1, 2), TFIIF (1, 2), TFIIH (1, 2, 4, 2I, 3A, 3C1, 3C2))
ATBF1 · BCL (6, 11A, 11B) · CTCF · E4F1 · EGR (1, 2, 3, 4) · ERV3 · GFI1 · GLI-Krüppel family (1, 2, 3, REST, S2, YY1) · HIC (1, 2) · HIVEP (1, 2, 3) · IKZF (1, 2, 3) · ILF (2, 3) · KLF (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17) · MTF1 · MYT1 · OSR1 · PRDM9 · SALL (1, 2, 3, 4) · SP (1, 2, 4, 7, 8) · TSHZ3 · WT1 · Zbtb7 (7A, 7B) · ZBTB (16, 17, 20, 32, 33, 40) · zinc finger (3, 7, 9, 10, 19, 22, 24, 33B, 34, 35, 41, 43, 44, 51, 74, 143, 146, 148, 165, 202, 217, 219, 238, 239, 259, 267, 268, 281, 295, 300, 318, 330, 346, 350, 365, 366, 384, 423, 451, 452, 471, 593, 638, 644, 649, 655)(2.4) Cys6(2.5) Alternating composition(3) Helix-turn-helix domains (3.1) HomeodomainARX · CDX (1, 2) · CRX · CUTL1 · DBX (1, 2) · DLX (3, 4, 5) · EMX2 · EN (1, 2) · FHL (1, 2, 3) · HESX1 · HHEX · HLX · Homeobox (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A7, A9, A10, A11, A13, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9, B13, C4, C5, C6, C8, C9, C10, C11, C13, D1, D3, D4, D8, D9, D10, D11, D12, D13) · HOPX · IRX (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, MKX) · LMX (1A, 1B) · MEIS (1, 2) · MEOX2 · MNX1 · MSX (1, 2) · NANOG · NKX (2-1, 2-2, 2-3, 2-5, 3-1, 3-2, 6-1, 6-2) · NOBOX · PBX (1, 2, 3) · PHF (1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 16, 17, 20, 21A) · PHOX (2A, 2B) · PITX (1, 2, 3) · POU domain (PIT-1, BRN-3: A, B, C, Octamer transcription factor: 1, 2, 3/4, 6, 7, 11) · OTX (1, 2) · PDX1 · SATB2 · SHOX2 · VAX1 · ZEB (1, 2)(3.2) Paired box(3.3) Fork head / winged helix(3.4) Heat Shock Factors(3.5) Tryptophan clusters(3.6) TEA domain(4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts (4.1) Rel homology region(4.2) STAT(4.3) p53(4.4) MADS box(4.6) TATA binding proteins(4.7) High-mobility group(4.10) Cold-shock domainCSDA, YBX1(4.11) Runt(0) Other transcription factors (0.2) HMGI(Y)(0.3) Pocket domain(0.6) Miscellaneoussee also transcription factor/coregulator deficiencies
B bsyn: dna (repl, cycl, reco, repr) · tscr (fact, tcrg, nucl, rnat, rept, ptts) · tltn (risu, pttl, nexn) · dnab, rnab/runp · stru (domn, 1°, 2°, 3°, 4°)Categories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 2 gene stubs
- Transcription factors
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
