- NFE2L1
-
Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 1 Identifiers Symbols NFE2L1; FLJ00380; LCR-F1; NRF1; TCF11 External IDs OMIM: 163260 MGI: 99421 HomoloGene: 20685 GeneCards: NFE2L1 Gene Gene Ontology Molecular function • sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factor activity
• transcription cofactor activity
• sequence-specific DNA binding
• protein dimerization activityCellular component • nucleus Biological process • regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
• transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
• heme biosynthetic process
• inflammatory response
• anatomical structure morphogenesisSources: Amigo / QuickGO RNA expression pattern 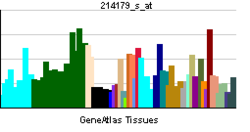
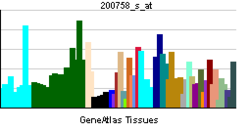
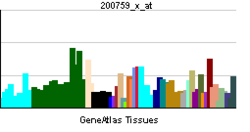
More reference expression data Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 4779 18023 Ensembl ENSG00000082641 ENSMUSG00000038615 UniProt Q14494 Q3U4L3 RefSeq (mRNA) NM_003204 NM_008686 RefSeq (protein) NP_003195 NP_032712 Location (UCSC) Chr 17:
46.13 – 46.14 MbChr 11:
96.68 – 96.69 MbPubMed search [1] [2] Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NFE2L1 gene.[1][2][3]
Contents
Interactions
NFE2L1 has been shown to interact with C-jun.[4]
References
- ^ Chan JY, Han XL, Kan YW (Jan 1994). "Cloning of Nrf1, an NF-E2-related transcription factor, by genetic selection in yeast". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90 (23): 11371–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.23.11371. PMC 47984. PMID 8248256. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=47984.
- ^ Chan JY, Kwong M, Lu R, Chang J, Wang B, Yen TS, Kan YW (Apr 1998). "Targeted disruption of the ubiquitous CNC-bZIP transcription factor, Nrf-1, results in anemia and embryonic lethality in mice". EMBO J 17 (6): 1779–87. doi:10.1093/emboj/17.6.1779. PMC 1170525. PMID 9501099. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1170525.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: NFE2L1 nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 1". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=4779.
- ^ Venugopal, R; Jaiswal A K (Dec. 1998). "Nrf2 and Nrf1 in association with Jun proteins regulate antioxidant response element-mediated expression and coordinated induction of genes encoding detoxifying enzymes". Oncogene (ENGLAND) 17 (24): 3145–56. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202237. ISSN 0950-9232. PMID 9872330.
Further reading
- Luna L, Skammelsrud N, Johnsen O et al. (1995). "Structural organization and mapping of the human TCF11 gene". Genomics 27 (2): 237–44. doi:10.1006/geno.1995.1037. PMID 7557987.
- Luna L, Johnsen O, Skartlien AH et al. (1995). "Molecular cloning of a putative novel human bZIP transcription factor on chromosome 17q22". Genomics 22 (3): 553–62. doi:10.1006/geno.1994.1428. PMID 8001966.
- Caterina JJ, Donze D, Sun CW et al. (1994). "Cloning and functional characterization of LCR-F1: a bZIP transcription factor that activates erythroid-specific, human globin gene expression". Nucleic Acids Res. 22 (12): 2383–91. doi:10.1093/nar/22.12.2383. PMC 523699. PMID 8036168. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=523699.
- Johnsen O, Skammelsrud N, Luna L et al. (1996). "Small Maf proteins interact with the human transcription factor TCF11/Nrf1/LCR-F1". Nucleic Acids Res. 24 (21): 4289–97. doi:10.1093/nar/24.21.4289. PMC 146217. PMID 8932385. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=146217.
- Toki T, Itoh J, Kitazawa J et al. (1997). "Human small Maf proteins form heterodimers with CNC family transcription factors and recognize the NF-E2 motif". Oncogene 14 (16): 1901–10. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1201024. PMID 9150357.
- Johnsen O, Murphy P, Prydz H, Kolsto AB (1998). "Interaction of the CNC-bZIP factor TCF11/LCR-F1/Nrf1 with MafG: binding-site selection and regulation of transcription". Nucleic Acids Res. 26 (2): 512–20. doi:10.1093/nar/26.2.512. PMC 147270. PMID 9421508. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=147270.
- Novotny V, Prieschl EE, Csonga R et al. (1999). "Nrf1 in a complex with fosB, c-jun, junD and ATF2 forms the AP1 component at the TNF alpha promoter in stimulated mast cells". Nucleic Acids Res. 26 (23): 5480–5. doi:10.1093/nar/26.23.5480. PMC 147998. PMID 9826775. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=147998.
- Venugopal R, Jaiswal AK (1999). "Nrf2 and Nrf1 in association with Jun proteins regulate antioxidant response element-mediated expression and coordinated induction of genes encoding detoxifying enzymes". Oncogene 17 (24): 3145–56. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202237. PMID 9872330.
- Murphy P, Kolstø A (2001). "Expression of the bZIP transcription factor TCF11 and its potential dimerization partners during development". Mech. Dev. 97 (1–2): 141–8. doi:10.1016/S0925-4773(00)00413-5. PMID 11025215.
- Jiang LQ, Wen SJ, Wang HY, Chen LY (2003). "Screening the proteins that interact with calpain in a human heart cDNA library using a yeast two-hybrid system". Hypertens. Res. 25 (4): 647–52. doi:10.1291/hypres.25.647. PMID 12358155.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139241.
- Husberg C, Murphy P, Bjørgo E et al. (2003). "Cellular localisation and nuclear export of the human bZIP transcription factor TCF11". Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1640 (2–3): 143–51. doi:10.1016/S0167-4889(03)00041-7. PMID 12729924.
- Newman JR, Keating AE (2003). "Comprehensive identification of human bZIP interactions with coiled-coil arrays". Science 300 (5628): 2097–101. doi:10.1126/science.1084648. PMID 12805554.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=528928.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Ma J, Dempsey AA, Stamatiou D et al. (2007). "Identifying leukocyte gene expression patterns associated with plasma lipid levels in human subjects". Atherosclerosis 191 (1): 63–72. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2006.05.032. PMID 16806233.
External links
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
Transcription factors and intracellular receptors (1) Basic domains (1.1) Basic leucine zipper (bZIP)Activating transcription factor (AATF, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) · AP-1 (c-Fos, FOSB, FOSL1, FOSL2, JDP2, c-Jun, JUNB, JUND) · BACH (1, 2) · BATF · BLZF1 · C/EBP (α, β, γ, δ, ε, ζ) · CREB (1, 3, L1) · CREM · DBP · DDIT3 · GABPA · HLF · MAF (B, F, G, K) · NFE (2, L1, L2, L3) · NFIL3 · NRL · NRF (1, 2, 3) · XBP1(1.2) Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)ATOH1 · AhR · AHRR · ARNT · ASCL1 · BHLHB2 · BMAL (ARNTL, ARNTL2) · CLOCK · EPAS1 · FIGLA · HAND (1, 2) · HES (5, 6) · HEY (1, 2, L) · HES1 · HIF (1A, 3A) · ID (1, 2, 3, 4) · LYL1 · MESP2 · MXD4 · MYCL1 · MYCN · Myogenic regulatory factors (MyoD, Myogenin, MYF5, MYF6) · Neurogenins (1, 2, 3) · NeuroD (1, 2) · NPAS (1, 2, 3) · OLIG (1, 2) · Pho4 · Scleraxis · SIM (1, 2) · TAL (1, 2) · Twist · USF1(1.3) bHLH-ZIP(1.4) NF-1(1.5) RF-X(1.6) Basic helix-span-helix (bHSH)(2) Zinc finger DNA-binding domains (2.1) Nuclear receptor (Cys4)subfamily 1 (Thyroid hormone (α, β), CAR, FXR, LXR (α, β), PPAR (α, β/δ, γ), PXR, RAR (α, β, γ), ROR (α, β, γ), Rev-ErbA (α, β), VDR)
subfamily 2 (COUP-TF (I, II), Ear-2, HNF4 (α, γ), PNR, RXR (α, β, γ), Testicular receptor (2, 4), TLX)
subfamily 3 (Steroid hormone (Androgen, Estrogen (α, β), Glucocorticoid, Mineralocorticoid, Progesterone), Estrogen related (α, β, γ))
subfamily 4 NUR (NGFIB, NOR1, NURR1) · subfamily 5 (LRH-1, SF1) · subfamily 6 (GCNF) · subfamily 0 (DAX1, SHP)(2.2) Other Cys4(2.3) Cys2His2General transcription factors (TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE (1, 2), TFIIF (1, 2), TFIIH (1, 2, 4, 2I, 3A, 3C1, 3C2))
ATBF1 · BCL (6, 11A, 11B) · CTCF · E4F1 · EGR (1, 2, 3, 4) · ERV3 · GFI1 · GLI-Krüppel family (1, 2, 3, REST, S2, YY1) · HIC (1, 2) · HIVEP (1, 2, 3) · IKZF (1, 2, 3) · ILF (2, 3) · KLF (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17) · MTF1 · MYT1 · OSR1 · PRDM9 · SALL (1, 2, 3, 4) · SP (1, 2, 4, 7, 8) · TSHZ3 · WT1 · Zbtb7 (7A, 7B) · ZBTB (16, 17, 20, 32, 33, 40) · zinc finger (3, 7, 9, 10, 19, 22, 24, 33B, 34, 35, 41, 43, 44, 51, 74, 143, 146, 148, 165, 202, 217, 219, 238, 239, 259, 267, 268, 281, 295, 300, 318, 330, 346, 350, 365, 366, 384, 423, 451, 452, 471, 593, 638, 644, 649, 655)(2.4) Cys6(2.5) Alternating composition(3) Helix-turn-helix domains (3.1) HomeodomainARX · CDX (1, 2) · CRX · CUTL1 · DBX (1, 2) · DLX (3, 4, 5) · EMX2 · EN (1, 2) · FHL (1, 2, 3) · HESX1 · HHEX · HLX · Homeobox (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A7, A9, A10, A11, A13, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9, B13, C4, C5, C6, C8, C9, C10, C11, C13, D1, D3, D4, D8, D9, D10, D11, D12, D13) · HOPX · IRX (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, MKX) · LMX (1A, 1B) · MEIS (1, 2) · MEOX2 · MNX1 · MSX (1, 2) · NANOG · NKX (2-1, 2-2, 2-3, 2-5, 3-1, 3-2, 6-1, 6-2) · NOBOX · PBX (1, 2, 3) · PHF (1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 16, 17, 20, 21A) · PHOX (2A, 2B) · PITX (1, 2, 3) · POU domain (PIT-1, BRN-3: A, B, C, Octamer transcription factor: 1, 2, 3/4, 6, 7, 11) · OTX (1, 2) · PDX1 · SATB2 · SHOX2 · VAX1 · ZEB (1, 2)(3.2) Paired box(3.3) Fork head / winged helix(3.4) Heat Shock Factors(3.5) Tryptophan clusters(3.6) TEA domain(4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts (4.1) Rel homology region(4.2) STAT(4.3) p53(4.4) MADS box(4.6) TATA binding proteins(4.7) High-mobility group(4.10) Cold-shock domainCSDA, YBX1(4.11) Runt(0) Other transcription factors (0.2) HMGI(Y)(0.3) Pocket domain(0.6) Miscellaneoussee also transcription factor/coregulator deficiencies
B bsyn: dna (repl, cycl, reco, repr) · tscr (fact, tcrg, nucl, rnat, rept, ptts) · tltn (risu, pttl, nexn) · dnab, rnab/runp · stru (domn, 1°, 2°, 3°, 4°)Categories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 17 gene stubs
- Transcription factors
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
