- Rev-ErbA beta
-
Nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group D, member 2 
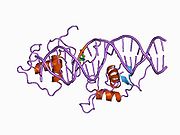
Structure of the ligand binding domain (LBD) of the Rev-erb? receptor based on PDB 2v0v. Depicted here is a dimer of comprising two LBD protein molecules.Available structures PDB 2V0V, 2V7C, 3CQV Identifiers Symbols NR1D2; BD73; EAR-1R; RVR External IDs OMIM: 602304 MGI: 2449205 HomoloGene: 3763 IUPHAR: NR1D2 GeneCards: NR1D2 Gene Gene Ontology Molecular function • sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factor activity
• steroid hormone receptor activity
• ligand-dependent nuclear receptor activity
• zinc ion binding
• sequence-specific DNA binding
• metal ion bindingCellular component • nucleus
• nucleoplasmBiological process • regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
• gene expression
• regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter by nuclear hormone receptorSources: Amigo / QuickGO RNA expression pattern 
More reference expression data Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 9975 353187 Ensembl ENSG00000174738 ENSMUSG00000021775 UniProt Q14995 Q4VAB7 RefSeq (mRNA) NM_001145425.1 NM_011584.4 RefSeq (protein) NP_001138897.1 NP_035714.3 Location (UCSC) Chr 3:
23.99 – 24.02 MbChr 14:
19.04 – 19.07 MbPubMed search [1] [2] This box: view · protein that in humans is encoded by the NR1D2 gene.[1][2] Rev-erbβ is a member of the Rev-ErbA family of transcription factors. Rev-erbβ, like Rev-erbα, belongs to the nuclear receptor superfamily and can modulate gene expression by directly binding to their promoters.[3][4]
Contents
Structure
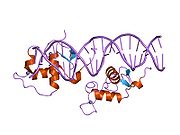
 Cartoon diagram of the ligand binding domain of Rev-ErbA beta (rainbow colored, N-terminus = blue, C-terminus = red) complexed with heme (space-filling model, carbon atoms = white, nitrogen = blue, oxygen = red, iron = magenta) based on the PDB 3CQV crystallographic coordinates.
Cartoon diagram of the ligand binding domain of Rev-ErbA beta (rainbow colored, N-terminus = blue, C-terminus = red) complexed with heme (space-filling model, carbon atoms = white, nitrogen = blue, oxygen = red, iron = magenta) based on the PDB 3CQV crystallographic coordinates.
Rev-erbβ is similar to Rev-erbα in its protein structure and function as a transcriptional repressor. The crystal structure of an unliganded Rev-erbβ ligand-binding domain (LBD) has been resolved (see figure to the right) and shows an extremely small ligand-binding pocket.[5] However, Rev-erbβ has been shown to interact with heme, which appears important for its function.[6]
The structure of Rev-erbβ complexed with heme (see figure to the left) shows a substantial movement of helices 1 (N-terminus ) and 11 (C-terminus ) which opens up a large binding pocket in the interior of the protein that is able to accommodate this ligand.[7]
Function
Rev-erbβ has been implicated in the control of lipid and energy homoeostasis in skeletal muscle.[8]
Rev-erbβ is also a circadian regulated gene; its mRNA displays rhythmic expression in vivo and in serum-synchronized cell cultures. However, it is currently unknown to what extent Rev-erbβ contributes to oscillations of the core circadian clock. However it has been shown heme suppresses hepatic gluconeogenic gene expression and glucose output through the related Rev-erbα receptor which mediates gene repression. Hence, the Rev-erbα receptor detects heme and thereby coordinates the cellular clock, glucose homeostasis, and energy metabolism.[9]
References
- ^ Dumas B, Harding HP, Choi HS, Lehmann KA, Chung M, Lazar MA, Moore DD (August 1994). "A new orphan member of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily closely related to Rev-Erb". Mol. Endocrinol. 8 (8): 996–1005. doi:10.1210/me.8.8.996. PMID 7997240.
- ^ Koh YS, Moore DD (April 1999). "Linkage of the nuclear hormone receptor genes NR1D2, THRB, and RARB: evidence for an ancient, large-scale duplication". Genomics 57 (2): 289–92. doi:10.1006/geno.1998.5683. PMID 10198169.
- ^ Bonnelye E, Vanacker JM, Desbiens X, Begue A, Stehelin D, Laudet V (1994). "Rev-erbβ, a new member of the nuclear receptor superfamily, is expressed in the nervous system during chicken development". Cell Growth Differ. 5 (12): 1357–65. PMID 7696184. http://cgd.aacrjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/5/12/1357.
- ^ Giambiagi N, Cassia R, Petropoulos I, Part D, Cereghini S, Zakin MM, Ochoa A (1995). "Rev-erb β 2, a novel isoform of the Rev-erb family of orphan nuclear receptors". Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 37 (6): 1091–1102. PMID 8747539.
- ^ Woo EJ, Jeong DG, Lim MY, Jun Kim S, Kim KJ, Yoon SM, Park BC, Eon Ryu S (2007). "Structural Insight into the Constitutive Repression Function of the Nuclear Receptor Rev-erbβ". J. Mol. Biol. 373 (3): 735–44. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.08.037. PMID 17870090.
- ^ Raghuram S, Stayrook KR, Huang P, Rogers PM, Nosie AK, McClure DB, Burris LL, Khorasanizadeh S, Burris TP, Rastinejad F (December 2007). "Identification of heme as the ligand for the orphan nuclear receptors REV-ERBα and REV-ERBβ". Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 14 (12): 1207–13. doi:10.1038/nsmb1344. PMC 2743565. PMID 18037887. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2743565.
- ^ PDB 3CQV; "Human nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group D, member 2 in complex with heme". The Structural Genomics Consortium (SGC). http://www.thesgc.com/SGC-WebPages/StructureDescription/3CQV.php. Retrieved 2008-08-09. ; Pardee K, Xu X, Dong A, Reinking J, Krause H, Schuetz A, Zhang R, Cui H, Arrowsmith CH, Weigelt J, Bountra C, Savchenko A, Bochkarev A, Edwards AM (2008). "Crystal structure of Reverb beta in complex with heme". To be Published.
- ^ Ramakrishnan SN, Lau P, Burke LJ, Muscat GE (2005). "Rev-erbβ regulates the expression of genes involved in lipid absorption in skeletal muscle cells: evidence for cross-talk between orphan nuclear receptors and myokines". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (10): 8651–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M413949200. PMID 15623503.
- ^ Yin L, Wu N, Curtin JC, Qatanani M, Szwergold NR, Reid RA, Waitt GM, Parks DJ, Pearce KH, Wisely GB, Lazar MA (December 2007). "Rev-erbα, a heme sensor that coordinates metabolic and circadian pathways". Science 318 (5857): 1786–9. doi:10.1126/science.1150179. PMID 18006707.
Further reading
- Ramakrishnan SN, Lau P, Crowther LM, Cleasby ME, Millard S, Leong GM, Cooney GJ, Muscat GE (October 2009). "Rev-erb beta regulates the Srebp-1c promoter and mRNA expression in skeletal muscle cells". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 388 (4): 654–9. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.08.045. PMID 19682428.
External links
v · d · ePDB gallery 1a6y: REVERBA ORPHAN NUCLEAR RECEPTOR/DNA COMPLEX1ga5: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE ORPHAN NUCLEAR RECEPTOR REV-ERB(ALPHA) DNA-BINDING DOMAIN BOUND TO ITS COGNATE RESPONSE ELEMENT1hlz: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE ORPHAN NUCLEAR RECEPTOR REV-ERB(ALPHA) DNA-BINDING DOMAIN BOUND TO ITS COGNATE RESPONSE ELEMENTv · d · eTranscription factors and intracellular receptors (1) Basic domains Activating transcription factor (AATF, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) · AP-1 (c-Fos, FOSB, FOSL1, FOSL2, JDP2, c-Jun, JUNB, JUND) · BACH (1, 2) · BATF · BLZF1 · C/EBP (α, β, γ, δ, ε, ζ) · CREB (1, 3, L1) · CREM · DBP · DDIT3 · GABPA · HLF · MAF (B, F, G, K) · NFE (2, L1, L2, L3) · NFIL3 · NRL · NRF (1, 2, 3) · XBP1ATOH1 · AhR · AHRR · ARNT · ASCL1 · BHLHB2 · BMAL (ARNTL, ARNTL2) · CLOCK · EPAS1 · FIGLA · HAND (1, 2) · HES (5, 6) · HEY (1, 2, L) · HES1 · HIF (1A, 3A) · ID (1, 2, 3, 4) · LYL1 · MESP2 · MXD4 · MYCL1 · MYCN · Myogenic regulatory factors (MyoD, Myogenin, MYF5, MYF6) · Neurogenins (1, 2, 3) · NeuroD (1, 2) · NPAS (1, 2, 3) · OLIG (1, 2) · Pho4 · Scleraxis · SIM (1, 2) · TAL (1, 2) · Twist · USF1(1.4) NF-1(1.5) RF-X(1.6) Basic helix-span-helix (bHSH)(2) Zinc finger DNA-binding domains subfamily 1 (Thyroid hormone (α, β), CAR, FXR, LXR (α, β), PPAR (α, β/δ, γ), PXR, RAR (α, β, γ), ROR (α, β, γ), Rev-ErbA (α, β), VDR)
subfamily 2 (COUP-TF (I, II), Ear-2, HNF4 (α, γ), PNR, RXR (α, β, γ), Testicular receptor (2, 4), TLX)
subfamily 3 (Steroid hormone (Androgen, Estrogen (α, β), Glucocorticoid, Mineralocorticoid, Progesterone), Estrogen related (α, β, γ))
subfamily 4 NUR (NGFIB, NOR1, NURR1) · subfamily 5 (LRH-1, SF1) · subfamily 6 (GCNF) · subfamily 0 (DAX1, SHP)(2.2) Other Cys4(2.3) Cys2His2General transcription factors (TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE (1, 2), TFIIF (1, 2), TFIIH (1, 2, 4, 2I, 3A, 3C1, 3C2))
ATBF1 · BCL (6, 11A, 11B) · CTCF · E4F1 · EGR (1, 2, 3, 4) · ERV3 · GFI1 · GLI-Krüppel family (1, 2, 3, REST, S2, YY1) · HIC (1, 2) · HIVEP (1, 2, 3) · IKZF (1, 2, 3) · ILF (2, 3) · KLF (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17) · MTF1 · MYT1 · OSR1 · PRDM9 · SALL (1, 2, 3, 4) · SP (1, 2, 4, 7, 8) · TSHZ3 · WT1 · Zbtb7 (7A, 7B) · ZBTB (16, 17, 20, 32, 33, 40) · zinc finger (3, 7, 9, 10, 19, 22, 24, 33B, 34, 35, 41, 43, 44, 51, 74, 143, 146, 148, 165, 202, 217, 219, 238, 239, 259, 267, 268, 281, 295, 300, 318, 330, 346, 350, 365, 366, 384, 423, 451, 452, 471, 593, 638, 644, 649, 655)(2.4) Cys6(2.5) Alternating composition(3) Helix-turn-helix domains ARX · CDX (1, 2) · CRX · CUTL1 · DBX (1, 2) · DLX (3, 4, 5) · EMX2 · EN (1, 2) · FHL (1, 2, 3) · HESX1 · HHEX · HLX · Homeobox (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A7, A9, A10, A11, A13, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9, B13, C4, C5, C6, C8, C9, C10, C11, C12, C13, D1, D3, D4, D8, D9, D10, D11, D12, D13) · HOPX · IRX (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, MKX) · LMX (1A, 1B) · MEIS (1, 2) · MEOX2 · MNX1 · MSX (1, 2) · NANOG · NKX (2-1, 2-2, 2-3, 2-5, 3-1, 3-2, 6-1, 6-2) · NOBOX · PBX (1, 2, 3) · PHF (1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 16, 17, 20, 21A) · PHOX (2A, 2B) · PITX (1, 2, 3) · POU domain (PIT-1, BRN-3: A, B, C, Octamer transcription factor: 1, 2, 3/4, 6, 7, 11) · OTX (1, 2) · PDX1 · SATB2 · SHOX2 · VAX1 · ZEB (1, 2)(3.2) Paired box(3.5) Tryptophan clusters(3.6) TEA domain(4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts (4.1) Rel homology region(4.3) p53(4.7) High-mobility group(4.10) Cold-shock domainCSDA, YBX1(4.11) Runt(0) Other transcription factors (0.2) HMGI(Y)(0.6) MiscellaneousCategories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 3 gene stubs
- Intracellular receptors
- Transcription factors
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Rev-ErbA — The Rev ErbA proteins are members of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular transcription factors. There are two forms of the receptor, alpha and beta, each encoded by a separate gene (gene|NR1D1 and gene|NR1D2 respectively).cite journal |… … Wikipedia
Thyroid hormone receptor beta — Thyroid hormone receptor, beta (erythroblastic leukemia viral (v erb a) oncogene homolog 2, avian) PDB rendering based on 1bsx … Wikipedia
Estrogen receptor beta — See also: Estrogen receptor Estrogen receptor 2 (ER beta) PDB rendering based on 1hj1 … Wikipedia
V-erbA-related gene — Nuclear receptor subfamily 2, group F, member 6 Identifiers Symbols NR2F6; EAR 2; EAR2; ERBAL2 External IDs … Wikipedia
Retinoic acid receptor beta — Retinoic acid receptor, beta PDB rendering based on 1dsz … Wikipedia
RAR-related orphan receptor beta — RAR related orphan receptor B PDB rendering based on 1k4w … Wikipedia
Liver X receptor beta — Nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group H, member 2 PDB rendering based on 1p8d … Wikipedia
Retinoid X receptor beta — Retinoid X receptor, beta PDB rendering based on 1by4 … Wikipedia
Estrogen-related receptor beta — PDB rendering based on 1lo1 … Wikipedia
Circadian oscillator — Circadian oscillators are components of the biological clocks that regulate the activities of organisms in relation to environmental cycles and provide an internal temporal framework.[1] All circadian clocks, regardless of phylogenetic origin,… … Wikipedia
Share the article and excerpts
Direct link
https://en-academic.com/dic.nsf/enwiki/7529559 Do a right-click on the link above
and select “Copy Link”
Rev-ErbA beta
- Rev-ErbA beta
-