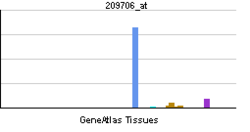
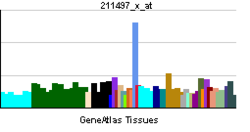
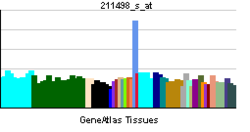
- NKX3-1
-
Homeobox protein Nkx-3.1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NKX3-1 gene.[1]
The homeodomain-containing transcription factor NKX3A is a putative prostate tumor suppressor that is expressed in a largely prostate-specific and androgen-regulated manner. Loss of NKX3A protein expression is a common finding in human prostate carcinomas and prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia.[supplied by OMIM][2]
Contents
Interactions
NKX3-1 has been shown to interact with SPDEF.[3]
References
- ^ He WW, Sciavolino PJ, Wing J, Augustus M, Hudson P, Meissner PS, Curtis RT, Shell BK, Bostwick DG, Tindall DJ, Gelmann EP, Abate-Shen C, Carter KC (September 1997). "A novel human prostate-specific, androgen-regulated homeobox gene (NKX3.1) that maps to 8p21, a region frequently deleted in prostate cancer". Genomics 43 (1): 69–77. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.4715. PMID 9226374.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: NKX3-1 NK3 transcription factor related, locus 1 (Drosophila)". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=4824.
- ^ Chen, Hui; Nandi Asit K, Li Xiang, Bieberich Charles J (January 2002). "NKX-3.1 interacts with prostate-derived Ets factor and regulates the activity of the PSA promoter". Cancer Res. (United States) 62 (2): 338–40. ISSN 0008-5472. PMID 11809674.
Further reading
- Shen MM, Abate-Shen C (2004). "Roles of the Nkx3.1 homeobox gene in prostate organogenesis and carcinogenesis.". Dev. Dyn. 228 (4): 767–78. doi:10.1002/dvdy.10397. PMID 14648854.
- Abdulkadir SA (2006). "Mechanisms of prostate tumorigenesis: roles for transcription factors Nkx3.1 and Egr1.". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1059: 33–40. doi:10.1196/annals.1339.018. PMID 16382041.
- Voeller HJ, Augustus M, Madike V, et al. (1997). "Coding region of NKX3.1, a prostate-specific homeobox gene on 8p21, is not mutated in human prostate cancers.". Cancer Res. 57 (20): 4455–9. PMID 9377551.
- Prescott JL, Blok L, Tindall DJ (1998). "Isolation and androgen regulation of the human homeobox cDNA, NKX3.1.". Prostate 35 (1): 71–80. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0045(19980401)35:1<71::AID-PROS10>3.0.CO;2-H. PMID 9537602.
- Choi CY, Kim YH, Kwon HJ, Kim Y (1999). "The homeodomain protein NK-3 recruits Groucho and a histone deacetylase complex to repress transcription.". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (47): 33194–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.47.33194. PMID 10559189.
- Carson JA, Fillmore RA, Schwartz RJ, Zimmer WE (2001). "The smooth muscle gamma-actin gene promoter is a molecular target for the mouse bagpipe homologue, mNkx3-1, and serum response factor.". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (50): 39061–72. doi:10.1074/jbc.M006532200. PMID 10993896.
- Bowen C, Bubendorf L, Voeller HJ, et al. (2000). "Loss of NKX3.1 expression in human prostate cancers correlates with tumor progression.". Cancer Res. 60 (21): 6111–5. PMID 11085535.
- Korkmaz KS, Korkmaz CG, Ragnhildstveit E, et al. (2001). "Full-length cDNA sequence and genomic organization of human NKX3A - alternative forms and regulation by both androgens and estrogens.". Gene 260 (1–2): 25–36. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(00)00453-4. PMID 11137288.
- Chen H, Nandi AK, Li X, Bieberich CJ (2002). "NKX-3.1 interacts with prostate-derived Ets factor and regulates the activity of the PSA promoter". Cancer Res. 62 (2): 338–40. PMID 11809674.
- Filmore RA, Dean DA, Zimmer WE (2003). "The smooth muscle gamma-actin gene is androgen responsive in prostate epithelia". Gene Expr. 10 (5–6): 201–11. PMID 12450213.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139241.
- Gelmann EP, Bowen C, Bubendorf L (2003). "Expression of NKX3.1 in normal and malignant tissues". Prostate 55 (2): 111–7. doi:10.1002/pros.10210. PMID 12661036.
- Skotheim RI, Korkmaz KS, Klokk TI, et al. (2004). "NKX3.1 Expression Is Lost in Testicular Germ Cell Tumors". Am. J. Pathol. 163 (6): 2149–54. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63571-7. PMC 1892359. PMID 14633588. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1892359.
- Korkmaz CG, Korkmaz KS, Manola J, et al. (2004). "Analysis of androgen regulated homeobox gene NKX3.1 during prostate carcinogenesis". J. Urol. 172 (3): 1134–9. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000136526.78535.b8. PMID 15311057.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=528928.
- Chen H, Bieberich CJ (2005). "Structural and functional analysis of domains mediating interaction between NKX-3.1 and PDEF". J. Cell. Biochem. 94 (1): 168–77. doi:10.1002/jcb.20297. PMID 15523673.
- Lind GE, Skotheim RI, Fraga MF, et al. (2005). "The loss of NKX3.1 expression in testicular – and prostate – cancers is not caused by promoter hypermethylation". Mol. Cancer 4 (1): 8. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-4-8. PMC 548671. PMID 15691383. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=548671.
- Asatiani E, Huang WX, Wang A, et al. (2005). "Deletion, methylation, and expression of the NKX3.1 suppressor gene in primary human prostate cancer". Cancer Res. 65 (4): 1164–73. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2688. PMID 15734999.
External links
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
Transcription factors and intracellular receptors (1) Basic domains (1.1) Basic leucine zipper (bZIP)Activating transcription factor (AATF, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) · AP-1 (c-Fos, FOSB, FOSL1, FOSL2, JDP2, c-Jun, JUNB, JUND) · BACH (1, 2) · BATF · BLZF1 · C/EBP (α, β, γ, δ, ε, ζ) · CREB (1, 3, L1) · CREM · DBP · DDIT3 · GABPA · HLF · MAF (B, F, G, K) · NFE (2, L1, L2, L3) · NFIL3 · NRL · NRF (1, 2, 3) · XBP1(1.2) Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)ATOH1 · AhR · AHRR · ARNT · ASCL1 · BHLHB2 · BMAL (ARNTL, ARNTL2) · CLOCK · EPAS1 · FIGLA · HAND (1, 2) · HES (5, 6) · HEY (1, 2, L) · HES1 · HIF (1A, 3A) · ID (1, 2, 3, 4) · LYL1 · MESP2 · MXD4 · MYCL1 · MYCN · Myogenic regulatory factors (MyoD, Myogenin, MYF5, MYF6) · Neurogenins (1, 2, 3) · NeuroD (1, 2) · NPAS (1, 2, 3) · OLIG (1, 2) · Pho4 · Scleraxis · SIM (1, 2) · TAL (1, 2) · Twist · USF1(1.3) bHLH-ZIP(1.4) NF-1(1.5) RF-X(1.6) Basic helix-span-helix (bHSH)(2) Zinc finger DNA-binding domains (2.1) Nuclear receptor (Cys4)subfamily 1 (Thyroid hormone (α, β), CAR, FXR, LXR (α, β), PPAR (α, β/δ, γ), PXR, RAR (α, β, γ), ROR (α, β, γ), Rev-ErbA (α, β), VDR)
subfamily 2 (COUP-TF (I, II), Ear-2, HNF4 (α, γ), PNR, RXR (α, β, γ), Testicular receptor (2, 4), TLX)
subfamily 3 (Steroid hormone (Androgen, Estrogen (α, β), Glucocorticoid, Mineralocorticoid, Progesterone), Estrogen related (α, β, γ))
subfamily 4 NUR (NGFIB, NOR1, NURR1) · subfamily 5 (LRH-1, SF1) · subfamily 6 (GCNF) · subfamily 0 (DAX1, SHP)(2.2) Other Cys4(2.3) Cys2His2General transcription factors (TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE (1, 2), TFIIF (1, 2), TFIIH (1, 2, 4, 2I, 3A, 3C1, 3C2))
ATBF1 · BCL (6, 11A, 11B) · CTCF · E4F1 · EGR (1, 2, 3, 4) · ERV3 · GFI1 · GLI-Krüppel family (1, 2, 3, REST, S2, YY1) · HIC (1, 2) · HIVEP (1, 2, 3) · IKZF (1, 2, 3) · ILF (2, 3) · KLF (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17) · MTF1 · MYT1 · OSR1 · PRDM9 · SALL (1, 2, 3, 4) · SP (1, 2, 4, 7, 8) · TSHZ3 · WT1 · Zbtb7 (7A, 7B) · ZBTB (16, 17, 20, 32, 33, 40) · zinc finger (3, 7, 9, 10, 19, 22, 24, 33B, 34, 35, 41, 43, 44, 51, 74, 143, 146, 148, 165, 202, 217, 219, 238, 239, 259, 267, 268, 281, 295, 300, 318, 330, 346, 350, 365, 366, 384, 423, 451, 452, 471, 593, 638, 644, 649, 655)(2.4) Cys6(2.5) Alternating composition(3) Helix-turn-helix domains (3.1) HomeodomainARX · CDX (1, 2) · CRX · CUTL1 · DBX (1, 2) · DLX (3, 4, 5) · EMX2 · EN (1, 2) · FHL (1, 2, 3) · HESX1 · HHEX · HLX · Homeobox (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A7, A9, A10, A11, A13, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9, B13, C4, C5, C6, C8, C9, C10, C11, C12, C13, D1, D3, D4, D8, D9, D10, D11, D12, D13) · HOPX · IRX (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, MKX) · LMX (1A, 1B) · MEIS (1, 2) · MEOX2 · MNX1 · MSX (1, 2) · NANOG · NKX (2-1, 2-2, 2-3, 2-5, 3-1, 3-2, 6-1, 6-2) · NOBOX · PBX (1, 2, 3) · PHF (1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 16, 17, 20, 21A) · PHOX (2A, 2B) · PITX (1, 2, 3) · POU domain (PIT-1, BRN-3: A, B, C, Octamer transcription factor: 1, 2, 3/4, 6, 7, 11) · OTX (1, 2) · PDX1 · SATB2 · SHOX2 · VAX1 · ZEB (1, 2)(3.2) Paired box(3.3) Fork head / winged helix(3.4) Heat Shock Factors(3.5) Tryptophan clusters(3.6) TEA domain(4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts (4.1) Rel homology region(4.2) STAT(4.3) p53(4.4) MADS box(4.6) TATA binding proteins(4.7) High-mobility group(4.10) Cold-shock domainCSDA, YBX1(4.11) Runt(0) Other transcription factors (0.2) HMGI(Y)(0.3) Pocket domain(0.6) Miscellaneoussee also transcription factor/coregulator deficiencies
B bsyn: dna (repl, cycl, reco, repr) · tscr (fact, tcrg, nucl, rnat, rept, ptts) · tltn (risu, pttl, nexn) · dnab, rnab/runp · stru (domn, 1°, 2°, 3°, 4°)Categories:- Human proteins
- Transcription factors
- Chromosome 8 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.