- DBP (gene)
-
D site of albumin promoter (albumin D-box) binding protein Identifiers Symbols DBP; DABP External IDs OMIM: 124097 MGI: 94866 HomoloGene: 1035 GeneCards: DBP Gene Gene Ontology Molecular function • sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factor activity
• sequence-specific DNA binding
• protein dimerization activityCellular component • nucleus Biological process • regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
• regulation of cell proliferation
• rhythmic processSources: Amigo / QuickGO RNA expression pattern 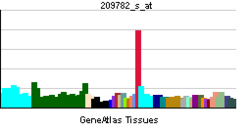
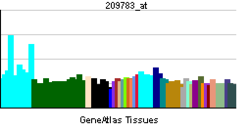
More reference expression data Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 1628 13170 Ensembl ENSG00000105516 ENSMUSG00000059824 UniProt Q10586 Q3USN7 RefSeq (mRNA) NM_001352 NM_016974.3 RefSeq (protein) NP_001343 NP_058670.2 Location (UCSC) Chr 19:
49.13 – 49.14 MbChr 7:
52.96 – 52.97 MbPubMed search [1] [2] D site of albumin promoter (albumin D-box) binding protein, also known as DBP, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the DBP gene.[1][2]
DBP is a member of the PAR bZIP (Proline and Acidic amino acid-Rich basic leucine ZIPper) transcription factor family.[3][1] DBP binds to a upstream promoter in the insulin gene.[4] Further, it may also regulate the HIF-1, one of the hypoxia inducible factors. [5]
References
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: DBP D site of albumin promoter (albumin D-box) binding protein". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=1628.
- ^ Szpirer C, Riviere M, Cortese R, Nakamura T, Islam MQ, Levan G, Szpirer J (June 1992). "Chromosomal localization in man and rat of the genes encoding the liver-enriched transcription factors C/EBP, DBP, and HNF1/LFB-1 (CEBP, DBP, and transcription factor 1, TCF1, respectively) and of the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor gene (HGF)". Genomics 13 (2): 293–300. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(92)90245-N. PMID 1535333. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/0888-7543(92)90245-N.
- ^ Khatib ZA, Inaba T, Valentine M, Look AT (September 1994). "Chromosomal localization and cDNA cloning of the human DBP and TEF genes". Genomics 23 (2): 344–51. doi:10.1006/geno.1994.1510. PMID 7835883.
- ^ Melloul D, Marshak S, Cerasi E (March 2002). "Regulation of insulin gene transcription". Diabetologia 45 (3): 309–26. doi:10.1007/s00125-001-0728-y. PMID 11914736.
- ^ Sethunarayanan SR (July 2011). "D-site of albumin promoter binding protein (DBP) may regulate hematopoiesis". Biology and Medicine 3 (3): 32–69. http://biolmedonline.com/Articles/Vol3_3_2011/Vol3_3_32-69.pdf.
Further reading
- Brown SA, Schibler U (1999). "The ins and outs of circadian timekeeping". Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 9 (5): 588–94. doi:10.1016/S0959-437X(99)00009-X. PMID 10508692.
- Szpirer C, Riviere M, Cortese R, et al. (1992). "Chromosomal localization in man and rat of the genes encoding the liver-enriched transcription factors C/EBP, DBP, and HNF1/LFB-1 (CEBP, DBP, and transcription factor 1, TCF1, respectively) and of the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor gene (HGF)". Genomics 13 (2): 293–300. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(92)90245-N. PMID 1535333.
- Khatib ZA, Inaba T, Valentine M, Look AT (1995). "Chromosomal localization and cDNA cloning of the human DBP and TEF genes". Genomics 23 (2): 344–51. doi:10.1006/geno.1994.1510. PMID 7835883.
- Nyunoya H, Morita T, Sato T, et al. (1994). "Cloning of a cDNA encoding a DNA-binding protein TAXREB302 that is specific for the tax-responsive enhancer of HTLV-I". Gene 148 (2): 371–3. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90716-1. PMID 7958972.
- Nyunoya H, Morita T, Sato T, et al. (1993). "Cloning of a cDNA encoding a DNA-binding protein TAXREB302 that is specific for the tax-responsive enhancer of HTLV-I". Gene 126 (2): 251–5. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(93)90375-D. PMID 8482542.
- Picketts DJ, Lillicrap DP, Mueller CR (1993). "Synergy between transcription factors DBP and C/EBP compensates for a haemophilia B Leyden factor IX mutation". Nat. Genet. 3 (2): 175–9. doi:10.1038/ng0293-175. PMID 8499951.
- Andersson B, Wentland MA, Ricafrente JY, et al. (1996). "A "double adaptor" method for improved shotgun library construction". Anal. Biochem. 236 (1): 107–13. doi:10.1006/abio.1996.0138. PMID 8619474.
- Shutler G, Glassco T, Kang X, et al. (1996). "Genomic structure of the human D-site binding protein (DBP) gene". Genomics 34 (3): 334–9. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.0295. PMID 8786133.
- Stubbs L, Carver E, Ashworth L, Lopez-Molina L (1997). "Location of the DBP transcription factor gene in human and mouse". Mamm. Genome 7 (1): 65–7. doi:10.1007/s003359900016. PMID 8903733.
- Yu W, Andersson B, Worley KC, et al. (1997). "Large-scale concatenation cDNA sequencing". Genome Res. 7 (4): 353–8. doi:10.1101/gr.7.4.353. PMC 139146. PMID 9110174. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139146.
- Begbie M, Mueller C, Lillicrap D (1999). "Enhanced binding of HLF/DBP heterodimers represents one mechanism of PAR protein transactivation of the factor VIII and factor IX genes". DNA Cell Biol. 18 (2): 165–73. doi:10.1089/104454999315556. PMID 10073576.
- Lamprecht C, Mueller CR (1999). "D-site binding protein transactivation requires the proline- and acid-rich domain and involves the coactivator p300". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (25): 17643–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.25.17643. PMID 10364202.
- Yan L, Miyake S, Okamura H (2000). "Distribution and circadian expression of dbp in SCN and extra-SCN areas in the mouse brain". J. Neurosci. Res. 59 (2): 291–5. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(20000115)59:2<291::AID-JNR16>3.0.CO;2-O. PMID 10650888.
- Smith JS, Tachibana I, Pohl U, et al. (2000). "A transcript map of the chromosome 19q-arm glioma tumor suppressor region". Genomics 64 (1): 44–50. doi:10.1006/geno.1999.6101. PMID 10708517.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139241.
- Newman JR, Keating AE (2003). "Comprehensive identification of human bZIP interactions with coiled-coil arrays". Science 300 (5628): 2097–101. doi:10.1126/science.1084648. PMID 12805554.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=528928.
- Sethunarayanan SR (2011). "D-site of albumin promoter binding protein may regulate hematopoiesis". Biol. Med. 3 (3): 32–69. http://biolmedonline.com/Articles/Vol3_3_2011/Vol3_3_32-69.pdf.
External links
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
Transcription factors and intracellular receptors (1) Basic domains (1.1) Basic leucine zipper (bZIP)Activating transcription factor (AATF, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) · AP-1 (c-Fos, FOSB, FOSL1, FOSL2, c-Jun, JUNB, JUND) · BACH (1, 2) · BATF · BLZF1 · C/EBP (α, β, γ, δ, ε, ζ) · CREB (1, 3, L1) · CREM · DBP · DDIT3 · GABPA · HLF · MAF (B, F, G, K) · NFE (2, L1, L2, L3) · NFIL3 · NRL · NRF (1, 2, 3) · XBP1(1.2) Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)ATOH1 · AhR · AHRR · ARNT · ASCL1 · BHLHB2 · BMAL (ARNTL, ARNTL2) · CLOCK · EPAS1 · FIGLA · HAND (1, 2) · HES (5, 6) · HEY (1, 2, L) · HES1 · HIF (1A, 3A) · ID (1, 2, 3, 4) · LYL1 · MESP2 · MXD4 · MYCL1 · MYCN · Myogenic regulatory factors (MyoD, Myogenin, MYF5, MYF6) · Neurogenins (1, 2, 3) · NeuroD (1, 2) · NPAS (1, 2, 3) · OLIG (1, 2) · Pho4 · Scleraxis · SIM (1, 2) · TAL (1, 2) · Twist · USF1(1.3) bHLH-ZIP(1.4) NF-1(1.5) RF-X(1.6) Basic helix-span-helix (bHSH)(2) Zinc finger DNA-binding domains (2.1) Nuclear receptor (Cys4)subfamily 1 (Thyroid hormone (α, β), CAR, FXR, LXR (α, β), PPAR (α, β/δ, γ), PXR, RAR (α, β, γ), ROR (α, β, γ), Rev-ErbA (α, β), VDR)
subfamily 2 (COUP-TF (I, II), Ear-2, HNF4 (α, γ), PNR, RXR (α, β, γ), Testicular receptor (2, 4), TLX)
subfamily 3 (Steroid hormone (Androgen, Estrogen (α, β), Glucocorticoid, Mineralocorticoid, Progesterone), Estrogen related (α, β, γ))
subfamily 4 NUR (NGFIB, NOR1, NURR1) · subfamily 5 (LRH-1, SF1) · subfamily 6 (GCNF) · subfamily 0 (DAX1, SHP)(2.2) Other Cys4(2.3) Cys2His2General transcription factors (TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE (1, 2), TFIIF (1, 2), TFIIH (1, 2, 4, 2I, 3A, 3C1, 3C2))
ATBF1 · BCL (6, 11A, 11B) · CTCF · E4F1 · EGR (1, 2, 3, 4) · ERV3 · GFI1 · GLI-Krüppel family (1, 2, 3, REST, S2, YY1) · HIC (1, 2) · HIVEP (1, 2, 3) · IKZF (1, 2, 3) · ILF (2, 3) · KLF (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17) · MTF1 · MYT1 · OSR1 · PRDM9 · SALL (1, 2, 3, 4) · SP (1, 2, 4, 7, 8) · TSHZ3 · WT1 · Zbtb7 (7A, 7B) · ZBTB (16, 17, 20, 32, 33, 40) · zinc finger (3, 7, 9, 10, 19, 22, 24, 33B, 34, 35, 41, 43, 44, 51, 74, 143, 146, 148, 165, 202, 217, 219, 238, 239, 259, 267, 268, 281, 295, 300, 318, 330, 346, 350, 365, 366, 384, 423, 451, 452, 471, 593, 638, 644, 649, 655)(2.4) Cys6(2.5) Alternating composition(3) Helix-turn-helix domains (3.1) HomeodomainARX · CDX (1, 2) · CRX · CUTL1 · DBX (1, 2) · DLX (3, 4, 5) · EMX2 · EN (1, 2) · FHL (1, 2, 3) · HESX1 · HHEX · HLX · Homeobox (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A7, A9, A10, A11, A13, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9, B13, C4, C5, C6, C8, C9, C10, C11, C13, D1, D3, D4, D8, D9, D10, D11, D12, D13) · HOPX · IRX (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, MKX) · LMX (1A, 1B) · MEIS (1, 2) · MEOX2 · MNX1 · MSX (1, 2) · NANOG · NKX (2-1, 2-2, 2-3, 2-5, 3-1, 3-2, 6-1, 6-2) · NOBOX · PBX (1, 2, 3) · PHF (1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 16, 17, 20, 21A) · PHOX (2A, 2B) · PITX (1, 2, 3) · POU domain (PIT-1, BRN-3: A, B, C, Octamer transcription factor: 1, 2, 3/4, 6, 7, 11) · OTX (1, 2) · PDX1 · SATB2 · SHOX2 · VAX1 · ZEB (1, 2)(3.2) Paired box(3.3) Fork head / winged helix(3.4) Heat Shock Factors(3.5) Tryptophan clusters(3.6) TEA domain(4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts (4.1) Rel homology region(4.2) STAT(4.3) p53(4.4) MADS box(4.6) TATA binding proteins(4.7) High-mobility group(4.10) Cold-shock domainCSDA, YBX1(4.11) Runt(0) Other transcription factors (0.2) HMGI(Y)(0.3) Pocket domain(0.6) Miscellaneoussee also transcription factor/coregulator deficiencies
B bsyn: dna (repl, cycl, reco, repr) · tscr (fact, tcrg, nucl, rnat, rept, ptts) · tltn (risu, pttl, nexn) · dnab, rnab/runp · stru (domn, 1°, 2°, 3°, 4°)Categories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 19 gene stubs
- Transcription factors
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
