- Estrogen receptor beta
-
See also: Estrogen receptor
Estrogen receptor beta (ER-β), also known as NR3A2 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group A, member 2), is a nuclear receptor which is activated by the sex hormone estrogen.[1] In humans, ER-β is encoded by the ESR2 gene.[2]
Contents
Function
Estrogen receptor β is a member of the family of estrogen receptors and the superfamily of nuclear receptor transcription factors. The gene product contains an N-terminal DNA binding domain and C-terminal ligand binding domain and is localized to the nucleus, cytoplasm, and mitochondria. Upon binding to 17-β-estradiol or related ligands, the encoded protein forms homo-dimers or hetero-dimers with estrogen receptor α that interact with specific DNA sequences to activate transcription. Some isoforms dominantly inhibit the activity of other estrogen receptor family members. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described, but the full-length nature of some of these variants has not been fully characterized.[3]
ER-β may have anti-proliferative effects and therefore oppose the actions of ER-α in reproductive tissue.[4] ER-β may also have an important role in adaptive function of the lung during pregnancy.[5]
Estrogen receptor β is a potent tumor suppressor and plays a crucial role in many cancer types such as prostate cancer.[6]
Tissue Distribution
ER-β is expressed by many tissues including blood monocytes and tissue macrophages, colonic and pulmonary epithelial cells and in prostatic epithelium and in malignant counterparts of these tissues. Also, ER-β is found throughout the brain at different concentrations in different neuron clusters.[7][8]
Interactions
Estrogen receptor beta has been shown to interact with:
- Estrogen receptor alpha[9][10]
- NCOA3,[11][12]
- NCOA6,[13][14]
- MAD2L1,[10]
- RBM39,[15] and
- Src.[16][17]
References
- ^ Kuiper GG, Enmark E, Pelto-Huikko M, Nilsson S, Gustafsson JA (June 1996). "Cloning of a novel receptor expressed in rat prostate and ovary". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93 (12): 5925–30. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.12.5925. PMC 39164. PMID 8650195. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=39164.
- ^ Mosselman S, Polman J, Dijkema R (August 1996). "ER beta: identification and characterization of a novel human estrogen receptor". FEBS Lett. 392 (1): 49–53. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(96)00782-X. PMID 8769313.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: ESR2 estrogen receptor 2 (ER beta)". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=2100.
- ^ Weihua Z, Saji S, Mäkinen S, Cheng G, Jensen EV, Warner M, Gustafsson JA (2000). "Estrogen receptor (ER) β, a modulator of ERα in the uterus". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (11): 5936–41. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.11.5936. PMC 18537. PMID 10823946. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=18537.
- ^ Carey MA, Card JW, Voltz JW, Germolec DR, Korach KS, Zeldin DC (2007). "The impact of sex and sex hormones on lung physiology and disease: lessons from animal studies". Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 293 (2): L272–8. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00174.2007. PMID 17575008.
- ^ Stettner M, Kaulfuss S, Burfeind P, Schweyer S, Strauss A, Ringert RH, Thelen P (2007). "The relevance of estrogen receptor-beta expression to the antiproliferative effects observed with histone deacetylase inhibitors and phytoestrogens in prostate cancer treatment". Mol Cancer Ther 5 (10): 2626–33. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0197. PMID 17913855.
- ^ Couse JF, Lindzey J, Grandien K, Gustafsson JA, Korach KS (1997). "Tissue distribution and quantitative analysis of estrogen receptor-alpha (ERα) and estrogen receptor-beta (ERβ) messenger ribonucleic acid in the wild-type and ERα-knockout mouse". Endocrinology 138 (11): 4613–21. doi:10.1210/en.138.11.4613. PMID 9348186.
- ^ Koehler KF, Helguero LA, Haldosén LA, Warner M, Gustafsson JA (2005). "Reflections on the discovery and significance of estrogen receptor β". Endocr. Rev. 26 (3): 465–78. doi:10.1210/er.2004-0027. PMID 15857973.
- ^ Ogawa S, Inoue S, Watanabe T, Hiroi H, Orimo A, Hosoi T, Ouchi Y, Muramatsu M (February 1998). "The complete primary structure of human estrogen receptor beta (hER beta) and its heterodimerization with ER alpha in vivo and in vitro". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 243 (1): 122–6. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.7893. PMID 9473491.
- ^ a b Poelzl G, Kasai Y, Mochizuki N, Shaul PW, Brown M, Mendelsohn ME (March 2000). "Specific association of estrogen receptor β with the cell cycle spindle assembly checkpoint protein, MAD2". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (6): 2836–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.050580997. PMC 16016. PMID 10706629. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=16016.
- ^ Wong CW, Komm B, Cheskis BJ (June 2001). "Structure-function evaluation of ER alpha and beta interplay with SRC family coactivators. ER selective ligands". Biochemistry 40 (23): 6756–65. doi:10.1021/bi010379h. PMID 11389589.
- ^ Leo C, Li H, Chen JD (February 2000). "Differential mechanisms of nuclear receptor regulation by receptor-associated coactivator 3". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (8): 5976–82. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.8.5976. PMID 10681591.
- ^ Lee SK, Jung SY, Kim YS, Na SY, Lee YC, Lee JW (February 2001). "Two distinct nuclear receptor-interaction domains and CREB-binding protein-dependent transactivation function of activating signal cointegrator-2". Mol. Endocrinol. 15 (2): 241–54. doi:10.1210/me.15.2.241. PMID 11158331.
- ^ Ko L, Cardona GR, Iwasaki T, Bramlett KS, Burris TP, Chin WW (January 2002). "Ser-884 adjacent to the LXXLL motif of coactivator TRBP defines selectivity for ERs and TRs". Mol. Endocrinol. 16 (1): 128–40. doi:10.1210/me.16.1.128. PMID 11773444.
- ^ Jung DJ, Na SY, Na DS, Lee JW (January 2002). "Molecular cloning and characterization of CAPER, a novel coactivator of activating protein-1 and estrogen receptors". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (2): 1229–34. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110417200. PMID 11704680.
- ^ Migliaccio A, Castoria G, Di Domenico M, de Falco A, Bilancio A, Lombardi M, Barone MV, Ametrano D, Zannini MS, Abbondanza C, Auricchio F (October 2000). "Steroid-induced androgen receptor–oestradiol receptor β–Src complex triggers prostate cancer cell proliferation". EMBO J. 19 (20): 5406–17. doi:10.1093/emboj/19.20.5406. PMC 314017. PMID 11032808. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=314017.
- ^ Slentz-Kesler K, Moore JT, Lombard M, Zhang J, Hollingsworth R, Weiner MP (October 2000). "Identification of the human Mnk2 gene (MKNK2) through protein interaction with estrogen receptor beta". Genomics 69 (1): 63–71. doi:10.1006/geno.2000.6299. PMID 11013076.
Further reading
- Pettersson K, Gustafsson JA (2001). "Role of estrogen receptor beta in estrogen action". Annu. Rev. Physiol. 63: 165–92. doi:10.1146/annurev.physiol.63.1.165. PMID 11181953.
- Warner M, Saji S, Gustafsson JA (2004). "The normal and malignant mammary gland: a fresh look with ER beta onboard". Journal of mammary gland biology and neoplasia 5 (3): 289–94. doi:10.1023/A:1009598828267. PMID 14973391.
- Saxon LK, Turner CH (2005). "Estrogen receptor beta: the antimechanostat?". Bone 36 (2): 185–92. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2004.08.003. PMID 15780944.
- Halachmi S, Marden E, Martin G et al. (1994). "Estrogen receptor-associated proteins: possible mediators of hormone-induced transcription". Science 264 (5164): 1455–8. doi:10.1126/science.8197458. PMID 8197458.
- Schwabe JW, Chapman L, Finch JT, Rhodes D (1993). "The crystal structure of the estrogen receptor DNA-binding domain bound to DNA: how receptors discriminate between their response elements". Cell 75 (3): 567–78. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(93)90390-C. PMID 8221895.
- Chen H, Lin RJ, Schiltz RL et al. (1997). "Nuclear receptor coactivator ACTR is a novel histone acetyltransferase and forms a multimeric activation complex with P/CAF and CBP/p300". Cell 90 (3): 569–80. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80516-4. PMID 9267036.
- Pace P, Taylor J, Suntharalingam S et al. (1997). "Human estrogen receptor beta binds DNA in a manner similar to and dimerizes with estrogen receptor alpha". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (41): 25832–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.41.25832. PMID 9325313.
- Brandenberger AW, Tee MK, Lee JY et al. (1997). "Tissue distribution of estrogen receptors alpha (ER-alpha) and beta (ER-beta) mRNA in the midgestational human fetus". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 82 (10): 3509–12. doi:10.1210/jc.82.10.3509. PMID 9329394.
- Enmark E, Pelto-Huikko M, Grandien K et al. (1998). "Human estrogen receptor beta-gene structure, chromosomal localization, and expression pattern". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 82 (12): 4258–65. doi:10.1210/jc.82.12.4258. PMID 9398750.
- Vladusic EA, Hornby AE, Guerra-Vladusic FK, Lupu R (1998). "Expression of estrogen receptor beta messenger RNA variant in breast cancer". Cancer Res. 58 (2): 210–4. PMID 9443393.
- Ogawa S, Inoue S, Watanabe T et al. (1998). "The complete primary structure of human estrogen receptor beta (hER beta) and its heterodimerization with ER alpha in vivo and in vitro". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 243 (1): 122–6. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.7893. PMID 9473491.
- Alves SE, Lopez V, McEwen BS, Weiland NG (1998). "Differential colocalization of estrogen receptor β (ERβ) with oxytocin and vasopressin in the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei of the female rat brain: An immunocytochemical study". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95 (6): 3281–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.6.3281. PMC 19733. PMID 9501254. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=19733.
- Brandenberger AW, Tee MK, Jaffe RB (1998). "Estrogen receptor alpha (ER-alpha) and beta (ER-beta) mRNAs in normal ovary, ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma and ovarian cancer cell lines: down-regulation of ER-beta in neoplastic tissues". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 83 (3): 1025–8. doi:10.1210/jc.83.3.1025. PMID 9506768.
- Moore JT, McKee DD, Slentz-Kesler K et al. (1998). "Cloning and characterization of human estrogen receptor beta isoforms". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 247 (1): 75–8. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1998.8738. PMID 9636657.
- Ogawa S, Inoue S, Watanabe T et al. (1998). "Molecular cloning and characterization of human estrogen receptor betacx: a potential inhibitor ofestrogen action in human". Nucleic Acids Res. 26 (15): 3505–12. doi:10.1093/nar/26.15.3505. PMC 147730. PMID 9671811. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=147730.
- Lu B, Leygue E, Dotzlaw H et al. (1998). "Estrogen receptor-beta mRNA variants in human and murine tissues". Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 138 (1–2): 199–203. doi:10.1016/S0303-7207(98)00050-1. PMID 9685228.
- Seol W, Hanstein B, Brown M, Moore DD (1998). "Inhibition of estrogen receptor action by the orphan receptor SHP (short heterodimer partner)". Mol. Endocrinol. 12 (10): 1551–7. doi:10.1210/me.12.10.1551. PMID 9773978.
- Hanstein B, Liu H, Yancisin MC, Brown M (1999). "Functional analysis of a novel estrogen receptor-beta isoform". Mol. Endocrinol. 13 (1): 129–37. doi:10.1210/me.13.1.129. PMID 9892018.
- Vidal O, Kindblom LG, Ohlsson C (1999). "Expression and localization of estrogen receptor-beta in murine and human bone". J. Bone Miner. Res. 14 (6): 923–9. doi:10.1359/jbmr.1999.14.6.923. PMID 10352100.
External links
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
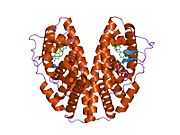
PDB gallery 1hj1: RAT OESTROGEN RECEPTOR BETA LIGAND-BINDING DOMAIN IN COMPLEX WITH PURE ANTIOESTROGEN ICI164,3841l2j: Human Estrogen Receptor beta Ligand-binding Domain in Complex with (R,R)-5,11-cis-diethyl-5,6,11,12-tetrahydrochrysene-2,8-diol1nde: Estrogen Receptor beta with Selective Triazine Modulator1qkm: HUMAN OESTROGEN RECEPTOR BETA LIGAND-BINDING DOMAIN IN COMPLEX WITH PARTIAL AGONIST GENISTEIN1qkn: RAT OESTROGEN RECEPTOR BETA LIGAND-BINDING DOMAIN IN COMPLEX WITH ANTAGONIST RALOXIFENE1u3q: Crystal Structure of Estrogen Receptor beta complexed with CL-2721u3r: Crystal Structure of Estrogen Receptor beta complexed with WAY-3381u3s: Crystal Structure of Estrogen Receptor beta complexed with WAY-7971u9e: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF ESTROGEN RECEPTOR BETA COMPLEXED WITH WAY-3971x76: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF ESTROGEN RECEPTOR BETA COMPLEXED WITH WAY-6971x78: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF ESTROGEN RECEPTOR BETA COMPLEXED WITH WAY-2441x7b: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF ESTROGEN RECEPTOR BETA COMPLEXED WITH ERB-0411x7j: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF ESTROGEN RECEPTOR BETA COMPLEXED WITH GENISTEIN1yy4: Crystal structure of estrogen receptor beta complexed with 1-chloro-6-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-naphthalen-2-ol1yye: Crystal structure of estrogen receptor beta complexed with way-2021961zaf: Crystal structure of estrogen receptor beta complexed with 3-Bromo-6-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-inden-1-one2fsz: A second binding site for hydroxytamoxifen within the coactivator-binding groove of estrogen receptor beta2giu: Human estrogen receptor beta ligand-binding domain in complex with compound 452i0g: Benzopyrans are Selective Estrogen Receptor beta Agonists (SERBAs) with Novel Activity in Models of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia2j7x: STRUCTURE OF ESTRADIOL-BOUND ESTROGEN RECEPTOR BETA LBD IN COMPLEX WITH LXXLL MOTIF FROM NCOA52j7y: STRUCTURE OF 17-EPIESTRIOL-BOUND ESTROGEN RECEPTOR BETA LBD IN COMPLEX WITH LXXLL MOTIF FROM NCOA5Transcription factors and intracellular receptors (1) Basic domains (1.1) Basic leucine zipper (bZIP)Activating transcription factor (AATF, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) · AP-1 (c-Fos, FOSB, FOSL1, FOSL2, JDP2, c-Jun, JUNB, JUND) · BACH (1, 2) · BATF · BLZF1 · C/EBP (α, β, γ, δ, ε, ζ) · CREB (1, 3, L1) · CREM · DBP · DDIT3 · GABPA · HLF · MAF (B, F, G, K) · NFE (2, L1, L2, L3) · NFIL3 · NRL · NRF (1, 2, 3) · XBP1(1.2) Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)ATOH1 · AhR · AHRR · ARNT · ASCL1 · BHLHB2 · BMAL (ARNTL, ARNTL2) · CLOCK · EPAS1 · FIGLA · HAND (1, 2) · HES (5, 6) · HEY (1, 2, L) · HES1 · HIF (1A, 3A) · ID (1, 2, 3, 4) · LYL1 · MESP2 · MXD4 · MYCL1 · MYCN · Myogenic regulatory factors (MyoD, Myogenin, MYF5, MYF6) · Neurogenins (1, 2, 3) · NeuroD (1, 2) · NPAS (1, 2, 3) · OLIG (1, 2) · Pho4 · Scleraxis · SIM (1, 2) · TAL (1, 2) · Twist · USF1(1.3) bHLH-ZIP(1.4) NF-1(1.5) RF-X(1.6) Basic helix-span-helix (bHSH)(2) Zinc finger DNA-binding domains (2.1) Nuclear receptor (Cys4)subfamily 1 (Thyroid hormone (α, β), CAR, FXR, LXR (α, β), PPAR (α, β/δ, γ), PXR, RAR (α, β, γ), ROR (α, β, γ), Rev-ErbA (α, β), VDR)
subfamily 2 (COUP-TF (I, II), Ear-2, HNF4 (α, γ), PNR, RXR (α, β, γ), Testicular receptor (2, 4), TLX)
subfamily 3 (Steroid hormone (Androgen, Estrogen (α, β), Glucocorticoid, Mineralocorticoid, Progesterone), Estrogen related (α, β, γ))
subfamily 4 NUR (NGFIB, NOR1, NURR1) · subfamily 5 (LRH-1, SF1) · subfamily 6 (GCNF) · subfamily 0 (DAX1, SHP)(2.2) Other Cys4(2.3) Cys2His2General transcription factors (TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE (1, 2), TFIIF (1, 2), TFIIH (1, 2, 4, 2I, 3A, 3C1, 3C2))
ATBF1 · BCL (6, 11A, 11B) · CTCF · E4F1 · EGR (1, 2, 3, 4) · ERV3 · GFI1 · GLI-Krüppel family (1, 2, 3, REST, S2, YY1) · HIC (1, 2) · HIVEP (1, 2, 3) · IKZF (1, 2, 3) · ILF (2, 3) · KLF (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17) · MTF1 · MYT1 · OSR1 · PRDM9 · SALL (1, 2, 3, 4) · SP (1, 2, 4, 7, 8) · TSHZ3 · WT1 · Zbtb7 (7A, 7B) · ZBTB (16, 17, 20, 32, 33, 40) · zinc finger (3, 7, 9, 10, 19, 22, 24, 33B, 34, 35, 41, 43, 44, 51, 74, 143, 146, 148, 165, 202, 217, 219, 238, 239, 259, 267, 268, 281, 295, 300, 318, 330, 346, 350, 365, 366, 384, 423, 451, 452, 471, 593, 638, 644, 649, 655)(2.4) Cys6(2.5) Alternating composition(3) Helix-turn-helix domains (3.1) HomeodomainARX · CDX (1, 2) · CRX · CUTL1 · DBX (1, 2) · DLX (3, 4, 5) · EMX2 · EN (1, 2) · FHL (1, 2, 3) · HESX1 · HHEX · HLX · Homeobox (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A7, A9, A10, A11, A13, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9, B13, C4, C5, C6, C8, C9, C10, C11, C12, C13, D1, D3, D4, D8, D9, D10, D11, D12, D13) · HOPX · IRX (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, MKX) · LMX (1A, 1B) · MEIS (1, 2) · MEOX2 · MNX1 · MSX (1, 2) · NANOG · NKX (2-1, 2-2, 2-3, 2-5, 3-1, 3-2, 6-1, 6-2) · NOBOX · PBX (1, 2, 3) · PHF (1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 16, 17, 20, 21A) · PHOX (2A, 2B) · PITX (1, 2, 3) · POU domain (PIT-1, BRN-3: A, B, C, Octamer transcription factor: 1, 2, 3/4, 6, 7, 11) · OTX (1, 2) · PDX1 · SATB2 · SHOX2 · VAX1 · ZEB (1, 2)(3.2) Paired box(3.3) Fork head / winged helix(3.4) Heat Shock Factors(3.5) Tryptophan clusters(3.6) TEA domain(4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts (4.1) Rel homology region(4.2) STAT(4.3) p53(4.4) MADS box(4.6) TATA binding proteins(4.7) High-mobility group(4.10) Cold-shock domainCSDA, YBX1(4.11) Runt(0) Other transcription factors (0.2) HMGI(Y)(0.3) Pocket domain(0.6) MiscellaneousCategories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 14 gene stubs
- Intracellular receptors
- Transcription factors
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.