- Estrone
-
Estrone 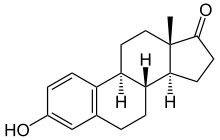
Systematic (IUPAC) name 3-hydroxy-13-methyl- 6,7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16- decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren- 17- one Clinical data Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status ? Pharmacokinetic data Protein binding >95% Half-life 19 hours Identifiers CAS number 53-16-7 
ATC code G03CA07 G03CC04 PubChem CID 5870 DrugBank DB00655 ChemSpider 5660 
UNII 2DI9HA706A 
KEGG D00067 
ChEBI CHEBI:17263 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1405 
Chemical data Formula C18H22O2 Mol. mass 270.366 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem Physical data Melt. point 254.5 °C (490 °F)  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Estrone (E1, and also oestrone) is an estrogenic hormone secreted by the ovary as well as adipose tissue.[1]
Estrone is one of several natural estrogens, which also include estriol and estradiol. Estrone is the least abundant of the three hormones; estradiol is present almost always in the reproductive female body, and estriol is abundant primarily during pregnancy.
Estrone is relevant to health and disease states because of its conversion to estrone sulfate, a long-lived derivative. Estrone sulfate acts as a reservoir that can be converted as needed to the more active estradiol.
Estrone is the predominant estrogen in postmenopausal women.[2]
Biosynthesis
Estrone is synthesized via aromatase from androstenedione, a derivative of progesterone. The conversion consists of the de-methylation of C-19 and the aromaticity of the 'A' ring. This reaction is similar to the conversion of testosterone to estradiol.
Additional images
References
- ^ "Estrone -PubChem". National Center for Biotechnology Information. http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=5870&loc=ec_rcs. Retrieved 2009-09-06.
- ^ Helen Varney, Jan M. Kriebs, Carolyn L. Gegor. Varney's midwifery, Fourth Edition. Jones and Bartlett Publishers, 2004, p. 340.
Estrogens and progestogens (G03C-D, L02) Progestogens/
progestins
(progesterone)AgonistAndrostene (Drospirenone) • 19-norprogesterone (Nomegestrol • Promegestone • Trimegestone) • 19-nortestosterone (Dienogest)Other/
ungroupedPregnenedione (Gestonorone) • Pregnene (Ethisterone) • Pregnadiene (Medrogestone • Melengestrol) • Norpregnane (Norgestrienone) • Lynestrenol • Norethynodrel • Tibolone • Dydrogesterone • Quingestanolantagonist: MifepristoneAsoprisnil • CDB-4124 • Ulipristal acetateEstrogens AgonistDiosgenin • Estradiol (Ethinylestradiol#/Mestranol • Estradiol 17 beta-cypionate# • Polyestradiol phosphate) • Estrone (Estrone sulfate) • Estriol • Promestriene • Equilenin • EquilinAfimoxifene • Arzoxifene • Bazedoxifene • Cyclofenil • Lasofoxifene • Ormeloxifene • Raloxifene • Tamoxifen • Toremifenepure antagonist: FulvestrantCholesterol and steroid metabolic intermediates Mevalonate pathway to HMG-CoAto DMAPPGeranyl-Prephytoene diphosphate · PhytoeneNon-mevalonate pathway To Cholesterol Farnesyl pyrophosphate · Squalene · 2,3-Oxidosqualene · Lanosterol
Lanosterol · Lathosterol · 7-Dehydrocholesterol · Cholesterol
Lanosterol · Zymosterol · 7-Dehydrodesmosterol · Desmosterol · CholesterolSteroid Corticosteroids
(C21 pregnane)Androgens
(C19 androstane)Estrogens
(C18 estrane)Nonhuman biochemical families: prot · nucl · carb (glpr, alco, glys) · lipd (fata/i, phld, strd, gllp, eico) · amac/i · ncbs/i · ttpy/iCategories:- Estrogens
- Biochemistry stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

