- Diosgenin
-
Diosgenin 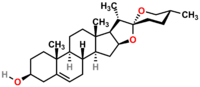
 (3β,25R)-spirost-5-en-3-ol
(3β,25R)-spirost-5-en-3-olIdentifiers CAS number 512-04-9 
PubChem 99474 ChemSpider 89870 
UNII K49P2K8WLX 
EC number 208-134-3 ChEMBL CHEMBL412437 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O1[C@@H]4[C@H]([C@@H]([C@]12OC[C@@H](CC2)C)C)[C@@]5(C)CC[C@@H]3[C@@]6(C(=C/C[C@H]3[C@@H]5C4)\C[C@@H](O)CC6)C
- InChI=1S/C27H42O3/c1-16-7-12-27(29-15-16)17(2)24-23(30-27)14-22-20-6-5-18-13-19(28)8-10-25(18,3)21(20)9-11-26(22,24)4/h5,16-17,19-24,28H,6-15H2,1-4H3/t16-,17+,19+,20-,21+,22+,23+,24+,25+,26+,27-/m1/s1

Key: WQLVFSAGQJTQCK-VKROHFNGSA-N
InChI=1/C27H42O3/c1-16-7-12-27(29-15-16)17(2)24-23(30-27)14-22-20-6-5-18-13-19(28)8-10-25(18,3)21(20)9-11-26(22,24)4/h5,16-17,19-24,28H,6-15H2,1-4H3/t16-,17+,19+,20-,21+,22+,23+,24+,25+,26+,27-/m1/s1
Key: WQLVFSAGQJTQCK-VKROHFNGBS
Properties Molecular formula C27H42O3 Molar mass 414.62 g mol−1  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Diosgenin, a steroid sapogenin, is the product of hydrolysis by acids, strong bases, or enzymes of saponins, extracted from the tubers of Dioscorea wild yam, such as the Kokoro. The sugar-free (aglycone), diosgenin is used for the commercial synthesis of cortisone, pregnenolone, progesterone, and other steroid products.
Contents
Sources
It is present in Costus speciosus, Smilax menispermoidea, species of Paris, Trigonella, and Trillium, and many species of Dioscorea - D. althaeoides, colletti, futschauensis, gracillima, hispida, hypoglauca, mexicana[1] nipponica, panthaica, parviflora, septemloba, and zingiberensis.[2]
Clinical uses
Diosgenin is the precursor for the semisynthesis of progesterone[3] which in turn was used in early combined oral contraceptive pills.[4] The unmodified steroid has estrogenic activity[5] and can reduce the level of serum cholesterol.[6]
Chemistry
Main article: Marker degradationThe glycoside dioscin from the Mexican wild yam root, Dioscorea, constituted the first plant source for steroid drugs.
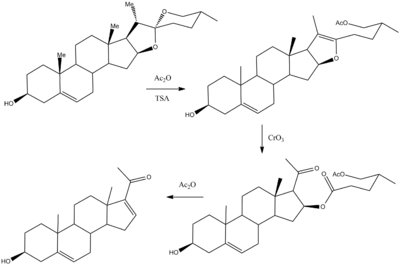
Hydrolysis of this saponin leads to scission of the trisaccharide at the 3-position and the formation of the aglycone, diosgenin. Treatment of this acetal with hot acetic anhydride in the presence of toluenesulfonic acid leads initially to protonation of one of the acetal oxygens followed by elimination to form an enol ether. Oxidation by means of chromium trioxide leads to preferential attack at the electron-rich enol ether double bond. In effect, this transformation converts the side chain at C-17 in diosgenin to the acetyl group required for many steroid drugs. Heating that intermediate in with alcoholic sodium hydroxide leads to the elimination of the ester grouping beta to the ketone; there is thus obtained 16-dehydropregnenolone acetate. The presence of the olefin at C-17 allows ready entry to C-19 androstanes and provides the necessary function for the synthesis of potent C-16- and C-16,17-substituted corticosteroids.
Marker, Russell E.; Wagner, R. B.; Ulshafer, Paul R.; Wittbecker, Emerson L.; Goldsmith, Dale P. J.; Ruof, Clarence H. (1947). "Steroidal sapogenins". Journal of the American Chemical Society 69 (9): 2167–2230. doi:10.1021/ja01201a032. PMID 20262743.
References
- ^ "Dioscorea mexicana information". Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN). United States Department of Agriculture. http://www.ars-grin.gov/cgi-bin/npgs/html/taxon.pl?14226. Retrieved 2008-09-14.
- ^ "2950 Diosgenin". http://tcm.cambridgesoft.com/tcm/showcompound.asp?monograph=2950&formgroup=basenp_form_group&dbname=TCM&formmode=edit. Retrieved 2007-05-29.
- ^ Marker RE, Krueger J (1940). "Sterols. CXII. Sapogenins. XLI. The Preparation of Trillin and its Conversion to Progesterone". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 62 (12): 3349–3350. doi:10.1021/ja01869a023.
- ^ Djerassi C (December 1992). "Steroid research at Syntex: "the pill" and cortisone". Steroids 57 (12): 631–41. doi:10.1016/0039-128X(92)90016-3. PMID 1481227.
- ^ Liu MJ, Wang Z, Ju Y, Wong RN, Wu QY (2005). "Diosgenin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human leukemia K562 cells with the disruption of Ca2+ homeostasis". Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 55 (1): 79–90. doi:10.1007/s00280-004-0849-3. PMID 15372201.
- ^ Cayen MN, Dvornik D (1979). "Effect of diosgenin on lipid metabolism in rats" (abstract page). J. Lipid Res. 20 (2): 162–74. PMID 438658. http://www.jlr.org/cgi/content/abstract/20/2/162.
External links
Categories:- Hormonal contraception
- Steroids
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.