- Arzoxifene
-
Arzoxifene 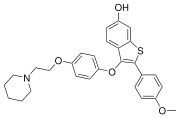 2-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-3-[4-(2-piperidin-1-ylethoxy)phenoxy]-1-benzothiophen-6-ol
2-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-3-[4-(2-piperidin-1-ylethoxy)phenoxy]-1-benzothiophen-6-olIdentifiers CAS number 182133-25-1 
PubChem 179337 ChemSpider 156104 
ChEMBL CHEMBL226267 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - COC1=CC=C(C=C1)C2=C(C3=C(S2) C=C(C=C3)O)OC4=CC=C(C=C4)OCCN5CCCCC5
Properties Molecular formula C28H29NO4S Molar mass 475.60 g/mol  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Arzoxifene is a selective estrogen receptor modulator.[1] It is a potent estrogen antagonist in mammary and uterine tissue while acting as an estrogen agonist to maintain bone density and lower serum cholesterol. Arzoxifene is a highly effective agent for prevention of mammary cancer induced in the rat by the carcinogen nitrosomethylurea and is significantly more potent than raloxifene in this regard. Arzoxifene is devoid of the uterotrophic effects of tamoxifen, suggesting that, in contrast to tamoxifen, it is unlikely that the clinical use of arzoxifene will increase the risk of developing endometrial carcinoma.
Clinical studies
In a phase 3 clinical study in postmenopausal women, arzoxifene was shown to increase bone spine and hip mineral density and had no effect on the uterus and endometrium.[2]
Lilly announced in August 2009 that preliminary results from a five year clinical study showed that arzoxifene met its primary endpoints of reduction in vertebral fractures and breast cancer in postmenopausal women. However arzoxifene failed to meet secondary endpoints of reduction in non-vertebral fractures and cardiovascular events and improvements in cognitive function. Based on these results, Lilly announced they are discontinuing further development of the drug and would not seek regulatory approval.[3]
Chemistry
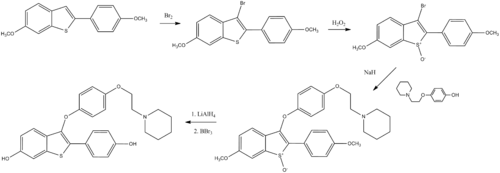
Palkowitz, Alan D.; Glasebrook, Andrew L.; Thrasher, K. Jeff; Hauser, Kenneth L.; Short, Lorri L.; Phillips, D. Lynn; Muehl, Brian S.; Sato, Masahiko et al. (1997). "Discovery and Synthesis of [6-Hydroxy-3-[4-[2-(1-piperidinyl)ethoxy]phenoxy]- 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)]benzo[b]thiophene: A Novel, Highly Potent, Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 40 (10): 1407–16. doi:10.1021/jm970167b. PMID 9154963.
References
- ^ Overk CR, Peng KW, Asghodom RT, et al. (2007). "Structure-activity relationships for a family of benzothiophene selective estrogen receptor modulators including raloxifene and arzoxifene". ChemMedChem 2 (10): 1520–6. doi:10.1002/cmdc.200700104. PMID 17654759.
- ^ Bolognese M, Krege JH, Utian WH, Feldman R, Broy S, Meats DL, Alam J, Lakshmanan M, Omizo M (July 2009). "Effects of arzoxifene on bone mineral density and endometrium in postmenopausal women with normal or low bone mass". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 94 (7): 2284–9. doi:10.1210/jc.2008-2143. PMID 19351734.
- ^ "Lilly Reports on Outcome of Phase III Study of Arzoxifene". Press Release. Eli Lilly and Company. 2009-08-18. http://newsroom.lilly.com/releasedetail.cfm?ReleaseID=403905. Retrieved 2009-08-24.

This pharmacology-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.