- Levonorgestrel
-
Levonorgestrel 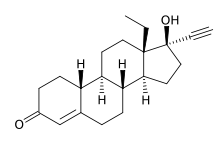

Systematic (IUPAC) name 13-ethyl-17-ethynyl-17-hydroxy- 1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16, 17- tetradecahydrocyclopenta[a] phenanthren-3-one Clinical data Trade names Norplant MedlinePlus a610021 Pregnancy cat. X Legal status ? Routes Implant; insert (extended-release); oral Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability ~100% Protein binding 55% Metabolism Hepatic via CYP3A4 Half-life 36 ± 13 hours Excretion Renal: 45%; Fecal:32% Identifiers CAS number 797-63-7 
ATC code G03AC03 G03AD01 PubChem CID 13109 DrugBank APRD00754 ChemSpider 12560 
UNII 5W7SIA7YZW 
KEGG D00950 
ChEBI CHEBI:6443 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1389 
Chemical data Formula C21H28O2 Mol. mass 312.446 g/mol  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Levonorgestrel (or l-norgestrel or D-norgestrel) is a second generation synthetic progestogen used as an active ingredient in some hormonal contraceptives.
Contents
Chemistry
Chemically, it is a hormonally active levorotatory enantiomer of the racemic mixture norgestrel. It is a gonane progestin derived from 19-nortestosterone.[1]
Its in vitro relative binding affinities at human steroid hormone receptors are: 323% that of progesterone at the progesterone receptor, 58% that of testosterone at the androgen receptor, 17% that of aldosterone at the mineralocorticoid receptor, 7.5% that of cortisol at the glucocorticoid receptor, and <0.02% that of estradiol at the estrogen receptor.[2]
If taken concommitantly with drugs that induce the CYP3A4 cytochrome liver enzyme, the levonorgestrel will be metabolized faster and have lower efficacy.(Citation?) A larger dose is required to maintain the high level of efficacy expected of a birth control medication.
Usage
Oral contraception
At low doses, levonorgestrel is used in monophasic and triphasic formulations of combined oral contraceptive pills, with available monophasic doses ranging from 100-250 µg, and triphasic doses of 50 µg/75 µg/125 µg.
At very low daily dose of 30 µg, levonorgestrel is used in some progestogen only pill formulations.
Emergency contraception
Levonorgestrel is used in emergency contraceptive pills (ECPs), both in a combined Yuzpe regimen which includes estrogen, and as a levonorgestrel-only method. The levonorgestrel-only method uses levonorgestrel 1500 μg (as a single dose or as two 750 μg doses 12 hours apart) taken within 3 days of unprotected sex, with one study indicating that beginning as late as 120 hours (5 days) after intercourse could be effective. There are many brand names of levonorgestrel-only ECPs, including: Escapelle, Plan B, Levonelle, NorLevo, Postinor-2, i-pill, "Next Choice" and 72-HOURS.[3]
Intrauterine system
Levonorgestrel is the active ingredient in the Mirena intrauterine system.
Contraceptive implants
Levonorgestrel is the active ingredient in Norplant and Jadelle.
Side effects
Possible side effects of levonorgestrel include nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, dizziness, breast tenderness, tiredness and weakness, headache, menstrual changes, and diarrhea.[4]
It decreases total and free testosterone, androstenedione, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS), dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and sex hormone–binding globulin (SHBG), but has no effect on sexual function or markers of androgen bioactivity.[5]
References
- ^ Edgren RA, Stanczyk FZ (1999). "Nomenclature of the gonane progestins". Contraception 60 (6): 313. doi:10.1016/S0010-7824(99)00101-8. PMID 10715364.
- ^ Sitruk-Ware R (2006). "New progestagens for contraceptive use". Hum Reprod Update 12 (2): 169–78. doi:10.1093/humupd/dmi046. PMID 16291771.
- ^ Trussell, James; Cleland, Kelly (2007-04-10). "Emergency Contraceptive Pills Worldwide". Princeton University. http://ec.princeton.edu/questions/dedicated.html. Retrieved 2007-05-28.
- ^ MedicineNet.com > LEVONORGESTREL - ORAL (lee-voh-nor-JEST-rell) Retrieved on April 3, 2010
- ^ Kovalevsky G, Ballagh SA, Stanczyk FZ, Lee J, Cooper J, Archer DF (April 2010). "Levonorgestrel effects on serum androgens, sex hormone-binding globulin levels, hair shaft diameter, and sexual function". Fertil. Steril. 93 (6): 1997–2003. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.12.095. PMID 19394598.
External links
- Levonelle manufacturer's product information from Schering
- Monograph for levonorgestrel - Uk Medicines Information
- U.S. National Library of Medicine: Drug Information Portal - Levonorgestrel
Estrogens and progestogens (G03C-D, L02) Progestogens/
progestins
(progesterone)AgonistAndrostene (Drospirenone) • 19-norprogesterone (Nomegestrol • Promegestone • Trimegestone) • 19-nortestosterone (Dienogest)Other/
ungroupedPregnenedione (Gestonorone) • Pregnene (Ethisterone) • Pregnadiene (Medrogestone • Melengestrol) • Norpregnane (Norgestrienone) • Lynestrenol • Norethynodrel • Tibolone • Dydrogesterone • Quingestanolantagonist: MifepristoneAsoprisnil • CDB-4124 • Ulipristal acetateEstrogens AgonistDiosgenin • Estradiol (Ethinylestradiol#/Mestranol • Estradiol 17 beta-cypionate# • Polyestradiol phosphate) • Estrone (Estrone sulfate) • Estriol • Promestriene • Equilenin • EquilinAfimoxifene • Arzoxifene • Bazedoxifene • Cyclofenil • Lasofoxifene • Ormeloxifene • Raloxifene • Tamoxifen • Toremifenepure antagonist: FulvestrantCategories:- Hormonal contraception
- Progestagens
- Enantiopure drugs
- Alkynes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
