- Dihydrotestosterone
-
Dihydrotestosterone 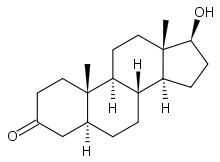
Systematic (IUPAC) name (5S,8R,9S,10S,13S,14S,17S)-17-hydroxy-10
,13-dimethyl-1,2,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17
-tetradecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one[citation needed]Clinical data Pregnancy cat. X Legal status ? Routes Intramuscular, transdermal Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability Oral 0-2% Metabolism Hepatic Excretion Renal Identifiers CAS number 521-18-6 
ATC code A14AA01 PubChem CID 10635 DrugBank DB02901 ChemSpider 10189 
UNII 08J2K08A3Y 
ChEBI CHEBI:16330 
ChEMBL CHEMBL27769 
Chemical data Formula C19H30O2 Mol. mass 290.442 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Dihydrotestosterone (5α-Dihydrotestosterone, commonly abbreviated to DHT) is an androgen or male sex hormone. The enzyme 5α-reductase synthesises DHT in the prostate, testes, hair follicles, and adrenal glands. This enzyme reduces the 4,5 double-bond of the hormone testosterone.
Contents
Effects on sexual development
In men, approximately 5% of testosterone undergoes 5α-reduction to form the more potent androgen, dihydrotestosterone. DHT has approximately three times greater affinity for androgen receptors than testosterone and has 15-30 times greater affinity than adrenal androgens.[1] During embryogenesis DHT has an essential role in the formation of the male external genitalia, while in the adult DHT acts as the primary androgen in the prostate and in hair follicles.[2]
An example illustrating the significance of DHT for the development of secondary sex characteristics is congenital 5-α-reductase (5-AR) deficiency. This gene lesion can result in pseudohermaphroditism. This condition typically presents with underdeveloped male genitalia and prostate. These individuals are often raised as girls due to their lack of conspicuous male genitalia. In the onset of puberty, although their DHT levels remain very low, their testosterone levels elevate normally. Their musculature develops like that of other adults. After puberty, men with this condition have a large deficiency of pubic and body hair, and no incidence of male pattern baldness.[3][4]
Unlike other androgens such as testosterone, DHT cannot be converted by the enzyme aromatase to estradiol. Therefore, it is frequently used in research settings to distinguish between the effects of testosterone caused by binding to the androgen receptor and those caused by testosterone's conversion to estradiol and subsequent binding to estrogen receptors.[5]
Pathology
DHT is the primary contributing factor in male pattern baldness.[6] However, female hair loss is more complex, and DHT is only one of several possible causes.[7] Women with increased levels of DHT may develop certain androgynous male secondary sex characteristics, including a deepened voice and facial hair. DHT plays a role in the development and exacerbation of benign prostatic hyperplasia, as well as prostate cancer, by enlarging the prostate gland.[8] Prostate growth and differentiation are highly dependent on sex steroid hormones, particularly DHT.[9]
Treatment
5α-reductase inhibitors are commonly used for the treatment of two DHT-related conditions, male pattern baldness (MPB), and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Dutasteride is approved for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia, and is prescribed off-label for the treatment of male pattern baldness, whereas finasteride is approved for both conditions. Dutasteride is three times more potent than finasteride in inhibiting the type II enzyme and 100 times more potent than finasteride in inhibiting the type I form of the DHT-producing enzyme.[10]
Metabolism
DHT is converted to 3α-Androstanediol and 3β-Androstanediol.[11]
See also
- Finasteride
- Dutasteride
- Male pattern baldness
- Management of baldness
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia
References
- ^ Principles of Orthomolecularism | Google books
- ^ National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) | The Effect of 5α-Reductase Inhibition With Dutasteride and Finasteride on Bone Mineral Density, Serum Lipoproteins, Hemoglobin, Prostate Specific Antigen and Sexual Function in Healthy Young Men
- ^ DHT | Is It All Bad? | Mesomorphosis.com
- ^ 5α-Reductase History and Clinical Importance | National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI)
- ^ Dihydrotestosterone: a rationale for its use as a non-aromatizable androgen replacement therapeutic agent
- ^ What Is DHT? What is its Role in Hair Loss? | Medical News TODAY
- ^ American Hair Loss Association | Women's Hair Loss / Causes of Hair Loss
- ^ Prostate Enlargement (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia | ehealthMD
- ^ Prostate Size and Risk of High-Grade, Advanced Prostate Cancer and Biochemical Progression After Radical Prostatectomy: A Search Database Study | Journal of Clinical Oncology
- ^ Update on Dutasteride | IAHRS Hair Transplant & Hair Loss Info Center
- ^ Fertil Steril. 1995 Oct;64(4):736-9. Metabolism of dihydrotestosterone to 5 alpha-androstane-3 alpha, 17 beta-diol glucuronide is greater in the peripheral compartment than in the splanchnic compartment. University of Southern California School of Medicine, Los Angeles, USA.
Cholesterol and steroid metabolic intermediates Mevalonate pathway to HMG-CoAto DMAPPGeranyl-Prephytoene diphosphate · PhytoeneNon-mevalonate pathway To Cholesterol Farnesyl pyrophosphate · Squalene · 2,3-Oxidosqualene · Lanosterol
Lanosterol · Lathosterol · 7-Dehydrocholesterol · Cholesterol
Lanosterol · Zymosterol · 7-Dehydrodesmosterol · Desmosterol · CholesterolSteroid DHEA · Androstenedione/5-Androstenediol · Testosterone · Dihydrotestosterone
DHEA sulfate · EpitestosteroneNonhuman biochemical families: prot · nucl · carb (glpr, alco, glys) · lipd (fata/i, phld, strd, gllp, eico) · amac/i · ncbs/i · ttpy/iCategories:- Androgens
- Biology of gender
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

