- Non-mevalonate pathway
-
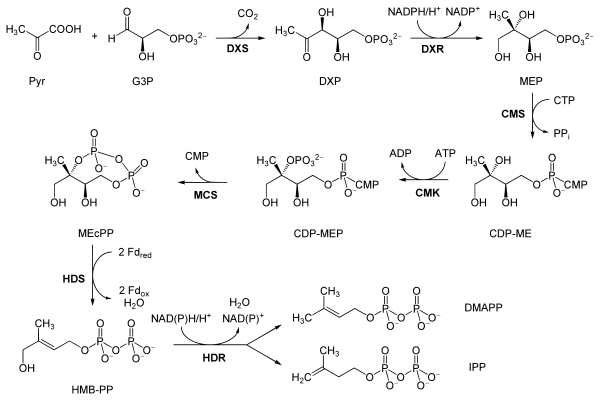
The non-mevalonate pathway or 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate/1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate pathway (MEP/DOXP pathway) of isoprenoid biosynthesis is an alternative metabolic pathway leading to the formation of isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP) that has been elucidated only recently.[1]
Contents
Diversity of isoprenoid biosynthesis
The classical mevalonate pathway or HMG-CoA reductase pathway is an important cellular metabolic pathway present in all higher eukaryotes and many bacteria. It is important for the production of IPP and DMAPP that serve as the basis for the biosynthesis of molecules used in processes as diverse as protein prenylation, cell membrane maintenance, hormones, protein anchoring and N-glycosylation.
In contrast to the classical mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis, plants and apicomplexan protozoa such as malaria parasites have the ability to produce their isoprenoids (terpenoids) using an alternative pathway, the non-mevalonate pathway, which takes place in their plastids.[2] In addition, most bacteria including important pathogens such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis synthesize IPP and DMAPP via the non-mevalonate pathway.
Reactions
The reactions are as follows:[3]
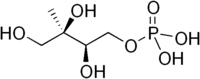
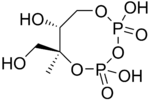
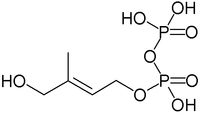
Reactants Enzyme Product Pyruvate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate DOXP synthase (Dxs) 1-Deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate (DOXP) DOXP DOXP reductase (Dxr, IspC) 2-C-methylerythritol 4-phosphate (MEP) MEP 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol synthase (YgbP, IspD) 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methylerythritol (CDP-ME) CDP-ME 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase (YchB, IspE) 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2-phosphate (CDP-MEP) CDP-MEP 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase (YgbB, IspF) 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclopyrophosphate (MEcPP) MEcPP HMB-PP synthase (GcpE, IspG) (E)-4-Hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate (HMB-PP) HMB-PP HMB-PP reductase (LytB, IspH) IPP and DMAPP
Inhibition
Fosmidomycin specifically inhibits DOXP reductoisomerase, a key enzyme in the non-mevalonate pathway, and therefore represents an attractive candidate as antibiotic or antimalarial drug.[4]
T cell activation
The intermediate HMB-PP is the natural activator for human Vγ9/Vδ2 T cells, the major γδ T cell population in peripheral blood.[5]
References
- ^ Rohmer M; Rohmer, Michel (1999). "The discovery of a mevalonate-independent pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis in bacteria, algae and higher plants". Nat Prod Rep 16 (5): 565–574. doi:10.1039/a709175c. PMID 10584331.
- ^ Lichtenthaler H (1999). "The 1-Deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis in plants". Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50: 47–65. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.50.1.47. PMID 15012203.
- ^ Eisenreich W, Bacher A, Arigoni D, Rohdich F. Biosynthesis of isoprenoids via the non-mevalonate pathway. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004;61:1401-1426. PMID 15197467
- ^ Jomaa H, Wiesner J, Sanderbrand S, Altincicek B, Weidemeyer C, Hintz M, Turbachova I, Eberl M, Zeidler J, Lichtenthaler HK, Soldati D, Beck E. Inhibitors of the nonmevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis as antimalarial drugs. Science 1999;285:1573-1576. PMID 10477522
- ^ Eberl M, Hintz M, Reichenberg A, Kollas AK, Wiesner J, Jomaa H. Microbial isoprenoid biosynthesis and human γδ T cell activation. FEBS Lett. 2003;544:4-10. PMID 12782281
Categories:- Metabolic pathways
- Cell biology
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.