- Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
-
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate 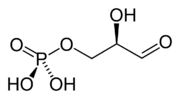
 2-hydroxy-3-oxopropyl dihydrogen phosphate
2-hydroxy-3-oxopropyl dihydrogen phosphateIdentifiers CAS number 142-10-9 PubChem 729 ChemSpider 709  , 393755 (L isomer), 388314 (D isomer)
, 393755 (L isomer), 388314 (D isomer)KEGG C00661 
MeSH Glyceraldehyde+3-Phosphate ChEBI CHEBI:17138 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=P(O)(O)OCC(O)C=O
Properties Molecular formula C3H7O6P Molar mass 170.058  3-phosphate (verify) (what is:
3-phosphate (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, also known as triose phosphate or 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde and abbreviated as G3P, GADP, GAP, TP, GALP or PGAL, is a chemical compound that occurs as an intermediate in several central metabolic pathways of all organisms. It is a phosphate ester of the 3-carbon sugar glyceraldehyde and has chemical formula C3H7O6P.
The CAS number of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is 142-10-9 and that of D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (one of the two optical isomers of the compound and the one most often occurring in living organisms) is 591-57-1.
Contents
An intermediate in both glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
Formation
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is formed from the following three compounds in reversible reactions:
- Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (F1,6BP), catalyzed by aldolase.
β-D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate fructose bisphosphate aldolase D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dihydroxyacetone phosphate 

+ 

fructose bisphosphate aldolase Compound C05378 at KEGG Pathway Database. Enzyme 4.1.2.13 at KEGG Pathway Database. Compound C00111 at KEGG Pathway Database. Compound C00118 at KEGG Pathway Database.
The numbering of the carbon atoms indicates the fate of the carbons according to their position in fructose 6-phosphate.
- Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP), catalyzed by triose phosphate isomerase.
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate triose phosphate isomerase D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate 


triose phosphate isomerase Compound C00111 at KEGG Pathway Database.Enzyme 5.3.1.1 at KEGG Pathway Database.Compound C00118 at KEGG Pathway Database.
- 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (1,3BPG), catalyzed by glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
As a substrate
- To produce 1,3-bisphospho-D-glycerate in glycolysis.
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase D-glycerate 1,3-bisphosphate 

NAD+ + Pi NADH + H+ 
NAD+ + Pi NADH + H+ Compound C00118 at KEGG Pathway Database. Enzyme 1.2.1.12 at KEGG Pathway Database. Reaction R01063 at KEGG Pathway Database. Compound C00236 at KEGG Pathway Database.
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is also of some importance since this is how glycerol (as DHAP) enters the glycolytic and gluconeogenetic pathways. Furthermore, it is a participant in and a product of the pentose phosphate pathway.
An intermediate in photosynthesis
During plant photosynthesis, 2 molecules of glycerate 3-phosphate (GP; also known as 3-phosphoglycerate) are produced by the first step of the light-independent reactions when ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) and carbon dioxide are catalysed by the rubisco enzyme. The GP is converted to D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) using the energy in ATP and the reducing power of NADPH as part of the Calvin cycle. This returns ADP, phosphate ions Pi, and NADP+ to the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis for their continued function. RuBP is regenerated for the Calvin cycle to continue.
G3P is generally considered the prime end-product of photosynthesis and it can be used as an immediate food nutrient, combined and rearranged to form monosaccharide sugars, such as glucose, which can be transported to other cells, or packaged for storage as insoluble polysaccharides such as starch.
Balance sheet
6 CO2 + 6 RuBP (+ energy from 12 ATP and 12 NADPH) →12 G3P (3-carbon)
10 G3P (+ energy from 6 ATP) → 6 RuBP (i.e. starting material regenerated)
2 G3P → glucose (6-carbon).
In tryptophan biosynthesis
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate occurs as a byproduct in the biosynthesis pathway of tryptophan, an essential amino acid that cannot be produced by the human body.
In thiamine biosynthesis
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate occurs as a reactant in the biosynthesis pathway of thiamine (Vitamin B1), another substance that cannot be produced by the human body.
External links
- D-Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and the reactions and pathways it participates in, from the KEGG PATHWAY Database
- Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and the reactions and pathways it participates in, from the KEGG PATHWAY Database
Glycolysis Metabolic Pathway Glucose Hexokinase Glucose 6-phosphate Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase Fructose 6-phosphate phosphofructokinase-1 Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate Fructose bisphosphate aldolase 
ATP ADP 
ATP ADP 


Dihydroxyacetone phosphate Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate Triosephosphate isomerase Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate 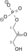
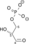

NAD+ + Pi NADH + H+ 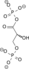
+ 
2 
2 Phosphoglycerate kinase 3-Phosphoglycerate Phosphoglycerate mutase 2-Phosphoglycerate Phosphopyruvate hydratase(Enolase) Phosphoenolpyruvate Pyruvate kinase Pyruvate ADP ATP 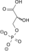
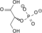
H2O 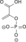
ADP ATP 
2 
2 
2 
2 Fructose Fructose-1-phosphate → DHAP/Glyceraldehyde → Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphateGalactose Galactose-1-phosphate → Glucose 1-phosphate → Glucose 6-phosphate → Fructose 6-phosphate
Uridine diphosphate galactose · Uridine diphosphate glucose
Galactitol · IditolMannose Categories:- Glycolysis
- Photosynthesis
- Organophosphates
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
