- 2-Phosphoglyceric acid
-
2-Phosphoglyceric acid  3-hydroxy-2-phosphonooxypropanoic acidOther names2PG
3-hydroxy-2-phosphonooxypropanoic acidOther names2PGIdentifiers CAS number 2553-59-5 PubChem 59 ChemSpider 58 
Jmol-3D images Image 1
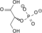
Image 2- C(C(C(=O)O)OP(=O)(O)O)O
O=P(O)(O)OC(C(=O)O)CO
Properties Molecular formula C3H7O7P Molar mass 186.06 g/mol  acid (verify) (what is:
acid (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references 2-Phosphoglyceric acid (2PG), or 2-phosphoglycerate, is a glyceric acid which serves as the substrate in the ninth step of glycolysis. It is catalyzed by enolase into phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), the penultimate step in the conversion of glucose to pyruvate.
In Glycolysis
3-phospho-D-glycerate Phosphoglyceromutase 2-phospho-D-glycerate Enolase phosphoenolpyruvate 


H2O 

H2O Phosphoglyceromutase Enolase Compound C00197 at KEGG Pathway Database. Enzyme 5.4.2.1 at KEGG Pathway Database. Compound C00631 at KEGG Pathway Database. Enzyme 4.2.1.11 at KEGG Pathway Database. Compound C00074 at KEGG Pathway Database.
See also
References
Glycolysis Metabolic Pathway Glucose Hexokinase Glucose 6-phosphate Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase Fructose 6-phosphate phosphofructokinase-1 Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate Fructose bisphosphate aldolase 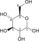
ATP ADP 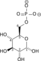
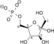
ATP ADP 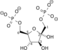


Dihydroxyacetone phosphate Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate Triosephosphate isomerase Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate 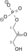
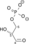

NAD+ + Pi NADH + H+ 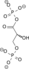
+ 
2 
2 Phosphoglycerate kinase 3-Phosphoglycerate Phosphoglycerate mutase 2-Phosphoglycerate Phosphopyruvate hydratase(Enolase) Phosphoenolpyruvate Pyruvate kinase Pyruvate ADP ATP 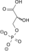
H2O 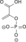
ADP ATP 
2 
2 
2 
2 
This article about metabolism is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. - C(C(C(=O)O)OP(=O)(O)O)O
