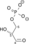
- 3-Phosphoglyceric acid
-
3-Phosphoglyceric acid 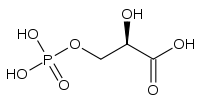
 (2R)-2-Hydroxy-3-phosphonooxypropanoic acid
(2R)-2-Hydroxy-3-phosphonooxypropanoic acidIdentifiers CAS number 820-11-1 
PubChem 439183 ChemSpider 388326 
ChEBI CHEBI:17794 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1160563 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - C([C@H](C(=O)O)O)OP(=O)(O)O
Properties Molecular formula C3H7O7P Molar mass 186.06 g mol−1  acid (verify) (what is:
acid (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references 3-Phosphoglyceric acid (3PG), or glycerate 3-phosphate (GP), is a biochemically significant 3-carbon molecule that is a metabolic intermediate in both glycolysis and the Calvin cycle.[citation needed] This chemical is often termed PGA when referring to the Calvin cycle. 3-Phosphoglycerate is the resultant of the split of 6-carbon intermediate that is so unstable that it splits instantly. And two 3-phosphoglycerate molecules are produced for each molecule of CO2.
Contents
Glycolysis
1,3-bisphospho-D-glycerate 3-phosphoglycerate kinase 3-phospho-D-glycerate Phosphoglyceromutase 2-phospho-D-glycerate 


ADP ATP 

ADP ATP 3-phosphoglycerate kinase Phosphoglyceromutase Compound C00236 at KEGG Pathway Database. Enzyme 2.7.2.3 at KEGG Pathway Database. Compound C00197 at KEGG Pathway Database. Enzyme 5.4.2.1 at KEGG Pathway Database. Compound C00631 at KEGG Pathway Database.
Calvin cycle
In the Calvin cycle, two glycerate 3-phosphate molecules are reduced to form two molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (PGAL). This is the first compound formed during the C3 or Calvin cycle. It is a reactive biomolecule that is easily reduced.
Amino acid synthesis
Glycerate 3-phosphate is also a precursor for serine, which, in turn, can create cysteine and glycine through the homocysteine cycle.
See also
Glycolysis Metabolic Pathway Glucose Hexokinase Glucose 6-phosphate Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase Fructose 6-phosphate phosphofructokinase-1 Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate Fructose bisphosphate aldolase 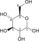
ATP ADP 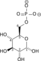
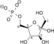
ATP ADP 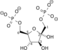


Dihydroxyacetone phosphate Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate Triosephosphate isomerase Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate 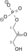

NAD+ + Pi NADH + H+ 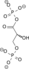
+ 
2 
2 Phosphoglycerate kinase 3-Phosphoglycerate Phosphoglycerate mutase 2-Phosphoglycerate Phosphopyruvate hydratase(Enolase) Phosphoenolpyruvate Pyruvate kinase Pyruvate ADP ATP 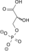
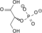
H2O 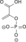
ADP ATP 
2 
2 
2 
2 K→acetyl-CoA G G→pyruvate→citrateG→glutamate→
α-ketoglutarateotherα-Ketoisovaleric acid · Isobutyryl-CoA · Methacrylyl-CoA · 3-Hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA · 3-Hydroxyisobutyric acid · 2-Methyl-3-oxopropanoic acidG→fumarateG→oxaloacetatesee urea cycleOther biochemical families: prot · nucl · carb (glpr, alco, glys) · lipd (fata/i, phld, strd, gllp, eico) · amac/i · ncbs/i · ttpy/iGlycinergics Receptor
ligandsAgonistsAlanine • Cycloserine • Dimethylglycine • Glycine • Hypotaurine • Methylglycine (Sarcosine) • Milacemide • Serine • Taurine • Trimethylglycine (Betaine)Reuptake
inhibitorsPlasmalemmalGlyT1 inhibitorsGlyT2 inhibitorsVIAAT InhibitorsEnzyme
inhibitorsSHMT InhibitorsGDC InhibitorsDAAO InhibitorsOthers 3-Phosphoglyceric acid • Serine
This article about metabolism is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
