- Creatinine
-
Not to be confused with creatine.
Creatinine 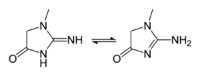
 2-Amino-1-methyl-5H-imidazol-4-one[citation needed]Systematic name2-Amino-1-methyl-1H-imidazol-4-ol[citation needed]Other names2-Amino-1-methylimidazol-4-ol[citation needed]
2-Amino-1-methyl-5H-imidazol-4-one[citation needed]Systematic name2-Amino-1-methyl-1H-imidazol-4-ol[citation needed]Other names2-Amino-1-methylimidazol-4-ol[citation needed]Identifiers CAS number 60-27-5 
PubChem 26009888, 588 minor tautomer ChemSpider 21640982 
UNII AYI8EX34EU 
EC number 200-466-7 UN number 1789 KEGG D03600 
MeSH Creatinine ChEBI CHEBI:16737 
ChEMBL CHEMBL65567 
Beilstein Reference 112061 3DMet B00175 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - CN1C=C(O)N=C1N
Properties Molecular formula C4N3H7O Molar mass 113.1179 g mol-1 Exact mass 113.058911861 g mol-1 Appearance White crystals Density 1.09 g cm-3 log P -1.76 Acidity (pKa) 12.309 Basicity (pKb) 1.688 Isoelectric point 11.19 Hazards EU classification  Xn
XnR-phrases R34, R36/37/38, R20/21/22 S-phrases S26, S36/37/39, S45, S24/25, S36 NFPA 704 Flash point 290 °C  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Creatinine (from the Greek κρέας, flesh, pronounced, krē-'a-tə-nēn, -ən cre·at·i·nine) is a break-down product of creatine phosphate in muscle, and is usually produced at a fairly constant rate by the body (depending on muscle mass). Creatinine starts to decompose above 295 °C.
In chemical terms, creatinine is a spontaneously formed cyclic derivative of creatine. Creatinine is chiefly filtered out of the blood by the kidneys (glomerular filtration and proximal tubular secretion). There is little-to-no tubular reabsorption of creatinine. If the filtering of the kidney is deficient, creatinine blood levels rise. Therefore, creatinine levels in blood and urine may be used to calculate the creatinine clearance (CrCl), which reflects the glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
The GFR is clinically important because it is a measurement of renal function. However, in cases of severe renal dysfunction, the creatinine clearance rate will be "overestimated" because the active secretion of creatinine will account for a larger fraction of the total creatinine cleared[clarification needed]. Ketoacids, cimetidine and trimethoprim reduce creatinine tubular secretion and therefore increase the accuracy of the GFR estimate, particularly in severe renal dysfunction. (In the absence of secretion, creatinine behaves like inulin.)
A more complete estimation of renal function can be made when interpreting the blood (plasma) concentration of creatinine along with that of urea. BUN-to-creatinine ratio (the ratio of blood urea nitrogen to creatinine) can indicate other problems besides those intrinsic to the kidney; for example, a urea level raised out of proportion to the creatinine may indicate a pre-renal problem such as volume depletion.
Men generally tend to have higher levels of creatinine because they have more skeletal muscle mass than women. Vegetarians have been shown to have lower creatinine levels.[1]
There exists several tautomers of creatinine. Ordered by contribution, they are:
- 2-Amino-1-methyl-1H-imidazol-4-ol or 2-Amino-1-methylimidazol-4-ol
- 2-Amino-1-methyl-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-4-one
- 2-Imino-1-methyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-imidazol-4-ol or 2-Imino-1-methyl-3H-imidazol-4-ol
- 2-Imino-1-methylimidazolidin-4-one
- 2-Imino-1-methyl-2,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-4-ol or 2-Imino-1-methyl-5H-imidazol-4-ol
Contents
Diagnostic use
Serum creatinine
Measuring serum creatinine is a simple test and it is the most commonly used indicator of renal function.
A rise in blood creatinine level is observed only with marked damage to functioning nephrons. Therefore, this test is not suitable for detecting early-stage kidney disease. A better estimation of kidney function is given by the creatinine clearance (CrCl) test. Creatinine clearance can be accurately calculated using serum creatinine concentration and some or all of the following variables: sex, age, weight, and race, as suggested by the American Diabetes Association without a 24-hour urine collection.[2] Some laboratories will calculate the CrCl if written on the pathology request form, and the necessary age, sex, and weight are included in the patient information.
A current concern in late 2010 relates to the adoption of a new analytical methodology, and a possible impact this may have in clinical medicine. All clinical laboratories in the US will soon use a new standardized Isotope Dilution Mass Spectrometry (IDMS) method to measure serum creatinine. IDMS appears to give lower values compared to older methods when the serum creatinine values are relatively low, for example 0.7 mg/dL. The IDMS method would result in a comparative overestimation of the corresponding calculated Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) in some patients with normal renal function. A few medicines are dosed even in normal renal function on that derived GFR. The dose, unless further modified, could now be higher than desired, potentially causing increased drug-related toxicity. To counter the effect of changing to IDMS, new FDA guidelines have suggested limiting doses to specified maximums with carboplatin, a chemotherapy drug.[3]
A recent Japanese study suggests that a lower-serum creatinine level is associated with an increased risk for the development of type 2 diabetes in Japanese men..[4]
Urine creatinine
Creatinine concentration is also checked during standard urine drug tests. Normal creatinine levels indicate that the test sample is undiluted, whereas low amounts of creatinine in the urine either indicate either a manipulated test or low individual baseline creatinine levels. Test samples that are considered manipulated due to low creatinine aren't tested and the test is sometimes considered failed.
It should be noted[citation needed] that diluted samples may not always be due to a conscious effort of subversion and diluted samples cannot be proved to be intentional, but are only assumed to be. Random urine creatinine levels have no standard reference ranges. They are usually used with other tests to reference levels of other substances measured in the urine. Diuretics, such as coffee and tea, cause more frequent urination, thus potently decreasing creatinine levels. A decrease in muscle mass will also cause a lower reading of creatinine, as will pregnancy.
Interpretation
In the United States, creatinine is typically reported in mg/dL, whereas, in Canada and a few European countries, μmol/litre may be used. 1 mg/dL of creatinine is 88.4 μmol/L.
The typical human reference ranges for serum creatinine are 0.5 to 1.0 mg/dL (about 45-90 μmol/L) for women and 0.7 to 1.2 mg/dL (60-110 μmol/L) for men. While a baseline (medicine) serum creatinine of 2.0 mg/dL (150 μmol/L) may indicate normal kidney function in a male body builder, a serum creatinine of 1.2 mg/dL (110 μmol/L) can indicate significant renal disease in an elderly female.[citation needed] for male reference range are 60-120 μmol/L and for female it is 50-110 μmol/L (Ref: Australian Medicine Handbook)
 Reference ranges for blood tests, comparing blood content of creatinine (shown in apple-green) with other constituents.
Reference ranges for blood tests, comparing blood content of creatinine (shown in apple-green) with other constituents.
More important than absolute creatinine level is the trend of serum creatinine levels over time.
Creatinine levels may increase when ACE inhibitors (ACEI) or angiotensin II receptor antagonists (or angiotensin receptor blockers, ARBs) are taken. Using both ACEI & ARB concomitantly will increase creatinine levels to a greater degree than either of the two drugs would individually. An increase of <30% is to be expected with ACEI or ARB use.
See also
- Cystatin C - novel marker of kidney function
References
- ^ Delanghe J; De Slypere JP, De Buyzere M, Robbrecht J, Wieme R, Vermeulen A (Aug 1989). "Normal reference values for creatine, creatinine, and carnitine are lower in vegetarians" (PDF). Clin. Chem. 35 (8): 1802–3. PMID 2758659. http://www.clinchem.org/cgi/reprint/35/8/1802.pdf. Retrieved 2009-03-01. "As shown, measured serum and erythrocyte creatine content, and estimated muscle creatine content, are lower in vegetarians than in the reference population"
- ^ Gross JL, de Azevedo MJ, Silveiro SP, Canani LH, Caramori ML, Zelmanovitz T (2005). "Diabetic nephropathy: diagnosis, prevention, and treatment". Diabetes Care 28 (1): 164–76. doi:10.2337/diacare.28.1.164. PMID 15616252.
- ^ http://www.fda.gov/AboutFDA/CentersOffices/CDER/ucm228974.htm accessioned 2010 October 22
- ^ Harita, N.; Hayashi, T.; Sato, K. K.; Nakamura, Y.; Yoneda, T.; Endo, G.; Kambe, H. (2008). [care.diabetesjournals.org/content/32/3/424 "Lower Serum Creatinine is a New Risk Factor of Type 2 Diabetes: the Kansai Healthcare Study"]. Diabetes Care 32: 424. doi:10.2337/dc08-1265
K→acetyl-CoA G G→pyruvate→citrateG→glutamate→
α-ketoglutarateotherα-Ketoisovaleric acid · Isobutyryl-CoA · Methacrylyl-CoA · 3-Hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA · 3-Hydroxyisobutyric acid · 2-Methyl-3-oxopropanoic acidG→fumarateG→oxaloacetatesee urea cycleOther biochemical families: prot · nucl · carb (glpr, alco, glys) · lipd (fata/i, phld, strd, gllp, eico) · amac/i · ncbs/i · ttpy/iMedical test: Serology, reference range: Clinical biochemistry blood tests (including BMP, CMP) (CPT 82000-84999) Fluid/electrolytes electrolytes (Na+/K+, Cl-/HCO3-) · renal function, BUN-to-creatinine ratio (BUN/Creatinine) · Ca
derived values: Plasma osmolality · Serum osmolal gapAcid-base Nutrition Iron tests: Transferrin saturation = Serum iron / Total iron-binding capacity; Ferritin · Transferrin · Transferrin receptorEndocrine ACTH stimulation test · Thyroid function tests (TSH)
Blood sugar: Glucose test · C-peptide · Fructosamine · Glycated hemoglobinMetabolic Cardiovascular Digestive Liver function tests: protein tests (Human serum albumin, Serum total protein) · ALP · transaminases (ALT, AST, AST/ALT ratio) · Bilirubin (Unconjugated, Conjugated)
Amylase · Lipase (Pancreatic lipase)Categories:- Guanidines
- Metabolism
- Renal physiology
- Imidazolidines
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

