- 5-alpha-reductase deficiency
-
5-alpha-reductase deficiency Classification and external resources 
5-alpha reductase produces dihydrotestosteroneICD-10 E29.1, Q56.3 ICD-9 257.2, 752.7 OMIM 264600 DiseasesDB 11 eMedicine ped/1980 5-Alpha-reductase deficiency (5-ARD) is an autosomal recessive intersex condition caused by a mutation of the 5-alpha reductase type 2 gene.[1]
Contents
Normal function
5-Alpha-reductase is an enzyme that converts testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in peripheral tissues. 5-Alpha-reductase deficiency-2 is biochemically characterized by low to low-normal levels of testosterone and decreased levels of 5α-DHT, creating a higher testosterone/DHT ratio.
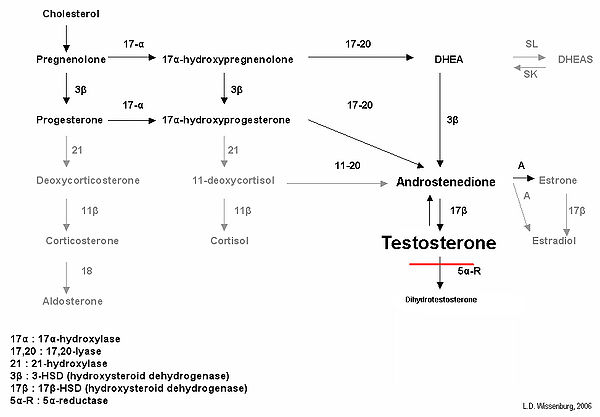 Biochemical effects of 5-alpha-reductase deficiency-2 in testosterone biosynthesis. Levels of testosterone are elevated, while levels of DHT are significantly decreased, leading to male undervirilization.
Biochemical effects of 5-alpha-reductase deficiency-2 in testosterone biosynthesis. Levels of testosterone are elevated, while levels of DHT are significantly decreased, leading to male undervirilization.
DHT is a potent androgen, necessary for the development of male external genitalia in utero.
Signs
The condition affects only genetic males (that is, those with a Y-chromosome) because DHT has no known role in female development.[2]
Individuals with 5-ARD can have normal male external genitalia, ambiguous genitalia, or normal female genitalia. They are born with male gonads, including testicles and Wolffian structures, but usually have female primary sex characteristics. As a consequence, they are often raised as girls, but usually have a male gender identity.[3][4]
In general, individuals with 5-ARD are capable of producing viable sperm. In individuals with feminized or ambiguous genitalia, there is a tendency towards a macroclitoris or microphallus, and the urethra may attach to the phallus. This structure may be capable of ejaculations as well as erections, but may be insufficient for intercourse.
At puberty, individuals often have primary amenorrhoea, and may experience virilization. This may include descending of the testes, hirsutism (facial/body hair considered normal in males - not to be confused with hypertrichosis), deepening of the voice, and enlargement of the clitoris. In adulthood, individuals do not experience male-pattern baldness.[1] As DHT is a far more potent androgen than testosterone alone, virilization in those lacking DHT may be absent or reduced compared to males with functional 5-alpha reductase. It is hypothesized that rising testosterone levels at the start of puberty (around age twelve) are able to generate sufficient levels of DHT either by the action of 5-alpha-reductase type 1 (active in the adult liver, non-genital skin and some brain areas) or through the expression of low levels of 5-alpha-reductase type 2 in the testes.
Infertility
There is an increased risk of cryptorchidism in 5-ARD, causing infertility, but also a higher risk of testicular cancer. Fertility is further compromised by the underdevelopment of seminal vesicles and prostate.
On the other hand, fertility depending on female characteristics is impossible; although the external genitalia may be female, the vagina consists of only the lower two-thirds of a normal vagina, creating a blind-ending vaginal pouch. Due to the normal action of Müllerian inhibiting factor produced by the testes in utero, individuals with 5-ARD lack a uterus and Fallopian tubes. Thus, individuals with 5-ARD are not able to carry a pregnancy, and, since they have testes and not ovaries, they are unable to create ova, which precludes such infertility treatments as surrogate motherhood.
Prevalence
The number of people with this condition varies relative to geographic location, depending on how much of a given population is interrelated.[citation needed] In 1974, Jullianne Imperato-McGinley has estimated an incidence of 1:90 males in the Dominican Republic.[5]
See also
- Intersexuality
- 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency
- Androgen insensitivity syndrome
- Gonadal dysgenesis
- Jeffrey Eugenides's Pulitzer Prize winning novel Middlesex
References
- ^ a b 5-alpha reductase deficiency at GPnotebook
- ^ eMedicine article on 5-ARD
- ^ Praveen, EP; Praveen EP, Desai AK, Khurana ML, Philip J, Eunice M, Khadgawat R, Kulshreshtha B, Kucheria K, Gupta DK, Seith A, Ammini AC. (February 2008). "Gender identity of children and young adults with 5alpha-reductase deficiency.". J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 21 (2): 173–9. PMID 18422030.
- ^ Imperato-Mcginley, Julianne; Julianne Imperato-McGinley, M.D., Ralph E. Peterson, M.D., Teofilo Gautier, M.D., and Erasmo Sturla, M.D. (May 31, 1979). "Androgens and the Evolution of Male-Gender Identity among Male Pseudohermaphrodites with 5α-Reductase Deficiency". New England Journal of Medicine 300 (22): 1233–1237. doi:10.1056/NEJM197905313002201. PMID 431680. http://www.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/NEJM197905313002201.
- ^ Imperato-McGinley, Julianne; Guerrero, Luis; Gautier, Teofilo; Peterson, Ralph Edward (Dec 27, 1974). "Steroid 5alpha-reductase deficiency in man: an inherited form of male pseudohermaphroditism". Science 186 (4170): 1213–1215. doi:10.1126/science.186.4170.1213. PMID 4432067.
External links
- OMIM article
- 5-Alpha-Reductase Deficiency at eMedicine
- "Whatever I feel..." Article in the New Internationalist
- "Guevote: The Way I Feel Is How I Am" A film by Rolando Sánchez
Inborn error of steroid metabolism Mevalonate pathway To cholesterol 7-Dehydrocholesterol path: Hydrops-ectopic calcification-moth-eaten skeletal dysplasia · CHILD syndrome · Conradi-Hünermann syndrome · Lathosterolosis · Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome
desmosterol path: DesmosterolosisSteroids aldosterone: Glucocorticoid remediable aldosteronism
cortisol/cortisone: CAH 17α hydroxylase · CAH 11β hydroxylase
both: CAH 3β dehydrogenase · CAH 21α hydroxylase · Apparent mineralocorticoid excess syndrome/11β dehydrogenaseTo androgens17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency · 5-alpha-reductase deficiency (Pseudovaginal perineoscrotal hypospadias)To estrogensAromatase deficiencyOtherCategories:- Intersexuality
- Endocrine gonad disorders
- Cholesterol and steroid metabolism disorders
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
