- Mevalonate kinase deficiency
-
Mevalonate kinase deficiency Classification and external resources 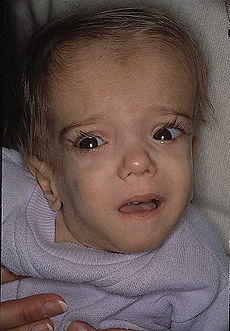
A patient with mevalonate kinase deficiency at the age of 21 months, displaying characteristic craniofacial features.OMIM 251170 DiseasesDB 29843 MeSH D054078 Mevalonate kinase deficiency, also called mevalonic aciduria,[1] is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that disrupts the biosynthesis of cholesterol and isoprenoids.[2]
Contents
Diagnosis
Mevalonate kinase deficiency causes an accumulation of mevalonic acid in the urine, resulting from insufficient activity of the enzyme mevalonate kinase[3] (ATP:mevalonate 5-phosphotransferase; EC 2.7.1.36).
The disorder was first described in 1985.[4]
Classified as an inborn error of metabolism, mevalonate kinase deficiency usually results in developmental delay, hypotonia, anemia, hepatosplenomegaly, various dysmorphic features, mental retardation, an overall failure to thrive and several other features.
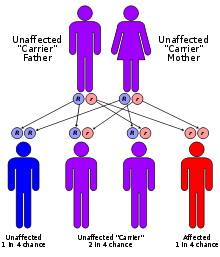 Mevalonate kinase deficiency has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance.
Mevalonate kinase deficiency has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance.
Additional images
See also
- Hyper-IgD syndrome
External links
- Mevalonate kinase deficiency
- Mevalonic aciduria at NIH's Office of Rare Diseases
References
- ^ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 251170
- ^ Mancini J, Philip N, Chabrol B, Divry P, Rolland MO, Pinsard N (May-Jun 1993). "Mevalonic aciduria in 3 siblings: a new recognizable metabolic encephalopathy". Pediatr. Neurol. 9 (3): 243–246. doi:10.1016/0887-8994(93)90095-T. PMID 8352861.
- ^ Bretón Martínez JR, Cánovas Martínez A, Casaña Pérez S, Escribá Alepuz J, Giménez Vázquez F (Oct 2007). "Mevalonic aciduria: report of two cases". J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 30 (5): 829. doi:10.1007/s10545-007-0618-7. PMID 17578678.
- ^ Berger R, Smit GP, Schierbeek H, Bijsterveld K, le Coultre R (Oct 1985). "Mevalonic aciduria: an inborn error of cholesterol biosynthesis?". Clin. Chim. Acta 152 (1-2): 219–222. doi:10.1016/0009-8981(85)90195-0. PMID 4053401.
Genetic disorder, organelle: Peroxisomal disorders and lysosomal structural disorders (E80.3, 277.86) Peroxisome biogenesis disorder Zellweger syndrome · Autosomal adrenoleukodystrophy · Infantile Refsum disease · Adult Refsum disease-2 · RCP 1Enzyme-related Acatalasia · RCP 2&3 · Mevalonate kinase deficiency · D-bifunctional protein deficiency · Adult Refsum disease-1Transporter-related Lysosomal See also: proteins, intermediatesB structural (perx, skel, cili, mito, nucl, sclr) · DNA/RNA/protein synthesis (drep, trfc, tscr, tltn) · membrane (icha, slcr, atpa, abct, othr) · transduction (iter, csrc, itra), trfkInborn error of steroid metabolism Mevalonate pathway Hyper-IgD syndrome · Mevalonate kinase deficiencyTo cholesterol 7-Dehydrocholesterol path: Hydrops-ectopic calcification-moth-eaten skeletal dysplasia · CHILD syndrome · Conradi-Hünermann syndrome · Lathosterolosis · Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome
desmosterol path: DesmosterolosisSteroids aldosterone: Glucocorticoid remediable aldosteronism
cortisol/cortisone: CAH 17α hydroxylase · CAH 11β hydroxylase
both: CAH 3β dehydrogenase · CAH 21α hydroxylase · Apparent mineralocorticoid excess syndrome/11β dehydrogenaseTo androgensTo estrogensAromatase deficiencyOtherCategories:- Cholesterol and steroid metabolism disorders
- Neurological disorders
- Autosomal recessive disorders
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

