- Mevalonate kinase
-
Mevalonate Kinase 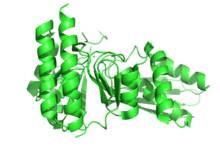
Crystallographic structure of mevalonate kinase from Staphylococcus aureus.[1] Identifiers EC number 2.7.1.36 CAS number 9026-52-2 Databases IntEnz IntEnz view BRENDA BRENDA entry ExPASy NiceZyme view KEGG KEGG entry MetaCyc metabolic pathway PRIAM profile PDB structures RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum Gene Ontology AmiGO / EGO Search PMC articles PubMed articles Mevalonate kinase 
PDB rendering based on 2r3v.Available structures PDB 2r3v Identifiers Symbols MVK; FLJ96772; LRBP; MK; MVLK External IDs OMIM: 251170 MGI: 107624 HomoloGene: 372 GeneCards: MVK Gene EC number 2.7.1.36 Gene Ontology Molecular function • nucleotide binding
• mevalonate kinase activity
• mevalonate kinase activity
• ATP binding
• transferase activity
• identical protein bindingCellular component • cytoplasm
• peroxisome
• cytosolBiological process • cholesterol biosynthetic process
• metabolic process
• isoprenoid biosynthetic processSources: Amigo / QuickGO Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 4598 17855 Ensembl ENSG00000110921 ENSMUSG00000041939 UniProt Q03426 Q9R008 RefSeq (mRNA) NM_000431.2 NM_023556.2 RefSeq (protein) NP_000422.1 NP_076045.1 Location (UCSC) Chr 12:
110.01 – 110.04 MbChr 5:
114.89 – 114.91 MbPubMed search [1] [2] Mevalonate kinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MVK gene.[2][3] Mevalonate kinases are found in a wide variety of organisms from bacteria to mammals. This enzyme catalyzes the following reaction;
- ATP + (R)-mevalonate
 ADP + (R)-5-phosphomevalonate
ADP + (R)-5-phosphomevalonate
Contents
Function
Mevalonate is a key intermediate, and mevalonate kinase a key early enzyme, in isoprenoid and sterol synthesis.[2]
Clinical significance
Defects can be associated with hyperimmunoglobulinemia D with recurrent fever.[4]
Mevalonate kinase deficiency caused by mutation of this gene results in mevalonic aciduria, a disease characterized psychomotor retardation, failure to thrive, hepatosplenomegaly, anemia and recurrent febrile crises. Defects in this gene also cause hyperimmunoglobulinaemia D and periodic fever syndrome, a disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of fever associated with lymphadenopathy, arthralgia, gastrointestinal dismay and skin rash.[2]
See also
References
- ^ PDB 2X7I; Oke M, Carter LG, Johnson KA, Liu H, McMahon SA, Yan X, Kerou M, Weikart ND, Kadi N, Sheikh MA, Schmelz S, Dorward M, Zawadzki M, Cozens C, Falconer H, Powers H, Overton IM, van Niekerk CA, Peng X, Patel P, Garrett RA, Prangishvili D, Botting CH, Coote PJ, Dryden DT, Barton GJ, Schwarz-Linek U, Challis GL, Taylor GL, White MF, Naismith JH (June 2010). "The Scottish Structural Proteomics Facility: targets, methods and outputs". J. Struct. Funct. Genomics 11 (2): 167–80. doi:10.1007/s10969-010-9090-y. PMC 2883930. PMID 20419351. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2883930.
- ^ a b c "Entrez Gene: mevalonate kinase". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=4598.
- ^ Schafer BL, Bishop RW, Kratunis VJ, Kalinowski SS, Mosley ST, Gibson KM, Tanaka RD (July 1992). "Molecular cloning of human mevalonate kinase and identification of a missense mutation in the genetic disease mevalonic aciduria". J. Biol. Chem. 267 (19): 13229–38. PMID 1377680.
- ^ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 260920
Further reading
- Ma J, Dempsey AA, Stamatiou D, et al. (2007). "Identifying leukocyte gene expression patterns associated with plasma lipid levels in human subjects.". Atherosclerosis 191 (1): 63–72. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2006.05.032. PMID 16806233.
- Willer CJ, Sanna S, Jackson AU, et al. (2008). "Newly identified loci that influence lipid concentrations and risk of coronary artery disease.". Nat. Genet. 40 (2): 161–9. doi:10.1038/ng.76. PMID 18193043.
- Naruto T, Nakagishi Y, Mori M, et al. (2009). "Hyper-IgD syndrome with novel mutation in a Japanese girl.". Mod Rheumatol 19 (1): 96–9. doi:10.1007/s10165-008-0130-4. PMID 18941711.
- Krisans SK (1992). "The role of peroxisomes in cholesterol metabolism.". Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 7 (4): 358–64. PMID 1356376.
- Houten SM, Wanders RJ, Waterham HR (2000). "Biochemical and genetic aspects of mevalonate kinase and its deficiency.". Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1529 (1-3): 19–32. PMID 11111075.
- Fu Z, Voynova NE, Herdendorf TJ, et al. (2008). "Biochemical and structural basis for feedback inhibition of mevalonate kinase and isoprenoid metabolism.". Biochemistry 47 (12): 3715–24. doi:10.1021/bi7024386. PMID 18302342.
- Kathiresan S, Willer CJ, Peloso GM, et al. (2009). "Common variants at 30 loci contribute to polygenic dyslipidemia.". Nat. Genet. 41 (1): 56–65. doi:10.1038/ng.291. PMC 2685478. PMID 19060906. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2685478.
- Hager EJ, Gibson KM (2007). "Mevalonate kinase deficiency and autoinflammation.". N. Engl. J. Med. 357 (18): 1871–2. doi:10.1056/NEJMc072799. PMID 17978300.
- Marques-Vidal P, Bochud M, Paccaud F, et al. (2010). "No interaction between alcohol consumption and HDL-related genes on HDL cholesterol levels.". Atherosclerosis 211 (2): 551–7. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.04.001. PMID 20430392.
- Lu Y, Dollé ME, Imholz S, et al. (2008). "Multiple genetic variants along candidate pathways influence plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol concentrations.". J. Lipid Res. 49 (12): 2582–9. doi:10.1194/jlr.M800232-JLR200. PMID 18660489.
- Samkari A, Borzutzky A, Fermo E, et al. (2010). "A novel missense mutation in MVK associated with MK deficiency and dyserythropoietic anemia.". Pediatrics 125 (4): e964-8. doi:10.1542/peds.2009-1774. PMID 20194276.
- Nakayama K, Bayasgalan T, Yamanaka K, et al. (2009). "Large scale replication analysis of loci associated with lipid concentrations in a Japanese population.". J. Med. Genet. 46 (6): 370–4. doi:10.1136/jmg.2008.064063. PMID 19487539.
- Koné-Paut I, Sanchez E, Le Quellec A, et al. (2007). "Autoinflammatory gene mutations in Behçet's disease.". Ann. Rheum. Dis. 66 (6): 832–4. doi:10.1136/ard.2006.068841. PMID 17213252.
- Weissglas-Volkov D, Aguilar-Salinas CA, Sinsheimer JS, et al. (2010). "Investigation of variants identified in caucasian genome-wide association studies for plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglycerides levels in Mexican dyslipidemic study samples.". Circ Cardiovasc Genet 3 (1): 31–8. doi:10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.109.908004. PMID 20160193.
- Simon A, van der Meer JW, Vesely R, et al. (2006). "Approach to genetic analysis in the diagnosis of hereditary autoinflammatory syndromes.". Rheumatology (Oxford) 45 (3): 269–73. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kei138. PMID 16234278.
- Gattorno M, Sormani MP, D'Osualdo A, et al. (2008). "A diagnostic score for molecular analysis of hereditary autoinflammatory syndromes with periodic fever in children.". Arthritis Rheum. 58 (6): 1823–32. doi:10.1002/art.23474. PMID 18512793.
- Fogarty MP, Xiao R, Prokunina-Olsson L, et al. (2010). "Allelic expression imbalance at high-density lipoprotein cholesterol locus MMAB-MVK.". Hum. Mol. Genet. 19 (10): 1921–9. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddq067. PMID 20159775.
- Nair AK, Young MA, Menon KM (2008). "Regulation of luteinizing hormone receptor mRNA expression by mevalonate kinase--role of the catalytic center in mRNA recognition.". FEBS J. 275 (13): 3397–407. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06490.x. PMID 18494797.
- Deo RC, Reich D, Tandon A, et al. (2009). "Genetic differences between the determinants of lipid profile phenotypes in African and European Americans: the Jackson Heart Study.". PLoS Genet. 5 (1): e1000342. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000342. PMID 19148283.
- Junyent M, Parnell LD, Lai CQ, et al. (2009). "Novel variants at KCTD10, MVK, and MMAB genes interact with dietary carbohydrates to modulate HDL-cholesterol concentrations in the Genetics of Lipid Lowering Drugs and Diet Network Study.". Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 90 (3): 686–94. doi:10.3945/ajcn.2009.27738. PMID 19605566.
External links
Transferases: phosphorus-containing groups (EC 2.7) 2.7.1-2.7.4:
phosphotransferase/kinase
(PO4)Hexo- · Gluco- · Fructo- (Hepatic) · Galacto- · Phosphofructo- (1, Liver, Muscle, Platelet, 2) · Riboflavin · Shikimate · Thymidine (ADP-thymidine) · NAD+ · Glycerol · Pantothenate · Mevalonate · Pyruvate · Deoxycytidine · PFP · Diacylglycerol · Phosphoinositide 3 (Class I PI 3, Class II PI 3) · Sphingosine · Glucose-1,6-bisphosphate synthase2.7.2: COOH acceptor2.7.6: diphosphotransferase
(P2O7)2.7.7: nucleotidyltransferase
(PO4-nucleoside)DNA-directed DNA polymerase: DNA polymerase I · DNA polymerase II · DNA polymerase III holoenzyme
DNA nucleotidylexotransferase/Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase
RNA-directed DNA polymerase: Reverse transcriptase (Telomerase)RNA nucleotidyltransferaseRNA polymerase/DNA-directed RNA polymerase: RNA polymerase I · RNA polymerase II · RNA polymerase III · RNA polymerase IV · Primase · RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
PNPaseUridylyltransferaseGlucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase · Galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferaseGuanylyltransferasemRNA capping enzymeOther2.7.8: miscellaneous PhosphatidyltransferasesCDP-diacylglycerol—glycerol-3-phosphate 3-phosphatidyltransferase · CDP-diacylglycerol—serine O-phosphatidyltransferase · CDP-diacylglycerol—inositol 3-phosphatidyltransferase · CDP-diacylglycerol—choline O-phosphatidyltransferaseGlycosyl-1-phosphotransferase2.7.10-2.7.13: protein kinase
(PO4; protein acceptor)see tyrosine kinasessee serine/threonine-specific protein kinases2.7.12: protein-dual-specificitysee serine/threonine-specific protein kinases2.7.13: protein-histidineB enzm: 1.1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8/10/11/13/14/15-18, 2.1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8, 2.7.10, 2.7.11-12, 3.1/2/3/4/5/6/7, 3.1.3.48, 3.4.21/22/23/24, 4.1/2/3/4/5/6, 5.1/2/3/4/99, 6.1-3/4/5-6 Mevalonate pathway To HMG-CoAAcetyl-Coenzyme A acetyltransferase · HMG-CoA synthase (regulated step)To DMAPPMevalonate kinase · Phosphomevalonate kinase · Pyrophosphomevalonate decarboxylase · Isopentenyl-diphosphate delta isomeraseGeranyl-To cholesterol To lanosterol7-Dehydrocholesterol pathDesmosterol pathTo Bile acids Steroidogenesis To pregnenoloneTo sex hormonesTo androgensTo estrogensOther/ungroupedCategories:- Human proteins
- EC 2.7.1
- Biochemistry stubs
- ATP + (R)-mevalonate
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

