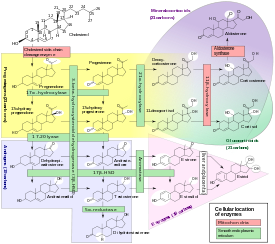
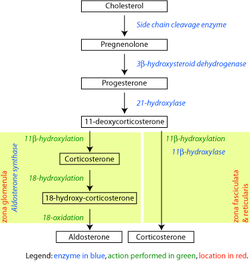
- 21-Hydroxylase
-
Steroid 21-monooxygenase Identifiers EC number 1.14.99.10 CAS number 9029-68-9 Databases IntEnz IntEnz view BRENDA BRENDA entry ExPASy NiceZyme view KEGG KEGG entry MetaCyc metabolic pathway PRIAM profile PDB structures RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum Gene Ontology AmiGO / EGO Search PMC articles PubMed articles Steroid 21-hydroxylase is a cytochrome P450 enzyme that is involved with the biosynthesis of the steroid hormones aldosterone and cortisol.[1]
In humans, 21-Hydroxylase is encoded by the gene CYP21A2.[2]
Contents
Names and classification
21-Hydroxylase is also called steroid 21-monooxygenase, 21α-Hydroxylase, and, less commonly 21β-Hydroxylase.
Function
This gene encodes a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. The cytochrome P450 proteins are monooxygenases which catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids. This protein localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum and hydroxylates steroids at the 21 position. Its activity is required for the synthesis of steroid hormones including cortisol and aldosterone.[3]
Reaction
21-Hydroxylase catalyses the hydroxylation of the carbon atom 21 in steroids (adding an "–OH"), which is necessary with the formation of these hormones.
Steroid numbering - #21 is near center topPathway
Clinical significance
A defect within the CYP21A2 gene causes a disturbance of the development of the enzyme, which leads to congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. A related pseudogene is located near this gene; gene conversion events involving the functional gene and the pseudogene are thought account for many cases of steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency.[3]
References
- ^ Ryan KJ, Engel LL (March 1957). "Hydroxylation of steroids at carbon 21". J. Biol. Chem. 225 (1): 103–14. PMID 13416221. http://www.jbc.org/content/225/1/103.full.pdf.
- ^ Higashi Y, Yoshioka H, Yamane M, Gotoh O, Fujii-Kuriyama Y (May 1986). "Complete nucleotide sequence of two steroid 21-hydroxylase genes tandemly arranged in human chromosome: a pseudogene and a genuine gene". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83 (9): 2841–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.83.9.2841. PMC 323402. PMID 3486422. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=323402.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: CYP21A2 cytochrome P450, family 21, subfamily A, polypeptide 2". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=1589.
Further reading
- White PC, Tusie-Luna MT, New MI, Speiser PW (1994). "Mutations in steroid 21-hydroxylase (CYP21).". Hum. Mutat. 3 (4): 373–8. doi:10.1002/humu.1380030408. PMID 8081391.
- Helmberg A (1993). "Twin genes and endocrine disease: CYP21 and CYP11B genes.". Acta Endocrinol. 129 (2): 97–108. PMID 8372604.
- de-Araujo M, Sanches MR, Suzuki LA, et al. (1996). "Molecular analysis of CYP21 and C4 genes in Brazilian families with the classical form of steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency.". Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 29 (1): 1–13. PMID 8731325.
- Yu CY (1999). "Molecular genetics of the human MHC complement gene cluster.". Exp. Clin. Immunogenet. 15 (4): 213–30. doi:10.1159/000019075. PMID 10072631.
- Forest MG, Tardy V, Nicolino M, et al. (2005). "21-Hydroxylase deficiency: an exemplary model of the contribution of molecular biology in the understanding and management of the disease.". Ann. Endocrinol. (Paris) 66 (3): 225–32. PMID 15988383.
External links
- GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on 21-Hydroxylase-Deficient Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
- OMIM entry on 21-Hydroxylase-Deficient Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
- Synthesis of Desoxycorticosterone from Progesterone through 21-Hydroxylase (Image)
- MeSH Steroid+21-Hydroxylase
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
Oxidoreductases: dioxygenases, including steroid hydroxylases (EC 1.14) 1.14.11: 2-oxoglutarate 1.14.13: NADH or NADPH Flavin-containing monooxygenase (FMO1, FMO2, FMO3, FMO4, FMO5) - Nitric oxide synthase (NOS1, NOS2, NOS3) - Cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase - Methane monooxygenase - 3A4 - Lanosterol 14 alpha-demethylase1.14.14: reduced flavin or flavoprotein 1.14.15: reduced iron-sulfur protein 1.14.16: reduced pteridine (BH4 dependent) 1.14.17: reduced ascorbate 1.14.18-19: other 1.14.99 - miscellaneous Mevalonate pathway To HMG-CoATo DMAPPGeranyl-To cholesterol To lanosterol7-Dehydrocholesterol pathDesmosterol pathTo Bile acids Steroidogenesis To pregnenolonecortisol/cortisone: 17α-hydroxylase · 11β dehydrogenase (HSD11B1, HSD11B2)
both: 3β dehydrogenase · 21α-hydroxylase · 11β-hydroxylaseTo sex hormonesTo androgensTo estrogensOther/ungroupedCytochromes, oxygenases: cytochrome P450 (EC 1.14) CYP1 CYP2 CYP3 (CYP3A) CYP4 CYP5-20 CYP21-51 Categories:- Human proteins
- Enzymes
- Cytochrome P450
- Metabolism
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.