- Dopamine beta hydroxylase
-
Dopamine β-hydroxylase (DBH) is an enzyme that converts dopamine to norepinephrine.
-
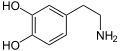
Norepinephrine. Note extra hydroxyl group.
DBH is a 290 kDa copper-containing oxygenase consisting of four identical subunits, and its activity requires ascorbate as a cofactor.[1] It is the only enzyme involved in the synthesis of small-molecule neurotransmitters that is membrane-bound, making norepinephrine and epinephrine the only transmitters synthesized inside vesicles. It is expressed in noradrenergic nerve terminals of the central and peripheral nervous systems, as well as in chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla.
DBH is inhibited by disulfiram,[2] tropolone,[3] and, most selectively, by nepicastat.[4]
See also
References
- ^ Rush RA, Geffen LB (1980). "Dopamine beta-hydroxylase in health and disease.". Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 12 (3): 241–77. doi:10.3109/10408368009108731. PMID 6998654.
- ^ Goldstein M, Anagnoste B, Lauber E, McKeregham MR (1964). "Inhibition of dopamine-beta-hydroxylase by Disulfiram.". Life Sci 3 (7): 763–7. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(64)90031-1. PMID 14203977.
- ^ Goldstein M, Lauber E, McKeregham MR (1964). "Inhibition of dopamine-beta-hydroxylase by tropolone and other chelating agents.". Biochem Pharmacol 13 (7): 1103–6. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(64)90109-1. PMID 14201135.
- ^ Stanley WC et al. (1997). "Catecholamine modulatory effects of nepicastat (RS-25560-197), a novel, potent and selective inhibitor of dopamine-beta-hydroxylase.". British Journal of Pharmacology 121 (8): 1803–9. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0701315. PMC 1564872. PMID 9283721. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1564872.
External links
- GeneReviews/NIH/NCBI/UW entry on Dopamine Beta-Hydroxylase Deficiency
- MeSH Dopamine+beta-Hydroxylase
Oxidoreductases: dioxygenases, including steroid hydroxylases (EC 1.14) 1.14.11: 2-oxoglutarate 1.14.13: NADH or NADPH Flavin-containing monooxygenase (FMO1, FMO2, FMO3, FMO4, FMO5) - Nitric oxide synthase (NOS1, NOS2, NOS3) - Cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase - Methane monooxygenase - 3A4 - Lanosterol 14 alpha-demethylase1.14.14: reduced flavin or flavoprotein 1.14.15: reduced iron-sulfur protein 1.14.16: reduced pteridine (BH4 dependent) 1.14.17: reduced ascorbate Dopamine beta hydroxylase1.14.18-19: other 1.14.99 - miscellaneous monoamine anabolism: Tyrosine hydroxylase · Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase · Dopamine beta hydroxylase · Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase
catabolism: Catechol-O-methyl transferase · Monoamine oxidaseglutamate→GABAanabolism: Glutamate decarboxylase
catabolism: 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase · 4-aminobutyrate transaminasearginine→NO choline→Acetylcholine anabolism: Choline acetyltransferase
catabolism: Cholinesterase (Acetylcholinesterase, Butyrylcholinesterase)This oxidoreductase article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.