- Steroid 11-beta-hydroxylase
-
Steroid 11β-hydroxylase is a steroid hydroxylase found in the zona fasciculata. Named officially the cytochrome P450 11B1, mitochondrial, it is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP11B1 gene.[1][2]
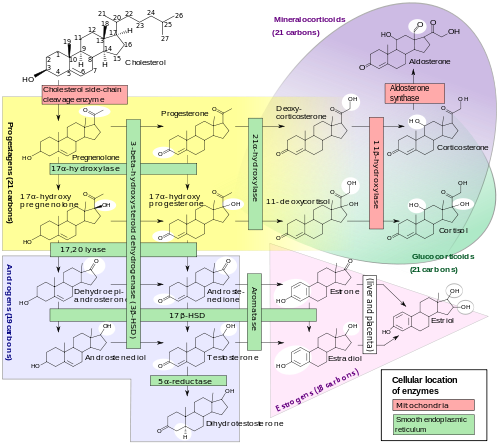
This gene encodes a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. The cytochrome P450 proteins are monooxygenases that catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids. This protein localizes to the mitochondrial inner membrane and is involved in the conversion of 11-deoxycortisol to cortisol in the adrenal cortex. Mutations in this gene cause congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11-beta-hydroxylase deficiency. Transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been noted for this gene.[2]
Contents
Function
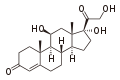
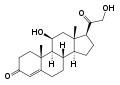
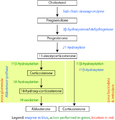
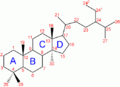
It generates cortisol from 11-deoxycortisol and corticosterone from 11-deoxycorticosterone. Note the extra "–OH" added at the 11 position (near the center, on ring "C"):
Clinical significance
A mutation is associated with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11β-hydroxylase deficiency.
Additional images
References
- ^ Lifton RP, Dluhy RG, Powers M, Rich GM, Gutkin M, Fallo F, Gill JR Jr, Feld L et al. (Jun 1993). "Hereditary hypertension caused by chimaeric gene duplications and ectopic expression of aldosterone synthase". Nat Genet 2 (1): 66–74. doi:10.1038/ng0992-66. PMID 1303253.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: CYP11B1 cytochrome P450, family 11, subfamily B, polypeptide 1". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=1584.
Further reading
- Helmberg A (1993). "Twin genes and endocrine disease: CYP21 and CYP11B genes". Acta Endocrinol. 129 (2): 97–108. PMID 8372604.
- Stowasser M, Gunasekera TG, Gordon RD (2002). "Familial varieties of primary aldosteronism". Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 28 (12): 1087–90. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1681.2001.03574.x. PMID 11903322.
- Helmberg A, Ausserer B, Kofler R (1992). "Frame shift by insertion of 2 basepairs in codon 394 of CYP11B1 causes congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase deficiency". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 75 (5): 1278–81. doi:10.1210/jc.75.5.1278. PMID 1430088.
- Pascoe L, Curnow KM, Slutsker L et al. (1992). "Glucocorticoid-suppressible hyperaldosteronism results from hybrid genes created by unequal crossovers between CYP11B1 and CYP11B2". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89 (17): 8327–31. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.17.8327. PMC 49911. PMID 1518866. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=49911.
- Kawamoto T, Mitsuuchi Y, Toda K et al. (1992). "Role of steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase and steroid 18-hydroxylase in the biosynthesis of glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids in humans". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89 (4): 1458–62. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.4.1458. PMC 48470. PMID 1741400. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=48470.
- White PC, Dupont J, New MI et al. (1991). "A mutation in CYP11B1 (Arg-448----His) associated with steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase deficiency in Jews of Moroccan origin". J. Clin. Invest. 87 (5): 1664–7. doi:10.1172/JCI115182. PMC 295260. PMID 2022736. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=295260.
- Kawamoto T, Mitsuuchi Y, Toda K et al. (1990). "Cloning of cDNA and genomic DNA for human cytochrome P-45011 beta". FEBS Lett. 269 (2): 345–9. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(90)81190-Y. PMID 2401360.
- Mornet E, Dupont J, Vitek A, White PC (1990). "Characterization of two genes encoding human steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase (P-450(11) beta)". J. Biol. Chem. 264 (35): 20961–7. PMID 2592361.
- Chua SC, Szabo P, Vitek A et al. (1987). "Cloning of cDNA encoding steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase (P450c11)". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84 (20): 7193–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.84.20.7193. PMC 299256. PMID 3499608. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=299256.
- Naiki Y, Kawamoto T, Mitsuuchi Y et al. (1994). "A nonsense mutation (TGG [Trp116]-->TAG [Stop]) in CYP11B1 causes steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase deficiency". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 77 (6): 1677–82. doi:10.1210/jc.77.6.1677. PMID 7903314.
- Joehrer K, Geley S, Strasser-Wozak EM et al. (1998). "CYP11B1 mutations causing non-classic adrenal hyperplasia due to 11 beta-hydroxylase deficiency". Hum. Mol. Genet. 6 (11): 1829–34. doi:10.1093/hmg/6.11.1829. PMID 9302260.
- Cargill M, Altshuler D, Ireland J et al. (1999). "Characterization of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in coding regions of human genes". Nat. Genet. 22 (3): 231–8. doi:10.1038/10290. PMID 10391209.
- Halushka MK, Fan JB, Bentley K et al. (1999). "Patterns of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in candidate genes for blood-pressure homeostasis". Nat. Genet. 22 (3): 239–47. doi:10.1038/10297. PMID 10391210.
- Cao PR, Bernhardt R (1999). "Interaction of CYP11B1 (cytochrome P-45011 beta) with CYP11A1 (cytochrome P-450scc) in COS-1 cells". Eur. J. Biochem. 262 (3): 720–6. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00414.x. PMID 10411633.
- Loidi L, Quinteiro C, Barros F et al. (2000). "The C494F variant in the CYP11B1 gene is a sequence polymorphism in the Spanish population". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 84 (12): 4749. doi:10.1210/jc.84.12.4749. PMID 10599751.
- Chabre O, Portrat-Doyen S, Chaffanjon P et al. (2000). "Bilateral laparoscopic adrenalectomy for congenital adrenal hyperplasia with severe hypertension, resulting from two novel mutations in splice donor sites of CYP11B1". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 85 (11): 4060–8. doi:10.1210/jc.85.11.4060. PMID 11095433.
- Fisher A, Friel EC, Bernhardt R et al. (2001). "Effects of 18-hydroxylated steroids on corticosteroid production by human aldosterone synthase and 11beta-hydroxylase". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86 (9): 4326–9. doi:10.1210/jc.86.9.4326. PMID 11549669.
- Hampf M, Dao NT, Hoan NT, Bernhardt R (2001). "Unequal crossing-over between aldosterone synthase and 11beta-hydroxylase genes causes congenital adrenal hyperplasia". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86 (9): 4445–52. doi:10.1210/jc.86.9.4445. PMID 11549691.
External links
Oxidoreductases: dioxygenases, including steroid hydroxylases (EC 1.14) 1.14.11: 2-oxoglutarate 1.14.13: NADH or NADPH Flavin-containing monooxygenase (FMO1, FMO2, FMO3, FMO4, FMO5) - Nitric oxide synthase (NOS1, NOS2, NOS3) - Cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase - Methane monooxygenase - 3A4 - Lanosterol 14 alpha-demethylase1.14.14: reduced flavin or flavoprotein 1.14.15: reduced iron-sulfur protein 1.14.16: reduced pteridine (BH4 dependent) 1.14.17: reduced ascorbate 1.14.18-19: other 1.14.99 - miscellaneous Mevalonate pathway To HMG-CoAAcetyl-Coenzyme A acetyltransferase · HMG-CoA synthase (regulated step)To DMAPPGeranyl-To cholesterol To lanosterol7-Dehydrocholesterol pathDesmosterol pathTo Bile acids Steroidogenesis To pregnenolonecortisol/cortisone: 17α-hydroxylase · 11β dehydrogenase (HSD11B1, HSD11B2)
both: 3β dehydrogenase · 21α-hydroxylase · 11β-hydroxylaseTo sex hormonesTo androgensTo estrogensOther/ungroupedCytochromes, oxygenases: cytochrome P450 (EC 1.14) CYP1 CYP2 CYP3 (CYP3A) CYP4 CYP5-20 CYP21-51 Mitochondrial proteins Outer membrane Intermembrane space Inner membrane oxidative phosphorylation (Coenzyme Q - cytochrome c reductase, Cytochrome c, NADH dehydrogenase, Succinate dehydrogenase)
pyrimidine metabolism (Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase)
mitochondrial shuttle (Malate-aspartate shuttle, Glycerol phosphate shuttle)
other (Glutamate aspartate transporter, Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, ATP synthase, Carnitine palmitoyltransferase II, Uncoupling protein)Matrix citric acid cycle (Citrate synthase, Aconitase, Isocitrate dehydrogenase, Oxoglutarate dehydrogenase, Succinyl coenzyme A synthetase, Fumarase, Malate dehydrogenase)
anaplerotic reactions (Aspartate transaminase, Glutamate dehydrogenase, Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex)
urea cycle (Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I, Ornithine transcarbamylase, N-Acetylglutamate synthase)
alcohol metabolism (ALDH2)
PMPCBOther/to be sorted steroidogenesis (Cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme, Steroid 11-beta-hydroxylase, Aldosterone synthase), Frataxin
Mitochondrial membrane transport protein (Mitochondrial permeability transition pore, Mitochondrial carrier)Mitochondrial DNA Complex I (MT-ND1, MT-ND2, MT-ND3, MT-ND4, MT-ND4L, MT-ND5, MT-ND6) - Complex III (MT-CYB) - Complex IV (MT-CO1, MT-CO2, MT-CO3)
ATP synthase (MT-ATP6, MT-ATP8)
tRNA (MT-TA, MT-TC, MT-TD, MT-TE, MT-TF, MT-TG, MT-TH, MT-TI, MT-TK, MT-TL1, MT-TL2, MT-TM, MT-TN, MT-TP, MT-TQ, MT-TR, MT-TS1, MT-TS2, MT-TT, MT-TV, MT-TW, MT-TY)Categories:- Human proteins
- Biochemistry stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.