- Monoamine oxidase
-
Monoamine oxidase Identifiers EC number 1.4.3.4 CAS number 9001-66-5 Databases IntEnz IntEnz view BRENDA BRENDA entry ExPASy NiceZyme view KEGG KEGG entry MetaCyc metabolic pathway PRIAM profile PDB structures RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum Gene Ontology AmiGO / EGO Search PMC articles PubMed articles monoamine oxidase A 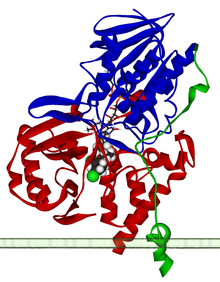
Ribbon diagram of a monomer of human MAO-A, with FAD and clorgiline bound, oriented as if attached to the outer membrane of a mitochondrion. From PDB 2BXS. Identifiers Symbol MAOA Entrez 4128 HUGO 6833 OMIM 309850 RefSeq NM_000240 UniProt P21397 Other data Locus Chr. X p11.4-p11.3 monoamine oxidase B 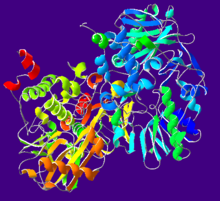
Cartoon diagram of human MAO-B. From PDB 1GOS. Identifiers Symbol MAOB Entrez 4129 HUGO 6834 OMIM 309860 RefSeq NM_000898 UniProt P27338 Other data Locus Chr. X p11.4-p11.3 L-Monoamine oxidases (MAO) (EC 1.4.3.4) are a family of enzymes that catalyze the oxidation of monoamines.[1][2] They are found bound to the outer membrane of mitochondria in most cell types in the body. The enzyme was originally discovered by Mary Bernheim in the liver and was named tyramine oxidase.[3][4] They belong to the protein family of flavin-containing amine oxidoreductases.
Contents
Subtypes and tissue distribution
In humans there are two types of MAO: MAO-A and MAO-B.[5]
- Both are found in neurons and astroglia.
- Outside the central nervous system:
- MAO-A is also found in the liver, gastrointestinal tract, and placenta.
- MAO-B is mostly found in blood platelets.
Function
Monoamine oxidases catalyze the oxidative deamination of monoamines. Oxygen is used to remove an amine group from a molecule, resulting in the corresponding aldehyde and ammonia. The general form of the catalyzed reaction (with R denoting an arbitrary group) is:

Monoamine oxidases contain the covalently bound cofactor FAD and are, thus, classified as flavoproteins.
Substrate specificities
They are well known enzymes in pharmacology, since they are the substrate for the action of a number of monoamine oxidase inhibitor drugs. MAO-A is particularly important in the catabolism of monoamines ingested in food. Both MAOs are also vital to the inactivation of monoaminergic neurotransmitters, for which they display different specificities.
- Serotonin, melatonin, norepinephrine, and epinephrine are mainly broken down by MAO-A.
- Phenethylamine and benzylamine are mainly broken down by MAO-B.
- Both forms break down dopamine, tyramine, and tryptamine equally[7].
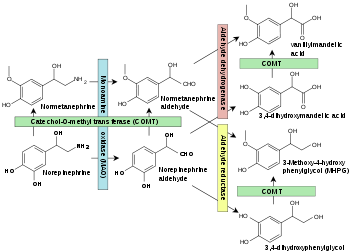
Specific reactions catalyzed by MAO include:
- Epinephrine or norepinephrine to 3,4-Dihydroxymandelic acid
- Metanephrine or normetanephrine to vanillylmandelic acid (VMA)
- Dopamine to dihydroxyphenylacetic acid
- 3-Methoxytyramine to homovanillic acid
Clinical significance
Because of the vital role that MAOs play in the inactivation of neurotransmitters, MAO dysfunction (too much or too little MAO activity) is thought to be responsible for a number of psychiatric and neurological disorders. For example, unusually high or low levels of MAOs in the body have been associated with depression,[8]schizophrenia,[9][10] substance abuse, attention deficit disorder, migraines, and irregular sexual maturation. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors are one of the major classes of drug prescribed for the treatment of depression, although they are often last-line treatment due to risk of the drug's interaction with diet or other drugs. Excessive levels of catecholamines (epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine) may lead to a hypertensive crisis, and excessive levels of serotonin may lead to serotonin syndrome.
In fact, MAO-A inhibitors act as antidepressant and antianxiety agents, whereas MAO-B inhibitors are used alone or in combination to treat Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases [11].
PET research has shown that MAO is also heavily depleted by use of tobacco cigarettes.[12]
Genetics
The genes encoding MAO-A and MAO-B are located side-by-side on the short arm of the X chromosome, and have about 70% sequence similarity. Rare mutations in the gene are associated with Brunner syndrome.
A study based on the Dunedin cohort concluded that maltreated children with a low-activity polymorphism in the promoter region of the MAO-A gene were more likely to develop antisocial conduct disorders than maltreated children with the high-activity variant.[13] Out of the 442 total males in the study (maltreated or not), 37% had the low activity variant. Of the 13 maltreated males with low MAO-A activity, 11 had been assessed as exhibiting adolescent conduct disorder and 4 were convicted for violent offenses. The suggested mechanism for this effect is the decreased ability of those with low MAO-A activity to quickly degrade norepinephrine, the synaptic neurotransmitter involved in sympathetic arousal and rage. This is alleged to provide direct support for the idea that genetic susceptibility to disease is not determined at birth, but varies with exposure to environmental influences. Note however that most of those with conduct disorder or convictions did not have low activity of MAO-A; maltreatment was found to have caused stronger predisposition for antisocial behavior than differences in MAO-A activity.
The claim that an interaction between low MAO-A activity and maltreatment would cause anti-social behavior has been criticized since the predisposition towards anti-social behavior could equally well have been caused by other genes inherited from abusive parents.[14]
A possible link between predisposition to novelty seeking and a genotype of the MAO-A gene has been found.[15]
A particular variant (or genotype) was over-represented in Māori, a Warrior gene. This supported earlier studies finding different proportions of variants in different ethnic groups. This is the case for many genetic variants, with 33% White/Non-Hispanic, 61% Asian/Pacific Islanders having the low-activity MAO-A promoter variant.[16]
See also
- Genetics and violence
References
- ^ Tipton KF, Boyce S, O'Sullivan J, Davey GP, Healy J (August 2004). "Monoamine oxidases: certainties and uncertainties". Curr. Med. Chem. 11 (15): 1965–82. PMID 15279561.
- ^ Edmondson DE, Mattevi A, Binda C, Li M, Hubálek F (August 2004). "Structure and mechanism of monoamine oxidase". Curr. Med. Chem. 11 (15): 1983–93. PMID 15279562.
- ^ Hare ML (1928). "Tyramine oxidase: A new enzyme system in liver". Biochem. J. 22 (4): 968–79. PMC 1252213. PMID 16744124. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1252213.
- ^ Slotkin TA (1999). "Mary Bernheim and the discovery of monoamine oxidase". Brain Res. Bull. 50 (5–6): 373. doi:10.1016/S0361-9230(99)00110-0. PMID 10643441.
- ^ Shih JC, Chen K (August 2004). "Regulation of MAO-A and MAO-B gene expression". Curr. Med. Chem. 11 (15): 1995–2005. PMID 15279563.
- ^ Figure 11-4 in: Rod Flower; Humphrey P. Rang; Maureen M. Dale; Ritter, James M. (2007). Rang & Dale's pharmacology. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 0-443-06911-5.
- ^ Kalgutkar, A. S.; Dalvie, D. K.; Castagnoli, N.; Taylor, T. J. Interactions of nitrogen-containing xenobiotics with monoamine oxidase (MAO) isozymes A and B: SAR studies on MAO substrates and inhibitors. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2001, 14, 1139–162.
- ^ Meyer JH, Ginovart N, Boovariwala A, Sagrati S, Hussey D, Garcia A, Young T, Praschak-Rieder N, Wilson AA, Houle S (November 2006). "Elevated monoamine oxidase a levels in the brain: an explanation for the monoamine imbalance of major depression". Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 63 (11): 1209–16. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.63.11.1209. PMID 17088501.
- ^ Domino EF, Khanna SS (March 1976). "Decreased blood platelet MAO activity in unmedicated chronic schizophrenic patients". Am J Psychiatry 133 (3): 323–6. PMID 943955.
- ^ Schildkraut JJ, Herzog JM, Orsulak PJ, Edelman SE, Shein HM, Frazier SH (April 1976). "Reduced platelet monoamine oxidase activity in a subgroup of schizophrenic patients". Am J Psychiatry 133 (4): 438–40. PMID 1267046.
- ^ Riederer, P.; Lachenmayer, L.; Laux, G. Clinical applications of MAO-inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 2033–2043.
- ^ Fowler JS, Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Pappas N, Logan J, MacGregor R, Alexoff D, Wolf AP, Warner D, Cilento R, Zezulkova I (1998). "Neuropharmacological actions of cigarette smoke: brain monoamine oxidase B (MAO B) inhibition". J Addict Dis 17 (1): 23–34. doi:10.1300/J069v17n01_03. PMID 9549600.
- ^ Caspi A, McClay J, Moffitt TE, Mill J, Martin J, Craig IW, Taylor A, Poulton R (August 2002). "Role of genotype in the cycle of violence in maltreated children". Science 297 (5582): 851–4. doi:10.1126/science.1072290. PMID 12161658.
- ^ Sesardic, Neven (2005). Making sense of heritability. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-82818-X.
- ^ Shiraishi H, Suzuki A, Fukasawa T, Aoshima T, Ujiie Y, Ishii G, Otani K (April 2006). "Monoamine oxidase A gene promoter polymorphism affects novelty seeking and reward dependence in healthy study participants". Psychiatr. Genet. 16 (2): 55–8. doi:10.1097/01.ypg.0000199447.62044.ef. PMID 16538181. Lay summary – medialifemagazine.com.
- ^ Sabol SZ, Hu S, Hamer D (September 1998). "A functional polymorphism in the monoamine oxidase A gene promoter". Hum. Genet. 103 (3): 273–9. doi:10.1007/s004390050816. PMID 9799080.
External links
- MAO-B Structure at eurekalert.org
- Calculated orientations of Monoamine oxidases in membrane
- Monoamine oxidase (MAO) at bmc.uu.se
- Slides showing the effects of tobacco smoking on MAO at nida.nih.gov
- Foods to avoid when taking MAO inhibitors at lycaeum.org
- Information Hyperlinked Over Proteins -- MAO-A
CH-NH2 oxidoreductases (EC 1.4) - primarily amino acid oxidoreductases 1.4.1: NAD/NADP acceptor 1.4.3: oxygen acceptor 1.4.4: disulfide acceptor 1.4.99: other acceptors monoamine anabolism: Tyrosine hydroxylase · Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase · Dopamine beta hydroxylase · Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase
catabolism: Catechol-O-methyl transferase · Monoamine oxidaseglutamate→GABAanabolism: Glutamate decarboxylase
catabolism: 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase · 4-aminobutyrate transaminasearginine→NO choline→Acetylcholine anabolism: Choline acetyltransferase
catabolism: Cholinesterase (Acetylcholinesterase, Butyrylcholinesterase)Categories:- Genes on chromosome X
- EC 1.4.3
- Integral membrane proteins
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.