- Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase
-
Dihydroorotate oxidase Identifiers EC number 1.3.3.1 CAS number 9029-03-2 Databases IntEnz IntEnz view BRENDA BRENDA entry ExPASy NiceZyme view KEGG KEGG entry MetaCyc metabolic pathway PRIAM profile PDB structures RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum Gene Ontology AmiGO / EGO Search PMC articles PubMed articles 
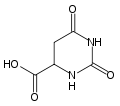
Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase from E. coli Identifiers Symbol DHO_dh Pfam PF01180 InterPro IPR001295 PROSITE PDOC00708 SCOP 1dor OPM family 59 OPM protein 1uum Available protein structures: Pfam structures PDB RCSB PDB; PDBe PDBsum structure summary Human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase Identifiers Symbol DHODH Entrez 1723 HUGO 2867 OMIM 126064 PDB 1D3G RefSeq NM_001361 UniProt Q02127 Other data EC number 1.3.3.1 Locus Chr. 16 q22 Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (EC 1.3.3.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the fourth step in the de novo biosynthesis of pyrimidine. It converts dihydroorotate to orotate:
- (S)-dihydroorotate + O2
 orotate + H2O2
orotate + H2O2
-
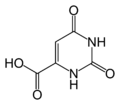
Orotic acid. Note the double bond in the ring.
Human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase is a ubiquitous FMN flavoprotein. In bacteria (gene pyrD), it is located on the inner side of the cytosolic membrane. In some yeasts, such as in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (gene URA1), it is a cytosolic protein, whereas, in other eukaryotes, it is found in the mitochondria.[1]
Contents
Human proteins containing this domain
DHODH; DPYD;
Clinical significance
The anti-inflammatory drug leflunomide has been shown to inhibit DHODH. Human DHODH has two domains: an alpha/beta-barrel domain containing the active site and an alpha-helical domain that forms the opening of a tunnel leading to the active site. Leflunomide has been shown to bind in this tunnel.[2] Leflunomide is being used for treatment of rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis.
Mutations in this gene have been shown to cause Miller syndrome [3] also known as Genee-Wiedemann syndrome, Wildervanck-Smith syndrome or post axial acrofacial dystosis (POADS).
References
- ^ Lacroute F, Thomas D, Nagy M (1992). "Divergent evolution of pyrimidine biosynthesis between anaerobic and aerobic yeasts". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89 (19): 8966–70. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.19.8966. PMC 50045. PMID 1409592. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=50045.
- ^ Liu S, Neidhardt EA, Grossman TH, Ocain T, Clardy J (January 2000). "Structures of human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase in complex with antiproliferative agents". Structure 8 (1): 25–33. doi:10.1016/S0969-2126(00)00077-0. PMID 10673429.
- ^ Ng SB, Buckingham KJ,Lee C, Bigham AW, Tabor HK, Dent KM, Huff CD, Shannon PT, Jabs EW, Nickerson DA, Shendure J, Bamshad MJ (December 2009). "Exome Sequencing identifies the cause of a mendelian disorder". Nature Genetics 42 (1): 30–5. doi:10.1038/ng.499. PMC 2847889. PMID 19915526. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2847889.
Further reading
- Rowland P, Björnberg O, Nielsen FS, Jensen KF, Larsen S (June 1998). "The crystal structure of Lactococcus lactis dihydroorotate dehydrogenase A complexed with the enzyme reaction product throws light on its enzymatic function". Protein Sci. 7 (6): 1269–79. doi:10.1002/pro.5560070601. PMC 2144028. PMID 9655329. http://www.proteinscience.org/cgi/content/abstract/7/6/1269.
External links
Oxidoreductases: CH-CH oxidoreductases (EC 1.3) 1.3.1: NAD/NADP acceptor 1.3.3: Oxygen acceptor 1.3.5: Quinone 1.3.99: Other acceptors Fumarate reductase · Butyryl CoA dehydrogenase · Acyl CoA dehydrogenase (ACADSB, ACADS) · 5α-reductase (SRD5A1, SRD5A2, SRD5A3) · Glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase · Isovaleryl coenzyme A dehydrogenaseB enzm: 1.1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8/10/11/13/14/15-18, 2.1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8, 2.7.10, 2.7.11-12, 3.1/2/3/4/5/6/7, 3.1.3.48, 3.4.21/22/23/24, 4.1/2/3/4/5/6, 5.1/2/3/4/99, 6.1-3/4/5-6 Purine metabolism AnabolismR5P->IMP: Ribose-phosphate diphosphokinase · Amidophosphoribosyltransferase · Phosphoribosylglycinamide formyltransferase · AIR synthetase (FGAM cyclase) · Phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase · Phosphoribosylaminoimidazolesuccinocarboxamide synthase · IMP synthase
IMP->AMP: Adenylosuccinate synthase · Adenylosuccinate lyase · reverse (AMP deaminase)
IMP->GMP: IMP dehydrogenase · GMP synthase · reverse (GMP reductase)CatabolismPyrimidine metabolism AnabolismCAD (Carbamoyl phosphate synthase II, Aspartate carbamoyltransferase, Dihydroorotase)
Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase · Orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase/Uridine monophosphate synthetase
CTP synthaseCatabolismDeoxyribonucleotides This article includes text from the public domain Pfam and InterPro IPR001295
This oxidoreductase article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. - (S)-dihydroorotate + O2