- Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
-
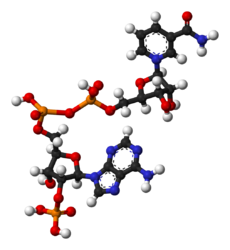
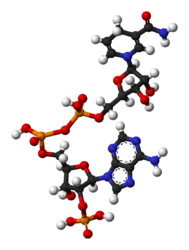
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate 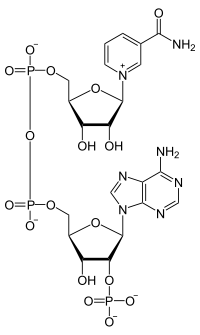
Identifiers CAS number 53-59-8 
PubChem 5885 ChemSpider 5674 
MeSH NADP ChEBI CHEBI:44409 
ChEMBL CHEMBL213053 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C(N)c1ccc[n+](c1)[C@@H]2O[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H]2O)COP([O-])(=O)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]5O[C@@H](n4cnc3c(ncnc34)N)[C@H](OP(=O)(O)O)[C@@H]5O
- InChI=1S/C21H28N7O17P3/c22-17-12-19(25-7-24-17)28(8-26-12)21-16(44-46(33,34)35)14(30)11(43-21)6-41-48(38,39)45-47(36,37)40-5-10-13(29)15(31)20(42-10)27-3-1-2-9(4-27)18(23)32/h1-4,7-8,10-11,13-16,20-21,29-31H,5-6H2,(H7-,22,23,24,25,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39)/t10-,11-,13-,14-,15-,16-,20-,21-/m1/s1

Key: XJLXINKUBYWONI-NNYOXOHSSA-N
InChI=1/C21H28N7O17P3/c22-17-12-19(25-7-24-17)28(8-26-12)21-16(44-46(33,34)35)14(30)11(43-21)6-41-48(38,39)45-47(36,37)40-5-10-13(29)15(31)20(42-10)27-3-1-2-9(4-27)18(23)32/h1-4,7-8,10-11,13-16,20-21,29-31H,5-6H2,(H7-,22,23,24,25,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39)/t10-,11-,13-,14-,15-,16-,20-,21-/m1/s1
Key: XJLXINKUBYWONI-NNYOXOHSBN
Properties Molecular formula C21H29N7O17P3 Molar mass 744.413  adenine dinucleotide phosphate (verify) (what is:
adenine dinucleotide phosphate (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP+ or TPN in older notation (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a coenzyme used in anabolic reactions, such as lipid and nucleic acid synthesis, which require NADPH as a reducing agent.
NADPH is the reduced form of NADP+. NADP+ differs from NAD+ in the presence of an additional phosphate group on the 2' position of the ribose ring that carries the adenine moiety.
Contents
In plants
In chlorophyll, NADP− is added by ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase in the last step of the electron chain of the light reactions of Photosynthesis. The NADPH produced is then used as reducing power for the biosynthetic reactions in the Calvin Cycle of photosynthesis. In its energized state, it is NADPH, now holding an extra electron. It is used primarily to create the proton gradient in chloroplasts during the light-dependent reactions.
In animals
The oxidative phase of the pentose phosphate pathway is the major source of NADPH in cells, producing approximately 60% of the NADPH required.
NADPH provides the reducing equivalents for biosynthetic reactions and the oxidation-reduction involved in protecting against the toxicity of ROS (reactive oxygen species), allowing the regeneration of GSH (reduced glutathione). NADPH is also used for anabolic pathways, such as lipid synthesis, cholesterol synthesis, and fatty acid chain elongation.
The NADPH system is also responsible for generating free radicals in immune cells. These radicals are used to destroy pathogens in a process termed the respiratory burst.[1]
It is the source of reducing equivalents for cytochrome P450 hydroxylation of aromatic compounds, steroids, alcohols, and drugs.
Ball-and-stick models of NADP+ and NADPH NADP+NADPHSee also
Enzyme cofactors Active forms TPP / ThDP (B1) · FMN, FAD (B2) · NAD+, NADH, NADP+, NADPH (B3) · Coenzyme A (B5) · PLP / P5P (B6) · Biotin (B7) · THFA / H4FA, DHFA / H2FA, MTHF (B9) · AdoCbl, MeCbl (B12) · Ascorbic Acid (C) · Phylloquinone (K1), Menaquinone (K2) · Coenzyme F420ATP · CTP · SAMe · PAPS · GSH · Coenzyme B · Cofactor F430 · Coenzyme M · Coenzyme Q · Heme / Haem (A, B, C, O) · Lipoic Acid · Methanofuran · Molybdopterin/Molybdenum cofactor · PQQ · THB / BH4 · THMPT / H4MPTBase forms vitamins: see vitaminsM: NUT
cof, enz, met
noco, nuvi, sysi/epon, met
drug(A8/11/12)
References
Categories:- Nucleotides
- Coenzymes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.