- 3'-Phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate
-
"PAPS" redirects here. For other uses, see Paps (disambiguation).
3'-Phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate 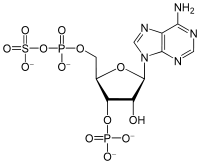 6-Amino-9-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3-hydroxy-5-
6-Amino-9-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3-hydroxy-5-[(hydroxy-sulfooxy-phosphoryl)oxymethyl]
-4-phosphonooxy-tetrahydrofuran-2-yl]purineOther namesPhosphoadenosine phosphosulfate
3'-Phospho-5'-adenylyl sulfateIdentifiers PubChem 10214 ChemSpider 9799 
ChEBI CHEBI:17980 IUPHAR ligand 1719 Jmol-3D images {{#if:S=C1=NC2=C(C(=N1)N)N=CN2C3C(C(C(O3) COP(=O)(O)OS(=O)(=O)O)OP(=O)(O)O)OO=S(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]3O[C@@H](n2cnc1c(ncnc12)N)[C@H](O)[C@@H]3OP(=O)(O)O|Image 1
Image 2- S=C1=NC2=C(C(=N1)N)N=CN2C3C(C(C(O3) COP(=O)(O)OS(=O)(=O)O)OP(=O)(O)O)O
O=S(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OC[C@H]3O[C@@H](n2cnc1c(ncnc12)N)[C@H](O)[C@@H]3OP(=O)(O)O
- InChI=1S/C10H15N5O13P2S/c11-8-5-9(13-2-12-8)15(3-14-5)10-6(16)7(27-29(17,18)19)4(26-10)1-25-30(20,21)28-31(22,23)24/h2-4,6-7,10,16H,1H2,(H,20,21)(H2,11,12,13)(H2,17,18,19)(H,22,23,24)/t4-,6-,7-,10-/m1/s1

Key: GACDQMDRPRGCTN-KQYNXXCUSA-N
InChI=1/C10H15N5O13P2S/c11-8-5-9(13-2-12-8)15(3-14-5)10-6(16)7(27-29(17,18)19)4(26-10)1-25-30(20,21)28-31(22,23)24/h2-4,6-7,10,16H,1H2,(H,20,21)(H2,11,12,13)(H2,17,18,19)(H,22,23,24)/t4-,6-,7-,10-/m1/s1
Key: GACDQMDRPRGCTN-KQYNXXCUBK
Properties Molecular formula C10H15N5O13P2S Molar mass 507.266  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references 3'-Phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate is a derivative of adenosine monophosphate that is phosphorylated at the 3' position and has a sulfate group attached to the 5' phosphate. This anion, abbreviated PAPS, serves as a coenzyme in sulfotransferase reactions. A related anion is adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate (APS), which is not phosphorylated at the 3' position.[1]
Formation and reduction
APS and PAPS are intermediates in the reduction of sulfate to sulfite, an exothermic conversion that is carried out by sulfate-reducing bacteria. In these organisms, sulfate serves as an electron acceptor, akin to the use of O2 as an electron acceptor by aerobic organisms. Sulfate is not reduced directly but must be activated by the formation of APS or PAPS. These carriers of activated sulfate are produced by reaction with ATP. The first reaction is catalysed by ATP sulfurase:
- SO42- + ATP → APS + PPi
The conversion of APS to PAPS is catalysed by APS kinase:
- APS + ATP → PAPS + ADP
Reduction of APS leads to sulfite, which is further reduced to hydrogen sulfide, which is excreted. This process is called dissimilatory sulfate reduction. Reduction of PAPS, a more elaborated sulfate ester, leads also to hydrogen sulfide. But in this case, the product is used in biosynthesis, e.g. for the production of cysteine. The latter process is called assimilatory sulfate reduction because the sulfate sulfur is assimilated.[2]
References
- ^ Negishi M, Pedersen LG, Petrotchenko E, et al. (2001). "Structure and function of sulfotransferases". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 390 (2): 149–57. doi:10.1006/abbi.2001.2368. PMID 11396917.
- ^ M. T. Madigan, J. M. Martinko, J. Parker “Brock Biology of Microorganisms” Prentice Hall, 1997. ISBN 0-13-520875-0.
Enzyme cofactors Active forms TPP / ThDP (B1) · FMN, FAD (B2) · NAD+, NADH, NADP+, NADPH (B3) · Coenzyme A (B5) · PLP / P5P (B6) · Biotin (B7) · THFA / H4FA, DHFA / H2FA, MTHF (B9) · AdoCbl, MeCbl (B12) · Ascorbic Acid (C) · Phylloquinone (K1), Menaquinone (K2) · Coenzyme F420ATP · CTP · SAMe · PAPS · GSH · Coenzyme B · Cofactor F430 · Coenzyme M · Coenzyme Q · Heme / Haem (A, B, C, O) · Lipoic Acid · Methanofuran · Molybdopterin/Molybdenum cofactor · PQQ · THB / BH4 · THMPT / H4MPTBase forms M: NUT
cof, enz, met
noco, nuvi, sysi/epon, met
drug(A8/11/12)
Categories:- Nucleotides
- Coenzymes
- Biochemistry stubs
- S=C1=NC2=C(C(=N1)N)N=CN2C3C(C(C(O3) COP(=O)(O)OS(=O)(=O)O)OP(=O)(O)O)O
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
