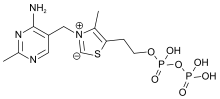
- Thiamine pyrophosphate
-
Thiamine pyrophosphate 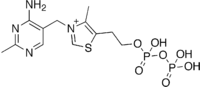 2-[3-[(4-amino-2-methylpyrimidin-5-yl)methyl]-4-methyl-1,3-thiazol-3-ium-5-yl]ethyl phosphono hydrogen phosphateOther namesThiamine diphosphate
2-[3-[(4-amino-2-methylpyrimidin-5-yl)methyl]-4-methyl-1,3-thiazol-3-ium-5-yl]ethyl phosphono hydrogen phosphateOther namesThiamine diphosphateIdentifiers CAS number 154-87-0 
PubChem 1132 ChemSpider 10670483 
UNII Q57971654Y 
MeSH Thiamine+pyrophosphate Jmol-3D images Image 1 - [Cl-].OP(=O)(O)OP(O)(O)=O.Cc2nc(N)c(C[n+]1csc(CCO)c1C)cn2
- InChI=1S/C12H17N4OS.ClH.H4O7P2/c1-8-11(3-4-17)18-7-16(8)6-10-5-14-9(2)15-12(10)13;;1-8(2,3)7-9(4,5)6/h5,7,17H,3-4,6H2,1-2H3,(H2,13,14,15);1H;(H2,1,2,3)(H2,4,5,6)/q+1;;/p-1

Key: NBSUTVXQOGUTJX-UHFFFAOYSA-M
InChI=1/C12H17N4OS.ClH.H4O7P2/c1-8-11(3-4-17)18-7-16(8)6-10-5-14-9(2)15-12(10)13;;1-8(2,3)7-9(4,5)6/h5,7,17H,3-4,6H2,1-2H3,(H2,13,14,15);1H;(H2,1,2,3)(H2,4,5,6)/q+1;;/p-1
Key: NBSUTVXQOGUTJX-REWHXWOFAB
Properties Molecular formula C12H19N4O7P2S+ Molar mass 425.314382 g/mol  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP or ThPP), or thiamine diphosphate (ThDP), is a thiamine (vitamin B1) derivative which is produced by the enzyme thiamine pyrophosphatase. Thiamine pyrophosphate is a coenzyme that is present in all living systems, in which it catalyzes several biochemical reactions. It was first discovered as an essential nutrient (vitamin) in humans through its link with the peripheral nervous system disease Beriberi, which results from a deficiency of thiamine in the diet.[1]
TPP works as a coenzyme in many enzymatic reactions, such as:
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex[2]
- Pyruvate decarboxylase complex in ethanol fermentation
- Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex
- Branched-chain amino acid dehydrogenase complex
- 2-hydroxyphytanoyl-CoA lyase
- Transketolase
Contents
Chemistry
Chemically, TPP consists of a pyrimidine ring which is connected to a thiazole ring, which is in turn connected to a pyrophosphate (diphosphate) functional group.
The part of TPP molecule that is most commonly involved in reactions is the thiazole ring, which contains nitrogen and sulfur. Thus, the thiazole ring is the "reagent portion" of the molecule. The C2 of this ring is capable of acting as an acid by donating its proton and forming a carbanion. Normally, reactions that form carbanions are highly unfavorable, but the positive charge on the tetravalent nitrogen just adjacent to the carbanion stabilizes the negative charge, making the reaction more favorable. (A compound with positive and negative charges on adjacent atoms is called an ylid or ylide, so sometimes the carbanion form of TPP is referred to as the "ylid form".[1][3]
Reaction mechanisms
In several reactions, including that of pyruvate decarboxylase, alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, and transketolase, TPP catalyses the reversible cleavage of a substrate compound at a carbon-carbon bond connecting a carbonyl group to an adjacent reactive group (usually a carboxylic acid or an alcohol). It achieves this in four basic steps:
- The carbanion of the TPP ylid nucleophilically attacks the carbonyl group on the substrate. (This forms a single bond between the TPP and the substrate.)
- The target bond on the substrate is broken, and its electrons are pushed towards the TPP. This creates a double bond between the substrate carbon and the TPP carbon and pushes the electrons in the N-C double bond in TPP entirely onto the nitrogen atom, reducing it from a positive to neutral form.
- In what is essentially the reverse of step two, the electrons push back in the opposite direction forming a new bond between the substrate carbon and another atom. (In the case of the decarboxylases, this creates a new carbon-hydrogen bond. In the case of transketolase, this attacks a new substrate molecule to form a new carbon-carbon bond.)
- In what is essentially the reverse of step one, the TPP-substrate bond is broken, reforming the TPP ylid and the substrate carbonyl.
References
- ^ a b Pavia, Donald L., Gary M. Lampman, George S. Kritz, Randall G. Engel (2006). Introduction to Organic Laboratory Techniques (4th Ed.). Thomson Brooks/Cole. pp. 304–5. ISBN 978-0-495-28069-9.
- ^ "PDBs for Biochemistry". Georgia State University. http://chemistry.gsu.edu/Glactone/PDB/Proteins/Krebs/1pyd.html. Retrieved 2009-02-07.
- ^ Voet, Donald; Judith Voet, Charlotte Pratt (2008). Fundamentals of Biochemistry. John Wiley & Sons Inc. p. 508. ISBN 978-0470-12930-2.
External links
Enzyme cofactors Active forms TPP / ThDP (B1) · FMN, FAD (B2) · NAD+, NADH, NADP+, NADPH (B3) · Coenzyme A (B5) · PLP / P5P (B6) · Biotin (B7) · THFA / H4FA, DHFA / H2FA, MTHF (B9) · AdoCbl, MeCbl (B12) · Ascorbic Acid (C) · Phylloquinone (K1), Menaquinone (K2) · Coenzyme F420ATP · CTP · SAMe · PAPS · GSH · Coenzyme B · Cofactor F430 · Coenzyme M · Coenzyme Q · Heme / Haem (A, B, C, O) · Lipoic Acid · Methanofuran · Molybdopterin/Molybdenum cofactor · PQQ · THB / BH4 · THMPT / H4MPTBase forms vitamins: see vitaminsM: NUT
cof, enz, met
noco, nuvi, sysi/epon, met
drug(A8/11/12)
Categories:- Cofactors
- Organophosphates
- Thiazoles
- Pyrimidines
- B vitamins
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.