- Phylloquinone
-
Phylloquinone 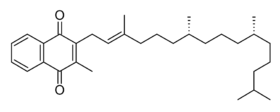 2-methyl-3-[(2E)-3,7,11,15-tetramethylhexadec-2-en-1-yl]naphthoquinone
2-methyl-3-[(2E)-3,7,11,15-tetramethylhexadec-2-en-1-yl]naphthoquinoneIdentifiers CAS number 84-80-0 PubChem 4812 ChemSpider 4447652 UNII A034SE7857 DrugBank DB01022 ChEBI CHEBI:18067 ChEMBL CHEMBL1550 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - CC1=C(C(=O)c2ccccc2C1=O)C/C=C(\C)/CCC[C@H](C)CCC[C@H](C)CCCC(C)C
- InChI=1S/C31H46O2/c1-22(2)12-9-13-23(3)14-10-15-24(4)16-11-17-25(5)20-21-27-26(6)30(32)28-18-7-8-19-29(28)31(27)33/h7-8,18-20,22-24H,9-17,21H2,1-6H3/b25-20+/t23-,24-/m1/s1
Key: MBWXNTAXLNYFJB-NKFFZRIASA-NInChI=1/C31H46O2/c1-22(2)12-9-13-23(3)14-10-15-24(4)16-11-17-25(5)20-21-27-26(6)30(32)28-18-7-8-19-29(28)31(27)33/h7-8,18-20,22-24H,9-17,21H2,1-6H3/b25-20+/t23-,24-/m1/s1
Key: MBWXNTAXLNYFJB-NKFFZRIABL
Properties Molecular formula C31H46O2 Molar mass 450.7 g mol−1 Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox references Phylloquinone is a polycyclic aromatic ketone, based on 2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone, with a 3-phytyl substituent.
It is a fat-soluble vitamin that is stable to air and moisture but decomposes in sunlight. It is found naturally in a wide variety of green plants.
Contents
Terminology
It is often called vitamin K1[1] or phytonadione. Sometimes a distinction is made with phylloquinone considered natural and phytonadione considered synthetic.[2]
A stereoisomer of phylloquinone is called vitamin k1 (note the difference in capitalization).
Mechanism
Its best known mechanism of action is as a cofactor in the formation of coagulation factors II (prothrombin), VII, IX and X by the liver. Vitamin K1 is commonly used to treat warfarin toxicity, and an antidote for coumatetralyl. It is also required for the formation of anticoagulant factors protein C and S. Vitamin K is also required for bone protein formation.
Phylloquinone is an electron acceptor in the electron transport chain of chloroplasts.
See also
References
- ^ Haroon Y, Shearer MJ, Rahim S, Gunn WG, McEnery G, Barkhan P (June 1982). "The content of phylloquinone (vitamin K1) in human milk, cows' milk and infant formula foods determined by high-performance liquid chromatography". J. Nutr. 112 (6): 1105–17. PMID 7086539. http://jn.nutrition.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=7086539.
- ^ "Vitamin K". http://www.umm.edu/altmed/articles/vitamin-k-000343.htm. Retrieved 2009-03-18.
Vitamins (A11) Fat soluble D2 (Ergosterol, Ergocalciferol#) · D3 (7-Dehydrocholesterol, Previtamin D3, Cholecalciferol, 25-hydroxycholecalciferol, Calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol), Calcitroic acid) · D4 (Dihydroergocalciferol) · D5 · D analogues (Dihydrotachysterol, Calcipotriol, Tacalcitol, Paricalcitol)Water soluble B1 (Thiamine#) · B2 (Riboflavin#) · B3 (Niacin, Nicotinamide#) · B5 (Pantothenic acid, Dexpanthenol, Pantethine) · B6 (Pyridoxine#, Pyridoxal phosphate, Pyridoxamine) · B7 (Biotin) · B9 (Folic acid, Dihydrofolic acid, Folinic acid) · B12 (Cyanocobalamin, Hydroxocobalamin, Methylcobalamin, Cobamamide) · CholineCombinations M: NUT
cof, enz, met
noco, nuvi, sysi/epon, met
drug(A8/11/12)
Antihemorrhagics (B02) Hemostatics
(coagulation)SystemicPhytomenadione (K1) • Menadione (K3)Other systemicEtamsylate • Carbazochrome • Batroxobin • thrombopoietin receptor agonist (Romiplostim, Eltrombopag)LocalAntifibrinolytics Categories:- Naphthoquinones
- Vitamers
- Vitamin K
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
