- Mitochondrial carrier
-
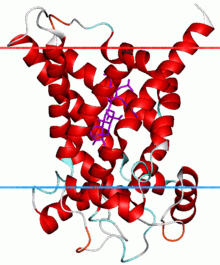
Mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier Identifiers Symbol Mito_carr Pfam PF00153 InterPro IPR001993 PROSITE PDOC00189 SCOP 1okc TCDB 2.A.29 OPM family 21 OPM protein 1okc Available protein structures: Pfam structures PDB RCSB PDB; PDBe PDBsum structure summary Mitochondrial carriers are proteins from the solute carrier family which transfers molecules across the membranes of the mitochondria.[1]
Contents
Function
A variety of substrate carrier proteins, which are involved in energy transfer, have been found in the inner membranes of mitochondria and other eukaryotic organelles such as the peroxisome.[2][3][4][5][6][7] Such proteins include: ADP, ATP carrier protein (ADP/ATP translocase); 2-oxoglutarate/malate carrier protein; phosphate carrier protein; tricarboxylate transport protein (or citrate transport protein); Graves disease carrier protein; yeast mitochondrial proteins MRS3 and MRS4; yeast mitochondrial FAD carrier protein; and many others.
Structure
All mitochondrial carriers are encoded by nuclear genes. Most contain a primary structure exhibiting regions of 100 homologous amino acid repeats, the N and C termini face the intermembrane space and there are six definable transmembrane segments in each carrier. All carriers also contain a common sequence, referred to as the MCF motif, in each repeated region, with some variation in one or two signature sequences.[1]
Amongst the members of the mitochondrial carrier family that have been identified, it is the ADP/ATP carrier (AAC) that is responsible for importing ADP into the mitochondria and exporting ATP out of the mitochondria and into the cytosol following synthesis.[8] The AAC is an integral membrane protein that is synthesised lacking a cleavable presequence, but instead contains internal targeting information.[9] It forms a dimer of two identical subunits[10] and consists of a basket shaped structure with six transmembrane helices that are tilted with respect to the membrane, 3 of them kinked at the level of proline residues.[1]
Substrates
Examples of transported compounds include:
- citrate - SLC25A1
- ornithine - SLC25A2, SLC25A15
- phosphate - SLC25A3, SLC25A23, SLC25A24 , SLC25A25
- adenine nucleotide - SLC25A4, SLC25A5, SLC25A6, SLC25A31
- dicarboxylate - SLC25A10
- oxoglutarate[disambiguation needed
 ] - SLC25A11
] - SLC25A11 - glutamate - SLC25A22
Examples
Human proteins containing this domain include:
- HDMCP, LOC153328, MCART1, MCART2, MCART6, MTCH1, MTCH2
- UCP1, UCP2, UCP3
- SLC25A1, SLC25A3, SLC25A4, SLC25A5, SLC25A6, SLC25A10, SLC25A11, SLC25A12, SLC25A13, SLC25A14, SLC25A16, SLC25A17, SLC25A18, SLC25A19, SLC25A21, SLC25A22, SLC25A23, SLC25A24, SLC25A25, SLC25A26, SLC25A27, SLC25A28, SLC25A29, SLC25A30, SLC25A31, SLC25A32, SLC25A33, SLC25A34, SLC25A35, SLC25A36, SLC25A37, SLC25A38, SLC25A39, SLC25A40, SLC25A41, SLC25A42, SLC25A43, SLC25A44, SLC25A45, SLC25A46
External links
References
- ^ a b c Nury H, Dahout-Gonzalez C, Trézéguet V, Lauquin GJ, Brandolin G, Pebay-Peyroula E (2006). "Relations between structure and function of the mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier". Annu. Rev. Biochem. 75: 713–41. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.75.103004.142747. PMID 16756509.
- ^ Klingenberg M (1990). "Mechanism and evolution of the uncoupling protein of brown adipose tissue". Trends Biochem. Sci. 15 (3): 108–112. doi:10.1016/0968-0004(90)90194-G. PMID 2158156.
- ^ Walker JE (1992). "The mitochondrial transporter family". Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2 (4): 519–526. doi:10.1016/0959-440X(92)90081-H.
- ^ Kuan J, Saier Jr MH (1993). "Expansion of the mitochondrial carrier family". Res. Microbiol. 144 (8): 671–672. doi:10.1016/0923-2508(93)90073-B. PMID 8140286.
- ^ Lawson JE, Nelson DR, Klingenberg M, Douglas MG (1993). "Site-directed mutagenesis of the yeast mitochondrial ADP/ATP translocator. Six arginines and one lysine are essential". J. Mol. Biol. 230 (4): 1159–1170. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1993.1233. PMID 8487299.
- ^ Palmieri F (1994). "Mitochondrial carrier proteins". FEBS Lett. 346 (1): 48–54. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(94)00329-7. PMID 8206158.
- ^ Jank B, Schweyen RJ, Link TA, Habermann B (1993). "PMP47, a peroxisomal homologue of mitochondrial solute carrier proteins". Trends Biochem. Sci. 18 (11): 427–428. PMID 8291088.
- ^ Endres M, Neupert W, Brunner M (June 1999). "Transport of the ADP/ATP carrier of mitochondria from the TOM complex to the TIM22.54 complex". EMBO J. 18 (12): 3214–21. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.12.3214. PMC 1171402. PMID 10369662. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1171402.
- ^ Ryan MT, Müller H, Pfanner N (July 1999). "Functional staging of ADP/ATP carrier translocation across the outer mitochondrial membrane". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (29): 20619–27. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.29.20619. PMID 10400693.
- ^ Falconi M, Chillemi G, Di Marino D, D'Annessa I, Morozzo della Rocca B, Palmieri L, Desideri A (November 2006). "Structural dynamics of the mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier revealed by molecular dynamics simulation studies". Proteins 65 (3): 681–91. doi:10.1002/prot.21102. PMID 16988954.
SLC11–20 - (12) electroneutral cation-Cl cotransporter (SLC12A1, SLC12A1, SLC12A2, SLC12A3, SLC12A4, SLC12A5, SLC12A6, SLC12A7, SLC12A8, SLC12A9)
- (14) urea transporter (SLC14A1, SLC14A2)
- (15) proton oligopeptide cotransporter (SLC15A1, SLC15A2, SLC15A3, SLC15A4)
- (16) monocarboxylate transporter (SLC16A1, SLC16A2, SLC16A3, SLC16A4, SLC16A5, SLC16A6, SLC16A7, SLC16A8, SLC16A9, SLC16A10, SLC16A11, SLC16A12, SLC16A13, SLC16A14)
SLC21–30 - (21) organic anion transporting (SLCO1A2, SLCO1B1, SLCO1B3, SLCO1B4, SLCO1C1) (SLCO2A1, SLCO2B1) (SLCO3A1) (SLCO4A1, SLCO4C1) (SLCO5A1) (SLCO6A1)
- (22) organic cation/anion/zwitterion transporter (SLC22A1, SLC22A2, SLC22A3, SLC22A4, SLC22A5, SLC22A6, SLC22A7, SLC22A8, SLC22A9, SLC22A10, SLC22A11, SLC22A12, SLC22A13, SLC22A14, SLC22A15, SLC22A16, SLC22A17, SLC22A18, SLC22A19, SLC22A20)
- (24) Na+/(Ca2+-K+) exchanger (SLC24A1, SLC24A2, SLC24A3, SLC24A4, SLC24A5, SLC24A6)
- (25) mitochondrial carrier (SLC25A1, SLC25A2, SLC25A3, SLC25A4, SLC25A5, SLC25A6, SLC25A7, SLC25A8, SLC25A9, SLC25A10, SLC25A11, SLC25A12, SLC25A13, SLC25A14, SLC25A15, SLC25A16, SLC25A17, SLC25A18, SLC25A19, SLC25A20, SLC25A21, SLC25A22, SLC25A23, SLC25A24, SLC25A25, SLC25A26, SLC25A27, SLC25A28, SLC25A29, SLC25A30, SLC25A31, SLC25A32, SLC25A33, SLC25A34, SLC25A35, SLC25A36, SLC25A37, SLC25A38, SLC25A39, SLC25A40, SLC25A41, SLC25A42, SLC25A43, SLC25A44, SLC25A45, SLC25A46)
SLC31–40 - (32) vesicular inhibitory amino-acid transporter (SLC32A1)
- (33) Acetyl-CoA transporter (SLC33A1)
- (35) nucleoside-sugar transporter (SLC35A1, SLC35A2, SLC35A3, SLC35A4, SLC35A5) (SLC35B1, SLC35B2, SLC35B3, SLC35B4) (SLC35C1, SLC35C2) (SLC35D1, SLC35D2, SLC35D3) (SLC35E1, SLC35E2, SLC35E3, SLC35E4)
- (36) proton-coupled amino-acid transporter (SLC36A1, SLC36A2, SLC36A3, SLC36A4)36A2 ·
- (37) sugar-phosphate/phosphate exchanger (SLC37A1, SLC37A2, SLC37A3, SLC37A4)
- (38) System A & N, sodium-coupled neutral amino-acid transporter (SLC38A1, SLC38A2, SLC38A3, SLC38A4, SLC38A5, SLC38A6, SLC38A10)
- (39) metal ion transporter (SLC39A1, SLC39A2, SLC39A3, SLC39A4, SLC39A5, SLC39A6, SLC39A7, SLC39A8, SLC39A9, SLC39A10, SLC39A11, SLC39A12, SLC39A13, SLC39A14)
- (40) basolateral iron transporter (SLC40A1)
SLC41–48 SLCO1–4
see also solute carrier disordersIon pumps
B memb: cead, trns (1A, 1C, 1F, 2A, 3A1, 3A2-3, 3D), othrCategories:- Protein domains
- Protein families
- Transmembrane proteins
- Membrane protein stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
