- Mitochondrial trifunctional protein
-
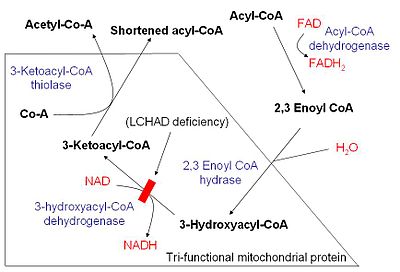 Schematic demonstrating mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation and effects of long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency, LCHAD deficiency
Schematic demonstrating mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation and effects of long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency, LCHAD deficiency
Mitochondrial trifunctional protein is a protein which catalyzes several reactions in beta oxidation. It has two subunits:
The three functions are long-chain 3-hydroxy acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase, 2-enoyl coenzyme A (CoA) hydratase, and long-chain 3-ketoacyl CoA thiolase.[1]
Pathology
Disorders are associated with:
References
External links
Synthesis Malonyl-CoA synthesisBeta-ketoacyl-ACP synthase · Β-Ketoacyl ACP reductase · 3-Hydroxyacyl ACP dehydrase · Enoyl ACP reductaseFatty acid desaturasesTriacyl glycerolDegradation Acyl transportGeneralOtherHydroxyacyl-Coenzyme A dehydrogenaseTo acetyl-CoAMitochondrial proteins Outer membrane Intermembrane space Inner membrane oxidative phosphorylation (Coenzyme Q - cytochrome c reductase, Cytochrome c, NADH dehydrogenase, Succinate dehydrogenase)
pyrimidine metabolism (Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase)
mitochondrial shuttle (Malate-aspartate shuttle, Glycerol phosphate shuttle)
other (Glutamate aspartate transporter, Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, ATP synthase, Carnitine palmitoyltransferase II, Uncoupling protein)Matrix citric acid cycle (Citrate synthase, Aconitase, Isocitrate dehydrogenase, Oxoglutarate dehydrogenase, Succinyl coenzyme A synthetase, Fumarase, Malate dehydrogenase)
anaplerotic reactions (Aspartate transaminase, Glutamate dehydrogenase, Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex)
urea cycle (Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I, Ornithine transcarbamylase, N-Acetylglutamate synthase)
alcohol metabolism (ALDH2)
PMPCBOther/to be sorted Mitochondrial DNA Complex I (MT-ND1, MT-ND2, MT-ND3, MT-ND4, MT-ND4L, MT-ND5, MT-ND6) - Complex III (MT-CYB) - Complex IV (MT-CO1, MT-CO2, MT-CO3)
ATP synthase (MT-ATP6, MT-ATP8)
tRNA (MT-TA, MT-TC, MT-TD, MT-TE, MT-TF, MT-TG, MT-TH, MT-TI, MT-TK, MT-TL1, MT-TL2, MT-TM, MT-TN, MT-TP, MT-TQ, MT-TR, MT-TS1, MT-TS2, MT-TT, MT-TV, MT-TW, MT-TY)see also mitochondrial diseases
B strc: edmb (perx), skel (ctrs), epit, cili, mito, nucl (chro)
This protein-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
