- Nucleotide salvage
-
A salvage pathway is a pathway in which nucleotides (purine and pyrimidine) are synthesized from intermediates in the degradative pathway for nucleotides.
Salvage pathways are used to recover bases and nucleosides that are formed during degradation of RNA and DNA. This is important in some organs because some tissues cannot undergo de novo synthesis.
The salvaged bases and nucleosides can then be converted back into nucleotides.
Contents
Substrates
The salvage pathway requires distinct substrates:
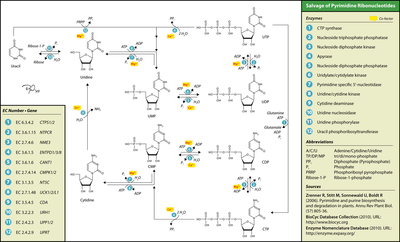
Pyrimidines
Uridine phosphorylase adds ribose-1-phospate to the free base uracil, forming uridine monophosphate. Uridine kinase then phosphorylates this nucleoside into its diphosphate and triphosphate forms. Deoxythymidine phosphorylase adds deoxyribose-1-phosphate to thymine, forming deoxythymidine monophosphate. Thymidine kinase can then phosphorylate this compound to deoxythymidine diphosphate and triphosphate.
Purines
Phosphoribosyltransferases add activated ribose-5-phosphate (called phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate or PRPP) to bases, creating nucleotide monophosphates. There are two types of phosphoribosyltransferases: adenosine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT) and hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT). Lesch-Nyhan syndrome is associated with a deficiency of HGPRT.
Nucleoside Enzyme Nucleotide hypoxanthine hypoxanthine/guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (HGPRT) IMP guanine hypoxanthine/guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (HGPRT) GMP adenine adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT) AMP External links
Metabolism (Catabolism, Anabolism) General Cellular respiration Aerobic RespirationSpecific paths HumanNonhumanOtherNucleotide metabolismOtherbiochemical families: prot · nucl · carb (glpr, alco, glys) · lipd (fata/i, phld, strd, gllp, eico) · amac/i · ncbs/i · ttpy/iPurine metabolism AnabolismR5P->IMP: Ribose-phosphate diphosphokinase · Amidophosphoribosyltransferase · Phosphoribosylglycinamide formyltransferase · AIR synthetase (FGAM cyclase) · Phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase · Phosphoribosylaminoimidazolesuccinocarboxamide synthase · IMP synthase
IMP->AMP: Adenylosuccinate synthase · Adenylosuccinate lyase · reverse (AMP deaminase)
IMP->GMP: IMP dehydrogenase · GMP synthase · reverse (GMP reductase)Nucleotide salvageCatabolismPyrimidine metabolism AnabolismCatabolismDeoxyribonucleotides Categories:- Genetics
- Genetics stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.