- Norepinephrine
-
Norepinephrine[1] 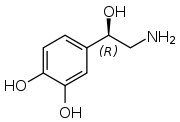
 4-[(1R)-2-amino-1-hydroxyethyl]benzene-1,2-diolOther names
4-[(1R)-2-amino-1-hydroxyethyl]benzene-1,2-diolOther namesIdentifiers CAS number (l) 51-41-2 (l)  , 138-65-8(dl)
, 138-65-8(dl)PubChem 439260 ChemSpider 388394 
DrugBank DB00368 KEGG D00076 
ChEBI CHEBI:18357 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1437 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - Oc1ccc(cc1O)[C@@H](O)CN
Properties Molecular formula C8H11NO3 Molar mass 169.18 g mol−1 Density 1.397±0.06 g/cm^3 (20° C and 760 Torr)[2] Melting point L: 216.5–218 °C (decomp.)
D/L: 191 °C (decomp.)Boiling point 442.6±40.0 °C (760 Torr)[2]
Vapor pressure 1.30e-8 Torr[2] Acidity (pKa) 9.57±0.10[2]  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Norepinephrine (INN) (abbreviated norepi or NE) is the US name for noradrenaline (BAN) (abbreviated NA or NAd), a catecholamine with multiple roles including as a hormone and a neurotransmitter.[3] Areas of the body that produce or are affected by norepinephrine are described as noradrenergic.
The terms noradrenaline (from the Latin) and norepinephrine (derived from Greek) are interchangeable, with noradrenaline the common name in most parts of the world. However, to avoid confusion and achieve consistency medical authorities have promoted norepinephrine as the favoured nomenclature, and this is the term used throughout this article.
One of the most important functions of norepinephrine is its role as the neurotransmitter released from the sympathetic neurons affecting the heart. An increase in norepinephrine from the sympathetic nervous system increases the rate of contractions.[4]
As a stress hormone, norepinephrine affects parts of the brain, such as the amygdala, where attention and responses are controlled.[5] Along with epinephrine, norepinephrine also underlies the fight-or-flight response, directly increasing heart rate, triggering the release of glucose from energy stores, and increasing blood flow to skeletal muscle. It increases the brain's oxygen supply.[6] Norepinephrine can also suppress neuroinflammation when released diffusely in the brain from the locus coeruleus.[7]
When norepinephrine acts as a drug it increases blood pressure by increasing vascular tone (tension of muscles) through α-adrenergic receptor activation. The resulting increase in vascular resistance triggers a compensatory reflex that overcomes the direct homeostatic effect of that increase on the heart, called the baroreceptor reflex, which otherwise would result in a drop in heart rate called reflex bradycardia.
Norepinephrine is synthesized from dopamine by dopamine β-hydroxylase.[8] It is released from the adrenal medulla into the blood as a hormone, and is also a neurotransmitter in the central nervous system and sympathetic nervous system where it is released from noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus. The actions of norepinephrine are carried out via the binding to adrenergic receptors.
Contents
Chemistry
Norepinephrine is a catecholamine and a phenethylamine. The natural stereoisomer is L-(−)-(R)-norepinephrine. The term "norepinephrine" is derived from the chemical prefix nor-, which indicates that norepinephrine is the next lower homolog of epinephrine. The two structures differ only in that epinephrine has a methyl group attached to its nitrogen, while the methyl group is replaced by a hydrogen atom in norepinephrine. The prefix nor- is likely derived as an abbreviation of the word "normal", used to indicate a demethylated compound.[9][10][11]
Origins
Norepinephrine is released when a host of physiological changes are activated by a stressful event.
In the brain, this is caused in part by activation of an area of the brain stems called the locus ceruleus. This nucleus is the origin of most norepinephrine pathways in the brain. Noradrenergic neurons project bilaterally (send signals to both sides of the brain) from the locus ceruleus along distinct pathways to many locations, including the cerebral cortex, limbic system, and the spinal cord, forming a neurotransmitter system.
Norepinephrine is also released from postganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system, to transmit the fight-or-flight response in each tissue respectively. The adrenal medulla can also be counted to such postganglionic nerve cells, although they release norepinephrine into the blood.
Norepinephrine system
The noradrenergic neurons in the brain form a neurotransmitter system, that, when activated, exerts effects on large areas of the brain. The effects are alertness and arousal, and influences on the reward system.
Anatomically, the noradrenergic neurons originate both in the locus coeruleus and the lateral tegmental field. The axons of the neurons in the locus coeruleus act on adrenergic receptors in:
On the other hand, axons of neurons of the lateral tegmental field act on adrenergic receptors in hypothalamus, for example.
This structure explains some of the clinical uses of norepinephrine, since a modification of the system affects large areas of the brain.
Mechanism
Norepinephrine is synthesized from tyrosine as a precursor, and packed into synaptic vesicles. It performs its action by being released into the synaptic cleft, where it acts on adrenergic receptors, followed by the signal termination, either by degradation of norepinephrine, or by uptake by surrounding cells.
Biosynthesis
Norepinephrine is synthesized by a series of enzymatic steps in the adrenal medulla and postganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system from the amino acid tyrosine:
Vesicular transport
Between the decarboxylation and the final β-oxidation, norepinephrine is transported into synaptic vesicles. This is accomplished by vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT) in the lipid bilayer. This transporter has equal affinity for norepinephrine, epinephrine and isoprenaline.[12]
Release
To perform its functions, norepinephrine needs to be released from synaptic vesicles. Many substances modulate this release, some inhibiting it and some stimulating it.
For instance, there are inhibitory α2 adrenergic receptors presynaptically, that gives negative feedback on release by homotropic modulation.
Receptor binding
Main article: Adrenergic receptorNorepinephrine performs its actions on the target cell by binding to and activating adrenergic receptors. The target cell expression of different types of receptors determines the ultimate cellular effect, and thus norepinephrine has different actions on different cell types.
Termination
Signal termination is a result of reuptake and degradation.
Uptake
Extracellular uptake of norepinephrine into the cytosol is either done presynaptically (uptake 1) or by non-neuronal cells in the vicinity (uptake 2). Furthermore, there is a vesicular uptake mechanism from the cytosol into synaptic vesicles.
Comparison of norepinephrine uptake Uptake Transporter Vmax (nmol/g/min)[13] KM[13] Specificity[14] Location Other substrates[14] Inhibitors [15] Uptake 1 Norepinephrine transporter[15] 1.2 0.3 norepinephrine > epinephrine > isoprenaline presynaptic - methylnoradrenaline (nasal decongestant)
- tyramine
- guanethidine
Uptake 2 100 250 epinephrine > norepinephrine > isoprenaline cell membrane of non-neuronal cells[12] Vesicular VMAT[15] -[15] ~0.2[15] norepinephrine > epinephrine > isoprenaline[15] Synaptic vesicle membrane[15] Degradation
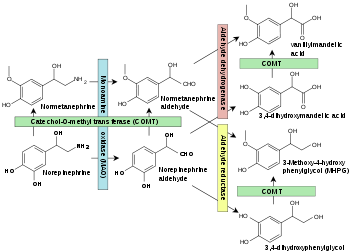 Norepinephrine degradation. Enzymes are shown in boxes.[16]
Norepinephrine degradation. Enzymes are shown in boxes.[16]
In mammals, norepinephrine is rapidly degraded to various metabolites. The principal metabolites are:
- Normetanephrine (via the enzyme catechol-O-methyl transferase, COMT)
- 3,4-Dihydroxymandelic acid (via monoamine oxidase, MAO)
- Vanillylmandelic acid (3-Methoxy-4-hydroxymandelic acid), also referred to as vanilmandelate or VMA (via MAO)
- 3-Methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylethylene glycol, "MHPG" or "MOPEG" (via MAO)
- Epinephrine (via PNMT)[17]
In the periphery, VMA is the major metabolite of catecholamines, and is excreted unconjugated in the urine. A minor metabolite (although the major one in the central nervous system) is MHPG, which is partly conjugated to sulfate or glucuronide derivatives and excreted in the urine.[18]
Noradrenergic agents
By indication
Norepinephrine may be used for the indications attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, depression and hypotension. Norepinephrine, as with other catecholamines, itself cannot cross the blood-brain barrier, so drugs such as amphetamines are necessary to increase brain levels.
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder
Norepinephrine, along with dopamine, has come to be recognized as playing a large role in attention and focus. For people with ADHD, psychostimulant medications such as methylphenidate (Ritalin/Concerta), dextroamphetamine (Dexedrine), and Adderall (a mixture of dextroamphetamine and racemic amphetamine salts) are prescribed to help increase levels of norepinephrine and dopamine. Atomoxetine (Strattera) is a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, and is a unique ADHD medication, as it affects only norepinephrine, rather than dopamine. As a result, Strattera has a lower abuse potential. However, it may not be as effective as the psychostimulants are with many people who have ADHD. Consulting with a physician is needed to find the appropriate medication and dosage. (Other SNRIs, currently approved as antidepressants, have also been used off-label for treatment of ADHD.)
Depression
Main article: Major depressive disorderDifferences in the norepinephrine system are implicated in depression. Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors are antidepressants that treat depression by increasing the amount of serotonin and norepinephrine available to postsynaptic cells in the brain. There is some recent evidence implying that SNRIs may also increase dopamine transmission.[19] This is because SNRIs work by inhibiting reuptake, i.e. preventing the serotonin and norepinephrine transporters from taking their respective neurotransmitters back to their storage vesicles for later use. If the norepinephrine transporter normally recycles some dopamine too, then SNRIs will also enhance dopaminergic transmission. Therefore, the antidepressant effects associated with increasing norepinephrine levels may also be partly or largely due to the concurrent increase in dopamine (particularly in the prefrontal cortex of the brain).
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) increase norepinephrine activity as well. Most of them also increase serotonin activity, but tend to produce unwanted side effects due to the nonspecific inactivation of histamine, acetylcholine and alpha-1 adrenergic receptors. Common side effects include sedation, dry mouth, constipation, sinus tachycardia, memory impairment, orthostatic hypotension, blurred vision and weight gain.[20] For this reason, they have largely been replaced by newer selective reuptake drugs. These include the SSRIs, e.g. fluoxetine (Prozac), which however have little or no effect on norepinephrine, and the newer SNRIs described above, such as venlafaxine (Effexor) and duloxetine (Cymbalta).
Schizophrenia
A commonly-known side effect associated with schizo-affective patients known as akathisia (commonly mistaken for schizophrenic symptoms) was found to be associated with increased levels of norepinephrine.[21] Data supports the efficacy of novel antipsychotics which deal with agonism of the NMDA glutamate receptors,[22] associated with regulating uptake of norepinephrine,[23] which in turn affects the trafficking of glutamate.[24] This suggests that schizophrenia may in fact have a greater association with abnormal norepinephrine-reuptake kinetics and less with dopamine, which may actually be responsible for a large part of the mechanism of glutamate release.[24]
Hypotension
Norepinephrine is also used as a vasopressor medication (for example, brand name Levophed) for patients with critical hypotension. It is given intravenously and acts on both α1 and α2 adrenergic receptors to cause vasoconstriction. Its effects are often limited to the increasing of blood pressure through agonist activity on α1 and α2 receptors and causing a resultant increase in peripheral vascular resistance. At high doses, and especially when it is combined with other vasopressors, it can lead to limb ischemia and limb death. Norepinephrine is mainly used to treat patients in vasodilatory shock states such as septic shock and neurogenic shock while showing fewer averse side effects compared to dopamine treatment.[25]
By site of action
Different medications affecting norepinephrine function have their targets at different points in the mechanism, from synthesis to signal termination.
Synthesis modulators
α-methyltyrosine is a substance that intervenes in norepinephrine synthesis by substituting tyrosine for tyrosine hydroxylase, and blocking this enzyme.
Vesicular transport modulators
This transportation can be inhibited by reserpine and tetrabenazine.[12]
Release modulators
Inhibitors of norepinephrine release Substance[26] Receptor[26] acetylcholine muscarinic receptor norepinephrine (itself)/epinephrine α2 receptor 5-HT 5-HT receptor adenosine P1 receptor PGE EP receptor histamine H2 receptor enkephalin δ receptor dopamine D2 receptor ATP P2 receptor Stimulators of norepinephrine release Substance[26] Receptor[26] adrenaline β2 receptor angiotensin II AT1 receptor Receptor binding modulators
Examples include alpha blockers for the α-receptors, and beta blockers for the β-receptors.
Termination modulators
Uptake modulators
Inhibitors[12] of uptake 1 include:
Inhibitors[12] of uptake 2 include:
Anti-Inflammatory agent role in Alzheimer’s Disease
The norepinephrine from locus ceruleus cells in addition to its neurotransmitter role locally diffuses from "varicosities". As such it provides an endogenous anti-inflammatory agent in the microenvironment around the neurons, glial cells, and blood vessels in the neocortex and hippocampus.[7] Up to 70% of norepinephrine projecting cells are lost in Alzheimer’s Disease. It has been shown that norepinephrine stimulates mouse microglia to suppress Aβ-induced production of cytokines and their phagocytosis of Aβ suggesting this loss might have a role in causing this disease.[7]
Nutritional sources
 Shown here is the chemical structure of tyrosine. The biosynthesis of norepinephrine depends upon the presence of tyrosine, an amino acid building block of many proteins in meat, nuts and eggs, for example.
Shown here is the chemical structure of tyrosine. The biosynthesis of norepinephrine depends upon the presence of tyrosine, an amino acid building block of many proteins in meat, nuts and eggs, for example.
The synthesis of norepinephrine depends on the presence of tyrosine, an amino acid found in proteins such as meat, nuts, and eggs. Dairy products such as cheese also contain high amounts of tyrosine (the amino acid is named for "tyros", the Greek word for cheese). However, the body can synthesise tyrosine from phenylalanine, an essential amino acid. Tyrosine is the precursor to dopamine, which in turn is a precursor to epinephrine and norepinephrine.
Serotonin, a neurotransmitter that is in many ways the opposite of the catecholamines, is also directly synthesized from an amino acid (tryptophan). However, tryptophan has a somewhat different process of degradation. When serotonin is catabolized in the body, it does not break down into useful substrates in the way that dopamine is further degraded into epinephrine and norepinephrine. Instead, it breaks down into 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIA), an organic acid which may be harmful in high amounts. Tryptophan can further be catabolized into kynurenate, quinolinate, and picolinate, harmful substances that are generally regarded as markers of bodily inflammation.
Banana peels contain significant amounts of norepinephrine and dopamine.[27]
See also
External links
- Mental Health: A report of surgeon general. Etiology of Anxiety Disorders
- http://www.biopsychiatry.com/nordop.htm
References
- ^ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 6612.
- ^ a b c d e "51-41-2". SciFinder. SciFinder. https://scifinder-cas-org.proxy.library.nd.edu:9443/scifinder/view/scifinder/scifinderExplore.jsf. Retrieved 14 November 2011.
- ^ "Norepinephrine definition". dictionary.reference.com. http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/Norepinephrine. Retrieved 2008-11-24.
- ^ Guyton, Arthur; Hall, John (2006). "Chapter 10: Rhythmical Excitation of the Heart". In Gruliow, Rebecca (Book). Textbook of Medical Physiology (11th ed.). Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: Elsevier Inc.. p. 122. ISBN 0-7216-0240-1.
- ^ Tanaka2000 Tanaka M, et al. (2000). Noradrenaline systems in the hypothalamus, amygdala and locus coeruleus are involved in the provocation of anxiety: basic studies. doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(00)00569-0
- ^ The Hormone Foundation. "The Endocrine System & Types of Hormones."
- ^ a b c Heneka MT, Nadrigny F, Regen T, Martinez-Hernandez A, Dumitrescu-Ozimek L, Terwel D, Jardanhazi-Kurutz D, Walter J, Kirchhoff F, Hanisch UK, Kummer MP. (2010). Locus ceruleus controls Alzheimer's disease pathology by modulating microglial functions through norepinephrine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 17:6058–6063 doi:10.1073/pnas.0909586107 PMID 20231476
- ^ "Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology" (PDF). Elsevier International. http://www.fleshandbones.com/readingroom/pdf/225.pdf. Link redirected to commercial site!
- ^ Sharma B, Satish A, Kumar R (1999). Dictionary of Drugs. Anmol Publications. ISBN 8126118202. http://books.google.com/?id=3JvArcoG2voC&printsec=frontcover#PPA166.
- ^ Gaddum JH (June 1956). "The Prefix 'Nor' in Chemical Nomenclature". Nature 177 (1046): 1046–1046. doi:10.1038/1771046b0.
- ^ Matthiessen A, Foster GC (1868). "Researches into the chemical constitution of narcotine and of its products of decomposition". Journal of the Chemical Society 358. http://books.google.com/?id=tKsOAAAAIAAJ&printsec=titlepage.
- ^ a b c d e Rang, H. P. (2003). Pharmacology. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 0-443-07145-4. Page 167
- ^ a b These values are from rat heart. Unless else specified in table, then ref is: Rang, H. P. (2003). Pharmacology. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 0-443-07145-4. Page 167
- ^ a b Unless else specified in table, then ref is: Rang, H. P. (2003). Pharmacology. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 0-443-07145-4. Page 167
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Unless else specified in boxes, then ref is: Rod Flower; Humphrey P. Rang; Maureen M. Dale; Ritter, James M. (2007). Rang & Dale's pharmacology. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 0-443-06911-5.
- ^ Figure 11-4 in: Rod Flower; Humphrey P. Rang; Maureen M. Dale; Ritter, James M. (2007). Rang & Dale's pharmacology. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 0-443-06911-5.
- ^ "Endokrynologia Kliniczna" ISBN 83-200-0815-8, page 502
- ^ Chapter 11 in: Rod Flower; Humphrey P. Rang; Maureen M. Dale; Ritter, James M. (2007). Rang & Dale's pharmacology. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 0-443-06911-5.
- ^ http://stahlonline.cambridge.org/prescribers_drug.jsf?page=0521683505c95_p539-544.html.therapeutics&name=Venlafaxine&title=Therapeutics
- ^ http://www.preskorn.com/columns/9803.html
- ^ http://books.google.com/books?id=AQeQa5AtpXoC&pg=PA215&lpg=PA215&source=bl&ots=_AZBdDkZOg&sig=cyrLwQRUUijGlvTRNVpmKoLJmpc&hl=en&ei=C9HMTI3mJ5DSsAPbhNzzDg&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=2&ved=0CBcQ6AEwAQ#v=onepage&q&f=false
- ^ http://www.nature.com/npp/journal/v31/n4/abs/1300838a.html
- ^ http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6WN4-4CCGGN1-9P&_user=10&_coverDate=11%2F30%2F1984&_rdoc=1&_fmt=high&_orig=search&_origin=search&_sort=d&_docanchor=&view=c&_searchStrId=1520587233&_rerunOrigin=scholar.google&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=10&md5=5e43884bdf1f204eb2356e02096708bc&searchtype=a
- ^ a b http://sciencelinks.jp/j-east/article/200707/000020070707A0194475.php
- ^ De Backer, Daniel; et al. (March 4, 2010). "Comparison of Dopamine and Norepinephrine in the Treatment of Shock". New England Journal of Medicine 362 (9): 11.
- ^ a b c d Unless else specified in table, then ref is: Rang, H. P. (2003). Pharmacology. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 0-443-07145-4. Page 129
- ^ Kanazawa, Kazuki; Hiroyuki Sakakibara (2000). "High content of Dopamine, a strong antioxidant, in Cavendish banana" (PDF). Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry 48 (3): 844–848. doi:10.1021/jf9909860. http://152.1.118.33/Files/Journal%20of%20Agricultural%20and%20Food%20Chemistry%202000%2048%20(3)%20844-848.pdf. Retrieved 8 November 2007.
Phenethylamines Phenethylamines Psychedelics: 2C-B • 2C-B-FLY • 2C-C • 2C-D • 2C-E • 2C-F • 2C-G • 2C-I • 2C-N • 2C-P • 2C-SE • 2C-T • 2C-T-2 • 2C-T-4 • 2C-T-7 • 2C-T-8 • 2C-T-9 • 2C-T-13 • 2C-T-15 • 2C-T-17 • 2C-T-21 • 2C-TFM • 2C-YN • Allylescaline • DESOXY • Escaline • Isoproscaline • Jimscaline • Macromerine • MEPEA • Mescaline • Metaescaline • Methallylescaline • Proscaline • Psi-2C-T-4 • TCB-2
Stimulants: 2-OH-PEA • β-Me-PEA • Hordenine • N-Me-PEA • Phenethylamine (PEA)
Entactogens: Lophophine • MDPEA • MDMPEA
Others: BOH • DMPEAAmphetamines
PhenylisopropylaminesPsychedelics: 3C-BZ • 3C-E • 3C-P • Aleph • Beatrice • Bromo-DragonFLY • D-Deprenyl • DMA • DMCPA • DMMDA • DOB • DOC • DOEF • DOET • DOI • DOM • DON • DOPR • DOTFM • Ganesha • MMDA • MMDA-2 • Psi-DOM • TMA • TeMA
Stimulants: 4-MA • 4-MMA • 4-MTA • 5-IT • Alfetamine • Amfecloral • Amfepentorex • Amphetamine (Dextroamphetamine, Levoamphetamine) • Amphetaminil • Benfluorex • Benzphetamine • Cathine • Clobenzorex • Dimethylamphetamine • Ephedrine (EPH) • Ethylamphetamine • Fencamfamine • Fencamine • Fenethylline • Fenfluramine (Dexfenfluramine) • Fenproporex • Fludorex • Furfenorex • Isopropylamphetamine • Lefetamine • Mefenorex • Methamphetamine (Dextromethamphetamine, Levomethamphetamine) • Methoxyphenamine • MMA • Norfenfluramine • Oxilofrine • Ortetamine • PBA • PCA • Phenpromethamine • PFA • PFMA • PIA • PMA • PMEA • PMMA • Phenylpropanolamine (PPA) • Prenylamine • Propylamphetamine • Pseudoephedrine (PSE) • Sibutramine • Tiflorex (Flutiorex) • Tranylcypromine • Xylopropamine • Zylofuramine
Entactogens: 5-APDB • 6-APB • 6-APDB • EDA • IAP • MDA • MDEA • MDHMA (FLEA) • MDMA ("Ecstasy") • MDOH • MMDMA • NAP • TAP
Others: Amiflamine • DFMDA • D-Deprenyl • L-Deprenyl (Selegiline)Phentermines Stimulants: Chlorphentermine • Cloforex • Clortermine • Etolorex • Mephentermine • Pentorex (Phenpentermine) • Phentermine
Entactogens: MDPH • MDMPHCathinones Stimulants: Amfepramone • Brephedrone • Buphedrone • Bupropion (Amfebutamone) • Cathinone (Propion) • Dimethylcathinone (Dimethylpropion, Metamfepramone) • Ethcathinone (Ethylpropion) • Flephedrone • Methcathinone (Methylpropion) • Mephedrone • Methedrone
Entactogens: Ethylone • MethylonePhenylisobutylamines Phenylalkylpyrrolidines Stimulants: α-PBP • α-PPP • α-PVP • MDPBP • MDPPP • MDPV • MOPPP • MPBP • MPHP • MPPP • Naphyrone • PEP • Prolintane • PyrovaleroneCatecholamines
(and relatives..)6-FNE • 6-OHDA • α-Me-DA • α-Me-TRA • Adrenochrome • Ciladopa • D-DOPA (Dextrodopa) • Dopamine • Epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Epinine • Fenclonine • Ibopamine • L-DOPA (Levodopa) • L-DOPS (Droxidopa) • L-Phenylalanine • L-Tyrosine • meta-Octopamine • meta-Tyramine • Metanephrine • Metirosine • Methyldopa • Nordefrin (Levonordefrin) • Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) • Normetanephrine • para-Octopamine • para-TyramineMiscellaneous Amidephrine • Arbutamine • Cafedrine • Denopamine • Dobutamine • Dopexamine • Etafedrine • Ethylnorepinephrine • Etilefrine • Famprofazone • Gepefrine • Isoprenaline (Isoproterenol) • Isoetarine • Metaraminol • Metaterol • Methoxamine • Norfenefrine • Orciprenaline • Phenylephrine (Neosynephrine) • Phenoxybenzamine • Prenalterol • Pronethalol • Propranolol • Salbutamol (Albuterol; Levosalbutamol) • Synephrine (Oxedrine) • Theodrenaline • XamoterolEndocrine system: hormones (Peptide hormones · Steroid hormones) Endocrine
glandsTestis: testosterone · AMH · inhibin
Ovary: estradiol · progesterone · activin and inhibin · relaxin (pregnancy)
Placenta: hCG · HPL · estrogen · progesteroneIslet-Acinar
AxisNon-end.
glandsThymus: Thymosin (Thymosin α1, Thymosin beta) · Thymopoietin · Thymulin
Digestive system: Stomach: gastrin · ghrelin · Duodenum: CCK · GIP · secretin · motilin · VIP · Ileum: enteroglucagon · peptide YY · Liver/other: Insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1, IGF-2)
Adipose tissue: leptin · adiponectin · resistin
Kidney: JGA (renin) · peritubular cells (EPO) · calcitriol · prostaglandin
Heart: Natriuretic peptide (ANP, BNP)Cardiac stimulants excluding cardiac glycosides (C01C) Adrenergic and
dopaminergic agentsαβmixedBothUnknown/ungroupedPhosphodiesterase inhibitors (PDE3I) Other cardiac stimulants Adrenergics Receptor ligands Agonists: 5-FNE • 6-FNE • Amidephrine • Anisodamine • Anisodine • Cirazoline • Dipivefrine • Dopamine • Ephedrine • Epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Etilefrine • Ethylnorepinephrine • Indanidine • Levonordefrin • Metaraminol • Methoxamine • Methyldopa • Midodrine • Naphazoline • Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) • Octopamine • Oxymetazoline • Phenylephrine • Phenylpropanolamine • Pseudoephedrine • Synephrine • Tetrahydrozoline
Antagonists: Abanoquil • Adimolol • Ajmalicine • Alfuzosin • Amosulalol • Arotinolol • Atiprosin • Benoxathian • Buflomedil • Bunazosin • Carvedilol • CI-926 • Corynanthine • Dapiprazole • DL-017 • Domesticine • Doxazosin • Eugenodilol • Fenspiride • GYKI-12,743 • GYKI-16,084 • Indoramin • Ketanserin • L-765,314 • Labetalol • Mephendioxan • Metazosin • Monatepil • Moxisylyte (Thymoxamine) • Naftopidil • Nantenine • Neldazosin • Nicergoline • Niguldipine • Pelanserin • Phendioxan • Phenoxybenzamine • Phentolamine • Piperoxan • Prazosin • Quinazosin • Ritanserin • RS-97,078 • SGB-1,534 • Silodosin • SL-89.0591 • Spiperone • Talipexole • Tamsulosin • Terazosin • Tibalosin • Tiodazosin • Tipentosin • Tolazoline • Trimazosin • Upidosin • Urapidil • Zolertine
* Note that many TCAs, TeCAs, antipsychotics, ergolines, and some piperazines like buspirone, trazodone, nefazodone, etoperidone, and mepiprazole all antagonize α1-adrenergic receptors as well, which contributes to their side effects such as orthostatic hypotension.Agonists: (R)-3-Nitrobiphenyline • 4-NEMD • 6-FNE • Amitraz • Apraclonidine • Brimonidine • Cannabivarin • Clonidine • Detomidine • Dexmedetomidine • Dihydroergotamine • Dipivefrine • Dopamine • Ephedrine • Ergotamine • Epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Esproquin • Etilefrine • Ethylnorepinephrine • Guanabenz • Guanfacine • Guanoxabenz • Levonordefrin • Lofexidine • Medetomidine • Methyldopa • Mivazerol • Naphazoline • Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) • Phenylpropanolamine • Piperoxan • Pseudoephedrine • Rilmenidine • Romifidine • Talipexole • Tetrahydrozoline • Tizanidine • Tolonidine • Urapidil • Xylazine • Xylometazoline
Antagonists: 1-PP • Adimolol • Aptazapine • Atipamezole • BRL-44408 • Buflomedil • Cirazoline • Efaroxan • Esmirtazapine • Fenmetozole • Fluparoxan • GYKI-12,743 • GYKI-16,084 • Idazoxan • Mianserin • Mirtazapine • MK-912 • NAN-190 • Olanzapine • Phentolamine • Phenoxybenzamine • Piperoxan • Piribedil • Rauwolscine • Rotigotine • SB-269,970 • Setiptiline • Spiroxatrine • Sunepitron • Tolazoline • Yohimbine
* Note that many atypical antipsychotics and azapirones like buspirone and gepirone (via metabolite 1-PP) antagonize α2-adrenergic receptors as well.βAgonists: 2-FNE • 5-FNE • Amibegron • Arbutamine • Arformoterol • Arotinolol • BAAM • Bambuterol • Befunolol • Bitolterol • Broxaterol • Buphenine • Carbuterol • Cimaterol • Clenbuterol • Denopamine • Deterenol • Dipivefrine • Dobutamine • Dopamine • Dopexamine • Ephedrine • Epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Etafedrine • Etilefrine • Ethylnorepinephrine • Fenoterol • Formoterol • Hexoprenaline • Higenamine • Indacaterol • Isoetarine • Isoprenaline (Isoproterenol) • Isoxsuprine • Labetalol • Levonordefrin • Levosalbutamol • Mabuterol • Methoxyphenamine • Methyldopa • Orciprenaline • Oxyfedrine • Phenylpropanolamine • Pirbuterol • Prenalterol • Ractopamine • Procaterol • Pseudoephedrine • Reproterol • Rimiterol • Ritodrine • Salbutamol (Albuterol) • Salmeterol • Solabegron • Terbutaline • Tretoquinol • Tulobuterol • Xamoterol • Zilpaterol • Zinterol
Antagonists: Acebutolol • Adaprolol • Adimolol • Afurolol • Alprenolol • Alprenoxime • Amosulalol • Ancarolol • Arnolol • Arotinolol • Atenolol • Befunolol • Betaxolol • Bevantolol • Bisoprolol • Bopindolol • Bormetolol • Bornaprolol • Brefonalol • Bucindolol • Bucumolol • Bufetolol • Buftiralol • Bufuralol • Bunitrolol • Bunolol • Bupranolol • Burocrolol • Butaxamine • Butidrine • Butofilolol • Capsinolol • Carazolol • Carpindolol • Carteolol • Carvedilol • Celiprolol • Cetamolol • Cicloprolol • Cinamolol • Cloranolol • Cyanopindolol • Dalbraminol • Dexpropranolol • Diacetolol • Dichloroisoprenaline • Dihydroalprenolol • Dilevalol • Diprafenone • Draquinolol • Dropranolol • Ecastolol • Epanolol • Ericolol • Ersentilide • Esatenolol • Esmolol • Esprolol • Eugenodilol • Exaprolol • Falintolol • Flestolol • Flusoxolol • Hydroxycarteolol • Hydroxytertatolol • ICI-118,551 • Idropranolol • Indenolol • Indopanolol • Iodocyanopindolol • Iprocrolol • Isoxaprolol • Isamoltane • Labetalol • Landiolol • Levobetaxolol • Levobunolol • Levocicloprolol • Levomoprolol • Medroxalol • Mepindolol • Metalol • Metipranolol • Metoprolol • Moprolol • Nadolol • Nadoxolol • Nafetolol • Nebivolol • Neraminol • Nifenalol • Nipradilol • Oberadilol • Oxprenolol • Pacrinolol • Pafenolol • Pamatolol • Pargolol • Parodilol • Penbutolol • Penirolol • PhQA-33 • Pindolol • Pirepolol • Practolol • Primidolol • Procinolol • Pronethalol • Propafenone • Propranolol • Ridazolol • Ronactolol • Soquinolol • Sotalol • Spirendolol • SR 59230A • Sulfinalol • TA-2005 • Talinolol • Tazolol • Teoprolol • Tertatolol • Terthianolol • Tienoxolol • Tilisolol • Timolol • Tiprenolol • Tolamolol • Toliprolol • Tribendilol • Trigevolol • Xibenolol • XipranololReuptake inhibitors Selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors: Amedalin • Atomoxetine (Tomoxetine) • Ciclazindol • Daledalin • Esreboxetine • Lortalamine • Mazindol • Nisoxetine • Reboxetine • Talopram • Talsupram • Tandamine • Viloxazine; Norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors: Amineptine • Bupropion (Amfebutamone) • Fencamine • Fencamfamine • Lefetamine • Levophacetoperane • LR-5182 • Manifaxine • Methylphenidate • Nomifensine • O-2172 • Radafaxine; Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors: Bicifadine • Desvenlafaxine • Duloxetine • Eclanamine • Levomilnacipran • Milnacipran • Sibutramine • Venlafaxine; Serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors: Brasofensine • Diclofensine • DOV-102,677 • DOV-21,947 • DOV-216,303 • JNJ-7925476 • JZ-IV-10 • Methylnaphthidate • Naphyrone • NS-2359 • PRC200-SS • SEP-225,289 • SEP-227,162 • Tesofensine; Tricyclic antidepressants: Amitriptyline • Butriptyline • Cianopramine • Clomipramine • Desipramine • Dosulepin • Doxepin • Imipramine • Lofepramine • melitracen • Nortriptyline • Protriptyline • Trimipramine; Tetracyclic antidepressants: Amoxapine • Maprotiline • Mianserin • Oxaprotiline • Setiptiline; Others: Cocaine • CP-39,332 • EXP-561 • Fezolamine • Ginkgo biloba • Indeloxazine • Nefazodone • Nefopam • Pridefrine • Tapentadol • Teniloxazine • Tramadol • ZiprasidoneEnzyme inhibitors 3,4-DihydroxystyreneDBHCGS-19281A • SKF-64139 • SKF-7698Nonselective: Benmoxin • Caroxazone • Echinopsidine • Furazolidone • Hydralazine • Indantadol • Iproclozide • Iproniazid • Isocarboxazid • Isoniazid • Linezolid • Mebanazine • Metfendrazine • Nialamide • Octamoxin • Paraxazone • Phenelzine • Pheniprazine • Phenoxypropazine • Pivalylbenzhydrazine • Procarbazine • Safrazine • Tranylcypromine; MAO-A selective: Amiflamine • Bazinaprine • Befloxatone • Befol • Brofaromine • Cimoxatone • Clorgiline • Esuprone • Harmala alkaloids (Harmine, Harmaline, Tetrahydroharmine, Harman, Norharman, etc) • Methylene Blue • Metralindole • Minaprine • Moclobemide • Pirlindole • Sercloremine • Tetrindole • Toloxatone • Tyrima; MAO-B selective: D-Deprenyl • Selegiline (L-Deprenyl) • Ladostigil • Lazabemide • Milacemide • Mofegiline • Pargyline • Rasagiline • Safinamide
* Note that MAO-B inhibitors also influence norepinephrine/epinephrine levels since they inhibit the breakdown of their precursor dopamine.COMTOthers Ferrous Iron (Fe2+) • S-Adenosyl-L-Methionine • Vitamin B3 (Niacin, Nicotinamide → NADPH) • Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine, Pyridoxamine, Pyridoxal → Pyridoxal Phosphate) • Vitamin B9 (Folic acid → Tetrahydrofolic acid) • Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid) • Zinc (Zn2+)OthersActivity enhancers: BPAP • PPAP; Release blockers: Bethanidine • Bretylium • Guanadrel • Guanazodine • Guanclofine • Guanethidine • Guanoxan; Toxins: Oxidopamine (6-Hydroxydopamine)List of adrenergic drugsNeurotransmitters Amino acids Alanine · Aspartate · Cycloserine · DMG · GABA · Glutamate · Glycine · Hypotaurine · Kynurenic acid (Transtorine) · NAAG (Spaglumic acid) · NMG (Sarcosine) · Serine · Taurine · TMG (Betaine)
Endocannabinoids 2-AG · 2-AGE (Noladin ether) · AEA (Anandamide) · NADA · OAE (Virodhamine) · Oleamide · PEA (Palmitoylethanolamide) · RVD-Hpα · Hp (Hemopressin)
Gasotransmitters Monoamines Dopamine · Epinephrine (Adrenaline) · Melatonin · NAS (Normelatonin) · Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) · Serotonin (5-HT)
Purines Trace amines 3-ITA · 5-MeO-DMT · Bufotenin · DMT · NMT · Octopamine · Phenethylamine · Synephrine · Thyronamine · Tryptamine · Tyramine
Others 1,4-BD · Acetylcholine · GBL · GHB · Histamine
See also Template:NeuropeptidesCategories:- Cardiac stimulants
- Catecholamines
- Hormones of the suprarenal medulla
- Neurotransmitters
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.