- Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase
-
aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase 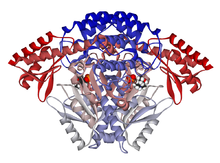
Ribbon diagram of a domestic pig DOPA decarboxylase dimer.[1] Identifiers EC number 4.1.1.28 CAS number 9042-64-2 Databases IntEnz IntEnz view BRENDA BRENDA entry ExPASy NiceZyme view KEGG KEGG entry MetaCyc metabolic pathway PRIAM profile PDB structures RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum Gene Ontology AmiGO / EGO Search PMC articles PubMed articles DOPA decarboxylase (aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase) Identifiers Symbol DDC Entrez 1644 HUGO 2719 OMIM 107930 RefSeq NM_000790 UniProt P20711 Other data EC number 4.1.1.28 Locus Chr. 7 p11 Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.28, synonyms: DOPA decarboxylase, tryptophan decarboxylase, 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase, AAAD) is a lyase enzyme.
Contents
Reactions
It catalyzes several different decarboxylation reactions:
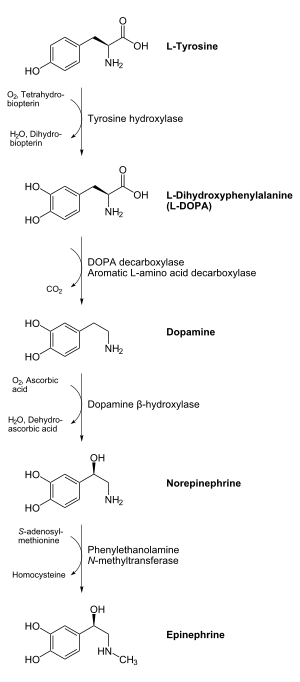
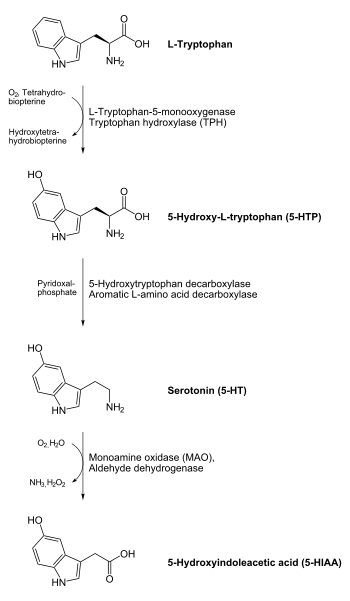
- L-DOPA to dopamine - a neurotransmitter
- 5-HTP to serotonin (5-HT) - also a neurotransmitter
- tryptophan to tryptamine - a precursor to many alkaloids found in plants and animals
The enzyme uses pyridoxal phosphate, the active form of vitamin B6, as a cofactor.
As a rate-limiting step
In normal dopamine and serotonin (5-HT) neurotransmitter synthesis, AAAD is not the rate-limiting step in either reaction. However, AAAD becomes the rate-limiting step of dopamine synthesis in patients treated with L-DOPA (such as in Parkinson's Disease), and the rate-limiting step of serotonin synthesis in people treated with 5-HTP (such as in mild depression or dysthymia). AAAD is inhibited by Carbidopa outside of the blood brain barrier to inhibit the premature conversion of L-DOPA to Dopamine in the treatment of Parkinson's.
AAAD is the rate-limiting enzyme in the formation of biogenic trace amines.
Interactive pathway map
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles. [2]
Nicotine Activity on Dopaminergic Neurons edit
Genetics
The gene encoding the enzyme is referred to as DDC and located on chromosome 7 in humans.[3] Single nucleotide polymorphisms and other gene variations have been investigated in relation to neuropsychiatric disorders, e.g., a one-base pair deletion at –601 and a four-base pair deletion at 722–725 in exon 1 in relation to bipolar disorder[4] and autism.[5]
See also
References
- ^ PDB 1JS3; Burkhard P, Dominici P, Borri-Voltattorni C, Jansonius JN, Malashkevich VN (November 2001). "Structural insight into Parkinson's disease treatment from drug-inhibited DOPA decarboxylase". Nat. Struct. Biol. 8 (11): 963–7. doi:10.1038/nsb1101-963. PMID 11685243.
- ^ The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "NicotineDopaminergic_WP1602". http://www.wikipathways.org/index.php/Pathway:WP1602.
- ^ Lisa J. Scherer, John D. McPherson, John J. Wasmuth and J. Lawrence Marsh (June 1992). "Human dopa decarboxylase: Localization to human chromosome 7p11 and characterization of hepatic cDNAs". Genomics 13 (2): 469–471. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(92)90275-W. PMID 1612608.
- ^ A. D. Borglum, T. G. Bruun, T. E. Kjeldsen, H. Ewald, O. Mors, G. Kirov, C. Russ, B. Freeman, D. A. Collier & T. A. Kruse (November 1999). "Two novel variants in the DOPA decarboxylase gene: association with bipolar affective disorder". Molecular Psychiatry 4 (6): 545–541. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4000559. PMID 10578236.
- ^ Marlene B. Lauritsen, Anders D. Borglum, Catalina Betancur, Anne Philippe, Torben A. Kruse, Marion Leboyer & Henrik Ewald (May 2002). "Investigation of two variants in the DOPA decarboxylase gene in patients with autism". American Journal of Medical Genetics 114 (4): 466–460. doi:10.1002/ajmg.10379. PMID 11992572.
External links
Carbon-carbon lyases (EC 4.1) 4.1.1: Carboxy-lyases Pyruvate decarboxylase · Oxaloacetate decarboxylase · Acetoacetate decarboxylase · Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase · Glutamate decarboxylase · Ornithine decarboxylase · Lysine decarboxylase · Phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase · Histidine decarboxylase · Uridine monophosphate synthetase/Orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase · Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase · Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase · Pyrophosphomevalonate decarboxylase · Uroporphyrinogen III decarboxylase · RuBisCO · Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase · Adenosylmethionine decarboxylase4.1.2: Aldehyde-lyases 4.1.3: Oxo-acid-lyases 4.1.99: Other B enzm: 1.1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8/10/11/13/14/15-18, 2.1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8, 2.7.10, 2.7.11-12, 3.1/2/3/4/5/6/7, 3.1.3.48, 3.4.21/22/23/24, 4.1/2/3/4/5/6, 5.1/2/3/4/99, 6.1-3/4/5-6 monoamine anabolism: Tyrosine hydroxylase · Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase · Dopamine beta hydroxylase · Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase
catabolism: Catechol-O-methyl transferase · Monoamine oxidaseglutamate→GABAanabolism: Glutamate decarboxylase
catabolism: 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase · 4-aminobutyrate transaminasearginine→NO choline→Acetylcholine anabolism: Choline acetyltransferase
catabolism: Cholinesterase (Acetylcholinesterase, Butyrylcholinesterase)Categories:- Genes on chromosome 7
- EC 4.1.1
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.