- Timolol
-
Timolol 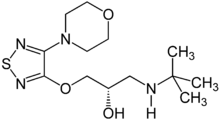
Systematic (IUPAC) name (S)-1-(tert-butylamino)-3-[(4-morpholin-4-yl-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)oxy]propan-2-ol Clinical data Trade names Timoptic AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a602022 Pregnancy cat. C(AU) C(US) Legal status ℞ Prescription only Routes oral, Ophthalmic Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability 60% Metabolism Hepatic: 80% Half-life 2.5-5 hours Excretion Renal Identifiers CAS number 26839-75-8 
ATC code C07AA06 PubChem CID 33624 IUPHAR ligand 565 DrugBank APRD00229 ChemSpider 31013 
UNII 5JKY92S7BR 
KEGG D08600 
ChEBI CHEBI:9599 
ChEMBL CHEMBL499 
Chemical data Formula C13H24N4O3S Mol. mass 316.421 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Timolol maleate is a non-selective beta-adrenergic receptor blocker.
Contents
Uses
In its oral form (Blocadren), it is used:
- to treat high blood pressure
- to prevent heart attacks
- to prevent migraine headaches[1]
In its ophthalmic form (brand names Timoptol in Italy; Timoptic), it is used to treat open-angle and occasionally secondary glaucoma by reducing aqueous humour production through blockage of the beta receptors on the ciliary epithelium. The pharmacological mechanism by which it actually does this is still unknown. First beta-blocker approved for topical use in treatment of glaucoma in the USA (1978). With monotherapy, depresses IOP 18-34% below baseline within first few treatments. However, there are short-term escape and long-term drift effects in some patients. That is, tolerance develops. May reduce extent of diurnal IOP curve up to 50%. IOP higher during sleep. 5-10x more potent beta-blocker than propranolol. Light sensitive; preserved with 0.01% benzalkonium Cl (and also comes BAC free). Can also be used in adjunctive therapy with pilocarpine or CAIs.
Side Effects
The most serious possible side effects include cardiac arrhythmias and severe bronchospasms. Timolol can also lead to fainting, congestive heart failure, depression, confusion, worsening of Raynaud's syndrome and impotence.
Usual dosage
- Children and Adults: Ophthalmic: Initial: 0.25% solution, instill 1 drop twice daily; increase to 0.5% solution if response not adequate; decrease to 1 drop/day if *controlled; do not exceed 2 drops twice daily of 0.5% solution Adults: Oral:
- Hypertension: Initial: 10 mg twice daily, increase gradually every 14 days, usual dosage: 20–40 mg/day in 2 divided doses; maximum: 60 mg/day
- Prevention of myocardial infarction: 10 mg twice daily initiated within 1–6 weeks after infarction
- Migraine headache: Initial: 10 mg twice daily, increase to maximum of 30 mg/day
Formulations
- Gel-forming solution, ophthalmic, as maleate (Timoptic-XE): 0.25% (2.5 mL, 5 mL); 0.5% (2.5 mL, 5 mL)
- Solution, ophthalmic, as hemihydrate (Betimol): 0.25% (5 mL, 10 mL, 15 mL); 0.5% (5 mL, 10 mL, 15 mL) [contains benzalkonium chloride]
- Solution, ophthalmic, as maleate: 0.25% (5 mL, 10 mL, 15 mL); 0.5% (5 mL, 10 mL, 15 mL) [contains benzalkonium chloride]
- Timoptic: 0.25% (5 mL, 10 mL); 0.5% (5 mL, 10 mL) [contains benzalkonium chloride]
- Solution, ophthalmic, as maleate [preservative free] (Timoptic OcuDose): 0.25% (0.2 mL);0.5% (0.2 mL) [single use]
- Tablet, as maleate (Blocadren): 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg
For ophthalmic use, timolol is also available combined with other medications:
- Combigan - timolol and brimonidine
- Cosopt - timolol maleate and dorzolamide hydrochloride
- DuoTrav - timolol and travoprost
- Xalacom (Pfizer) - timolol and latanoprost
Brand names
- In Canada: Apo-Timol, Apo-Timop, Gen-Timolol, Nu-Timolol, Phoxal-timolol, PMS-Timolol, Tim-AK, Timoptic, Timoptic-XE.
- In the United States: Betimol, Blocadren, Istalol, Timoptic, Timoptic-XE, Timoptic OcuDose.
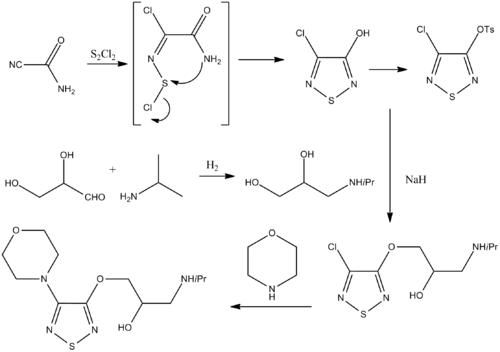
Chemical synthesis
References
- ^ Dawn A. Marcus; Philip A. Bain (27 February 2009). Effective Migraine Treatment in Pregnant and Lactating Women: A Practical Guide. シュプリンガー・ジャパン株式会社. pp. 141–. ISBN 9781603274388. http://books.google.com/books?id=Z5YWpjj89NEC&pg=PA141. Retrieved 14 November 2010.
External links
Beta blockers (C07) Beta, nonselective Alprenolol • Bopindolol • Bupranolol • Carteolol • Cloranolol • Mepindolol • Nadolol • Oxprenolol • Penbutolol • Pindolol • Propranolol • Sotalol • Tertatolol • TimololBeta1 selective Acebutolol • Atenolol • Betaxolol • Bevantolol • Bisoprolol • Celiprolol • Epanolol • Esmolol • Nebivolol • Metoprolol • Practolol • S-atenolol • TalinololAlpha + beta Other/ungrouped Ophthalmologicals: antiglaucoma preparations and miotics (S01E) Sympathomimetics Parasympathomimetics muscarinicmuscarinic/nicotinicCarbonic anhydrase inhibitors/
(sulfonamides)Beta blocking agents Prostaglandin analogues (F2α) Other agents M: EYE
anat(g/a/p)/phys/devp/prot
noco/cong/tumr, epon
proc, drug(S1A/1E/1F/1L)
This drug article relating to the cardiovascular system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.