- Nicergoline
-
Nicergoline 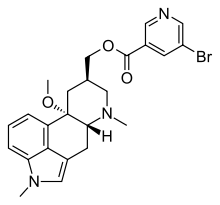
Systematic (IUPAC) name [(8β)-10-methoxy-1,6-dimethylergolin-8-yl]methyl 5-bromopyridine-3-carboxylate Clinical data AHFS/Drugs.com International Drug Names Pregnancy cat. Not recommended Legal status ℞ Prescription only Routes Oral, IM, IV Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability <5% Protein binding >90% Metabolism Extensive first-pass metabolism Half-life 13–20 hours Identifiers CAS number 27848-84-6 ATC code C04AE02 PubChem CID 34040 DrugBank APRD00617 ChemSpider 31373 
UNII JCV8365FWN 
KEGG D01290 
Chemical data Formula C24H26BrN3O3 Mol. mass 484.386 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Nicergoline (INN, marketed under the trade name Sermion) is an ergot derivative used to treat senile dementia and other disorders with vascular origins. It has been found to increase mental agility and enhance clarity and perception. It decreases vascular resistance and increases arterial blood flow in the brain, improving the utilization of oxygen and glucose by brain cells. It has similar vasoactive properties in other areas of the body, particularly the lungs.
It is used for vascular disorders such as cerebral thrombosis and atherosclerosis, arterial blockages in the limbs, Raynaud's disease, vascular migraines, and retinopathy.
Nicergoline has been registered in over fifty countries and has been used for more than three decades for the treatment of cognitive, affective, and behavioral disorders of older people.[1]
Contents
Clinical uses
Nicerogline is used in the following cases:
- Acute and chronic cerebral metabolic-vascular disorders (cerebral arteriosclerosis, thrombosis and cerebral embolism, transitory cerebral ischaemia). Acute and chronic peripheral metabolic-vascular disorders (organic and functional arteriopathies of the limbs), Raynaud’s disease and other syndromes caused by altered peripheral irrigation.
- Migraines of vascular origin
- Coadjutant therapy in clinical situations accompanied by platelet hyper-aggregability, arterial tension.
- Corio-retinal vascular disorders: , diabetic retinopathy, macular degeneration and retinal angiosclerosis
- Oto-vestibular problems of a vascular nature: dizziness, auditory hallucinations, hypoacusis.
Dosages for known conditions are usually administered at 5–10 mg three times a day, however anti-aging preventative purposes may want to consider 5 mg once or twice a day more adequate.[2]
Contraindications
Persons suffering from acute bleeding, myocardial infarction (heart conditions), hypertension, bradycardia or using alpha or beta receptor agonists should consult with their physician before use. Although toxicology studies have not shown nicergoline to have any teratogenic effect, the use of this medicine during pregnancy should be limited to those cases where it is absolutely necessary.
Nicergoline is considered unsafe in porphyria.[3]
Adverse effects
The side effects of nicergoline are usually limited to nausea, hot flushes, mild gastric upset, hypotension and dizziness.[3] At high dosages bradycardia, increased appetite, agitation, diarrhea and perspiration have been known to occur. A single case of acute interstitial nephritis has been reported.[4]
Interactions
Nicergoline is known to enhance the cardiac depressive effects of propranolol.[3] At high dosages, it is advisable to seek one’s physician's guidance if combining with potent vasodilators such as bromocriptine, Gingko biloba, picamilon, vinpocetine or xantinol nicotinate.
Mechanism of action
Nicergoline is an ergot alkaloid derivative that acts as a potent and selective alpha-1A adrenergic receptor antagonist.[5] The IC50 of nicergoline in vitro has been reported to be 0.2 nM.[6] The primary action of nicergoline is to increase arterial blood flow by vasodilation. Furthermore, it is known that nicergoline inhibits platelet aggregation. Studies have shown that nicergoline also increases nerve growth factor in the aged brain.
References
- ^ Fioravanti M, Flicker L (2001). "Efficacy of nicergoline in dementia and other age associated forms of cognitive impairment". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (4): CD003159. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003159. PMID 11687175.
- ^ Nicergoline drug insert, Pharmacia & Upjohn, October 2000
- ^ a b c Sweetman SC, ed (2009). "Supplementary drugs and other substances". Martindale: The complete drug reference (36th ed.). London: Pharmaceutical Press. pp. 2352. ISBN 978-0-85369-840-1.
- ^ Kim MJ, Chang JH, Lee SK, et al. (2002). "Acute interstitial nephritis due to nicergoline (Sermion)". Nephron 92 (3): 676–9. doi:10.1159/000064096. PMID 12372954.
- ^ Alvarez-Guerra M, Bertholom N, Garay RP (1999). "Selective blockade by nicergoline of vascular responses elicited by stimulation of alpha 1A-adrenoceptor subtype in the rat". Fundam Clin Pharmacol 13 (1): 50–8. PMID 10027088.
- ^ Moretti A, Carfagna N, Caccia C, Carpentieri M (1988). "Effect of ergolines on neurotransmitter systems in the rat brain". Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 294: 33–45. PMID 2906797.
External links
- National Electronic Library for Medicines Nicergoline for dementia and other age associated forms of cognitive impairment.
Peripheral vasodilators (C04) 2-amino-1-phenylethanol derivatives Imidazoline derivatives/
Alpha blockersNiacin and derivatives Purine derivatives Ergot alkaloids Other peripheral vasodilators Cyclandelate • Phenoxybenzamine • Vincamine • Moxisylyte • Bencyclane • Vinburnine • Sulcotidil • Buflomedil • Naftidrofuryl • Butalamine • Visnadine • Cetiedil • Cinepazide • Ifenprodil • Azapetine • FasudilCategories:- Antidementia agents
- Nicotinates
- Organobromides
- Ethers
- Ergolines
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
