- Imidazoline
-
Imidazoline 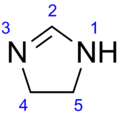 4,5-Dihydro-1H-imidazole
4,5-Dihydro-1H-imidazoleIdentifiers CAS number 504-75-6 
PubChem 68156 ChemSpider 61464 
ChEBI CHEBI:53094 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - N\1=C\NCC/1
Properties Molecular formula C3H6N2 Molar mass 70.09 g mol−1  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Imidazoline is a nitrogen-containing heterocycle with formula C3H6N2, derived from imidazole. The ring contains an imine bond, and the carbons at the 4 and 5 positions are singly bonded, rather than doubly bonded for the case of imidazole. Imidazolines are structurally related to guanidines and amidines.
 Second generation Grubbs' catalyst
Second generation Grubbs' catalyst
Like imidazole, imidazoline-based compounds have been used as N-heterocyclic carbene ligands on various transition metals. It is found in the commercially available second generation Grubbs' catalyst.
Biological role
Many imidazolines are biologically active.[1] Most bio-active derivatives bear a substituent (aryl or alkyl group) on the carbon between the nitrogen centers. Some generic names include oxymetazoline, xylometazoline, tetrahydrozoline, and naphazoline.
See also
References
- ^ N. MacInnes and S. Duty (2004). "Locomotor effects of imidazoline I2-site-specific ligands and monoamine oxidase inhibitors in rats with a unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine lesion of the nigrostriatal pathway". Br J Pharmacol 143 (8): 952–959. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0706019. PMC 1575965. PMID 15545290. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1575965.
Categories:- Imidazolines
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

