- Thyroxine
-
Thyroxine 
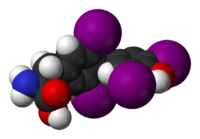 (2S)-2-amino-3-[4-(4-hydroxy-3,5-diiodophenoxy)-3,5-diiodophenyl]propanoic acid
(2S)-2-amino-3-[4-(4-hydroxy-3,5-diiodophenoxy)-3,5-diiodophenyl]propanoic acidIdentifiers CAS number 51-48-9 
PubChem 5819 UNII Q51BO43MG4 
DrugBank APRD00235 MeSH Thyroxine ChEBI CHEBI:30660 
ChEMBL CHEMBL559 
ATC code H03 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - NC(Cc1cc(I)c(Oc2cc(I)c(O)
c(I)c2)c(I)c1)C(O)=O
Properties Molecular formula C15H11I4NO4 Molar mass 776.87 g mol−1 Melting point 231–233 °C [1]
Solubility in water slightly soluble (0,105 mg·l-1 at 25 °C) [2] Hazards R-phrases - S-phrases S22, S24/25 Related compounds Related compounds Triiodothyronine (tri-iodated)
Thyronine (without iodine) (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Thyroxine, or 3,5,3',5'-tetraiodothyronine (often abbreviated as T4), a form of thyroid hormones, is the major hormone secreted by the follicular cells of the thyroid gland.
Contents
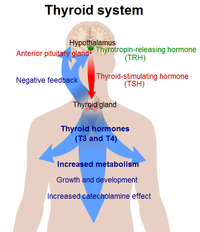
Synthesis and regulation
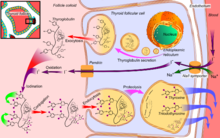
Thyroxine is synthesized via the iodination and covalent bonding of the phenyl portions of tyrosine residues found in an initial peptide, thyroglobulin, which is secreted into thyroid granules. These iodinated diphenyl compounds are cleaved from their peptide backbone upon being stimulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone.
Transport
T4 is transported in blood, with 99.95% of the secreted T4 being protein-bound, principally to thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG), and, to a lesser extent, to transthyretin and serum albumin. The half-life of thyroxine once released into the blood circulatory system is about 1 week.
Effects
T4 is involved in controlling the rate of metabolic processes in the body and influencing physical development. Administration of thyroxine has been shown to significantly increase the concentration of nerve growth factor in the brains of adult mice.[5]
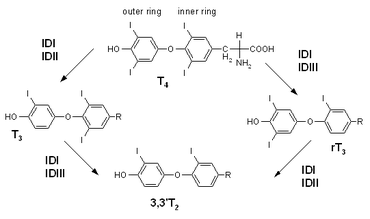
Thyroxine is a prohormone and a reservoir for the active thyroid hormone triiodothyronine (T3), which is about four times more potent. T4 is converted in the tissues by deiodinases, including thyroid hormone iodine peroxidase (TPO), to T3. The "D" isomer is called "Dextrothyroxine"[6] and is used as a lipid modifying agent.[7]
History
Thyroxine was first isolated in pure form in 1914 at the Mayo Clinic by Edward Calvin Kendall from extracts of hog thyroid glands.[8] The hormone was synthesised in 1927 by British chemists Charles Robert Harington and George Barger. It is marketed e.g. by Sandoz as Thyrex in form of 25, 100 and 150 µg tablets.
Measurement
Thyroxine can be measured as free thyroxine, which is an indicator of thyroxine activity in the body. It can also be measured as total thyroxine, which also depends on the thyroxine that is bound to thyroxine-binding globulin. A related parameter is the free thyroxine index, which is total thyroxine multiplied by thyroid hormone uptake, which, in turn, is a measure of the unbound thyroxine binding globulins.[9]
The normal human adult range of T4 in blood is 4 - 11 µg/dL
See also
Reactions
References
- ^ Harington in: Biochem. J. 1926, 20, 310.
- ^ Thyroxine in the ChemIDplus database
- ^ Walter F., PhD. Boron (2003). Medical Physiology: A Cellular And Molecular Approaoch. Elsevier/Saunders. pp. 1300. ISBN 1-4160-2328-3.
- ^ References used in image are found in image article in Commons: References.
- ^ Walker et al. (27 April 1979) Thyroxine increases nerve growth factor concentration in adult mouse brain. Science. Vol. 204, No. 4391. pp. 427 - 429.
- ^ MeSH Dextrothyroxine
- ^ C10AX01
- ^ E.C. Kendall in J. Am. Med. Assoc., 1915, Vol. 64, pp 2042-2043: The isolation in crystalline form of the compound containing iodin, which occurs in the thyroid: Its chemical nature and physiologic activity.
- ^ Military Obstetrics & Gynecology > Thyroid Function Tests In turn citing: Operational Medicine 2001, Health Care in Military Settings, NAVMED P-5139, May 1, 2001, Bureau of Medicine and Surgery, Department of the Navy, 2300 E Street NW, Washington, D.C., 20372-5300
Endocrine system: hormones (Peptide hormones · Steroid hormones) Endocrine
glandsTestis: testosterone · AMH · inhibin
Ovary: estradiol · progesterone · activin and inhibin · relaxin (pregnancy)
Placenta: hCG · HPL · estrogen · progesteroneIslet-Acinar
AxisNon-end.
glandsThymus: Thymosin (Thymosin α1, Thymosin beta) · Thymopoietin · Thymulin
Digestive system: Stomach: gastrin · ghrelin · Duodenum: CCK · GIP · secretin · motilin · VIP · Ileum: enteroglucagon · peptide YY · Liver/other: Insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1, IGF-2)
Adipose tissue: leptin · adiponectin · resistin
Kidney: JGA (renin) · peritubular cells (EPO) · calcitriol · prostaglandin
Heart: Natriuretic peptide (ANP, BNP)Categories:- Hormones of the thyroid gland
- Hormones of the hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axis
- Iodinated tyrosine derivatives
- Halogen-containing natural products
- Thyroid hormones
- Aromatic compounds
- NC(Cc1cc(I)c(Oc2cc(I)c(O)
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.