- Serum albumin
-
This article is about the family of mammalian albumin proteins. For the human variant, see human serum albumin. For the cow variant, see bovine serum albumin.
Serum albumin, often referred to simply as albumin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ALB gene.[1][2][3]
Serum albumin is the most abundant plasma protein in mammals. Albumin is essential for maintaining the osmotic pressure needed for proper distribution of body fluids between intravascular compartments and body tissues. It also acts as a plasma carrier by non-specifically binding several hydrophobic steroid hormones and as a transport protein for hemin and fatty acids. Too much serum albumin in the body can be harmful.
Contents
Function
Major contributors to oncotic pressure (known also as colloid osmotic pressure) of plasma; carriers for various substances.
Albumin is a soluble, monomeric protein which comprises about one-half of the blood serum protein. Albumin functions primarily as a carrier protein for steroids, fatty acids, and thyroid hormones and plays a role in stabilizing extracellular fluid volume. Albumin is a globular un-glycosylated serum protein of molecular weight 65,000. Albumin is synthesized in the liver as preproalbumin which has an N-terminal peptide that is removed before the nascent protein is released from the rough endoplasmic reticulum. The product, proalbumin, is in turn cleaved in the Golgi vesicles to produce the secreted albumin.[3]
Types
Serum albumin is widely distributed in mammals. Examples include:
- The human version is human serum albumin.
- Bovine serum albumin, or BSA, is commonly used in immunodiagnostic procedures, clinical chemistry reagents, cell culture media, protein chemistry research and molecular biology laboratories (usually to leverage its non-specific protein binding properties).
Physical properties
Albumin (when ionized in water at pH 7.4, as found in the body) is negatively charged. The glomerular basement membrane is also negatively charged in the body; some studies suggest that this prevents the filtration of albumin in the urine. According to this theory, that charge plays a major role in the selective exclusion of albumin from the glomerular filtrate. A defect in this property results in nephrotic syndrome leading to albumin loss in the urine. Nephrotic syndrome patients are sometimes given albumin to replace the lost albumin.
Because smaller animals (for example rats) function at a lower blood pressure, they need less oncotic pressure to balance this, and thus need less albumin to maintain proper fluid distribution.
Structure
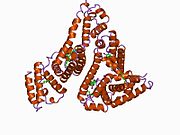
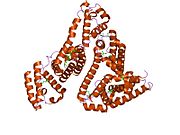
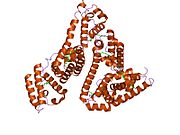
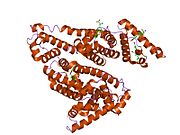
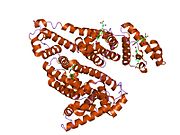
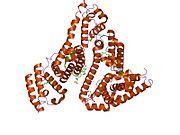
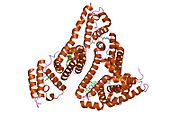
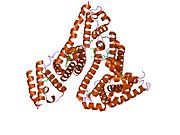
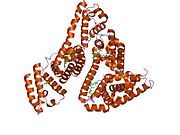
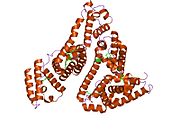
The general structure of albumin is characterized by several long α (alpha) helices, this allows it to maintain a relatively static shape, something essential for regulating blood pressure.
Serum albumin contains eleven distinct binding domains for hydrophobic compounds. One hemin and six long-chain fatty acids can bind to serum albumin at the same time.[4]
Serum albumin family 
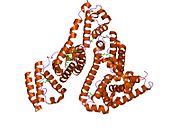
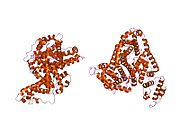
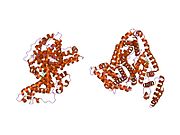
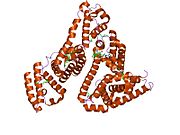
Structure of human serum albumin.[5] Identifiers Symbol Serum_albumin Pfam PF00273 Pfam clan CL0282 InterPro IPR014760 SMART SM00103 PROSITE PS51438 SCOP 1ao6 Available protein structures: Pfam structures PDB RCSB PDB; PDBe PDBsum structure summary See also
- Human serum albumin
- Bovine serum albumin
- Blood plasma fractionation
- Chromatography in blood processing
References
- ^ Hawkins JW, Dugaiczyk A (1982). "The human serum albumin gene: structure of a unique locus". Gene 19 (1): 55–8. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(82)90188-3. PMID 6292049.
- ^ Harper ME, Dugaiczyk A (July 1983). "Linkage of the evolutionarily-related serum albumin and alpha-fetoprotein genes within q11-22 of human chromosome 4". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 35 (4): 565–72. PMC 1685723. PMID 6192711. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1685723.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: albumin". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=213.
- ^ Zunszain PA, Ghuman J, Komatsu T, Tsuchida E, Curry S (July 2003). "Crystal structural analysis of human serum albumin complexed with hemin and fatty acid". BMC Struct. Biol. 3: 6. doi:10.1186/1472-6807-3-6. PMC 166163. PMID 12846933. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=166163.
- ^ Sugio S, Kashima A, Mochizuki S, Noda M, Kobayashi K (June 1999). "Crystal structure of human serum albumin at 2.5 A resolution". Protein Eng. 12 (6): 439–46. doi:10.1093/protein/12.6.439. PMID 10388840.
External links
- The Serum Albumin Protein
- RCSB Protein Data Bank : Molecule of the Month - Serum Albumin
- Albumin binding prediction
PDB gallery 1ao6: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN1bj5: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH MYRISTIC ACID1bke: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN IN A COMPLEX WITH MYRISTIC ACID AND TRI-IODOBENZOIC ACID1bm0: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN1e78: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN1e7a: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH THE GENERAL ANESTHETIC PROPOFOL1e7b: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH THE GENERAL ANESTHETIC HALOTHANE1e7c: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH MYRISTIC ACID AND THE GENERAL ANESTHETIC HALOTHANE1e7e: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH DECANOIC ACID (CAPRIC ACID)1e7f: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH DODECANOIC ACID (LAURIC ACID)1e7g: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH TETRADECANOIC ACID (MYRISTIC ACID) HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH MYRISTIC ACID1e7h: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH HEXADECANOIC ACID (PALMITIC ACID)1e7i: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH OCTADECANOIC ACID (STEARIC ACID)1gni: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH CIS-9-OCTADECENOIC ACID (OLEIC ACID)1gnj: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH CIS-5,8,11,14-EICOSATETRAENOIC ACID (ARACHIDONIC ACID)1h9z: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH MYRISTIC ACID AND THE R-(+) ENANTIOMER OF WARFARIN1ha2: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH MYRISTIC ACID AND THE S-(-) ENANTIOMER OF WARFARIN1hk1: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH THYROXINE (3,3',5,5'-TETRAIODO-L-THYRONINE)1hk2: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN MUTANT R218H COMPLEXED WITH THYROXINE (3,3',5,5'-TETRAIODO-L-THYRONINE)1hk3: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN MUTANT R218P COMPLEXED WITH THYROXINE (3,3',5,5'-TETRAIODO-L-THYRONINE)1hk4: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH THYROXINE (3,3',5,5'-TETRAIODO-L-THYRONINE) AND MYRISTIC ACID (TETRADECANOIC ACID)1hk5: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN MUTANT R218H COMPLEXED WITH THYROXINE (3,3',5,5'-TETRAIODO-L-THYRONINE) AND MYRISTIC ACID (TETRADECANOIC ACID)1n5u: X-RAY STUDY OF HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH HEME1o9x: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH TETRADECANOIC ACID (MYRISTIC ACID) AND HEMIN1tf0: Crystal structure of the GA module complexed with human serum albumin1uor: X-RAY STUDY OF RECOMBINANT HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN. PHASES DETERMINED BY MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT METHOD, USING LOW RESOLUTION STRUCTURE MODEL OF TETRAGONAL FORM OF HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN1ysx: Solution structure of domain 3 from human serum albumin complexed to an anti-apoptotic ligand directed against Bcl-xL and Bcl-22bx8: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH AZAPROPAZONE2bxa: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH 3-CARBOXY-4-METHYL-5-PROPYL-2-FURANPROPANOIC ACID (CMPF)2bxb: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH OXYPHENBUTAZONE2bxc: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH PHENYLBUTAZONE2bxd: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH WARFARIN2bxe: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH DIFLUNISAL2bxf: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH DIAZEPAM2bxg: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH IBUPROFEN2bxh: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH INDOXYL SULFATE2bxi: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH MYRISTATE AND AZAPROPAZONE2bxk: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH MYRISTATE, AZAPROPAZONE AND INDOMETHACIN2bxl: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH MYRISTATE AND 3,5-DIIODOSALICYLIC ACID2bxm: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH MYRISTATE AND INDOMETHACIN2bxn: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH MYRISTATE AND IODIPAMIDE2bxo: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH MYRISTATE AND OXYPHENBUTAZONE2bxp: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH MYRISTATE AND PHENYLBUTAZONE2bxq: HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN COMPLEXED WITH MYRISTATE, PHENYLBUTAZONE AND INDOMETHACIN2i2z: Human serum albumin complexed with myristate and aspirin2i30: Human serum albumin complexed with myristate and salicylic acidProteins: Globular proteins Serum globulins serpins: alpha-1 (Alpha 1-antichymotrypsin, Alpha 1-antitrypsin) · alpha-2 (Alpha 2-antiplasmin) · Antithrombin (Heparin cofactor II)
carrier proteins: alpha-1 (Transcortin) · alpha-2 (Ceruloplasmin) · Retinol binding protein
other: alpha-1 (Orosomucoid) · alpha-2 (alpha-2-Macroglobulin, Haptoglobin)carrier proteins: Sex hormone-binding globulin · Transferrin
other: Angiostatin · Hemopexin · Beta-2 microglobulin · Factor H · Plasminogen · ProperdinOtherOther globulins Albumins Serum albuminOthersee also disorders of globin and globulin proteins
B proteins: BY STRUCTURE: membrane, globular (en, ca, an), fibrous
This protein-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.