- Transcortin
-
Serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A (alpha-1 antiproteinase, antitrypsin), member 6, also Corticosteroid-Binding Globulin or Transcortin 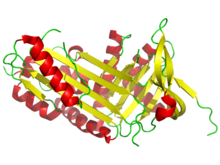
Structure of corticosteroid-binding globulin in complex with cortisol. Identifiers Symbol SERPINA6 Alt. symbols CBG Entrez 866 HUGO 1540 OMIM 122500 RefSeq NM_001750 UniProt P08185 Other data Locus Chr. 14 q32.1 Transcortin, also corticosteroid-binding globulin or CBG, is officially called serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A (alpha-1 antiproteinase, antitrypsin), member 6.
It is an alpha-globulin.
Contents
Binding
Transcortin binds several steroid hormones:
- Cortisol. Approximately 75% of the cortisol in circulation is bound to this plasma protein. (The rest is bound to serum albumin.) The cortisol is thought to be biologically active only when it is not bound to transcortin.
- 11-Deoxycorticosterone (DOC)
Production
Transcortin is produced by the liver and is regulated by estrogens. Therefore, plasma transcortin levels increase during pregnancy, and are decreased in cirrhosis.
Clinical
Mutations in this gene are rare. To date only five cases have been reported.[1] All cases have been associated with generalised pain and fatigue. This mechanism for these symptoms is not known. This condition must be distinguished from secondary hypocortisolism. Exogenous hydrocortisone does not appear to improve the fatigue.
References
- ^ Torpy DJ, Lundgren BA, Ho JT, Lewis JG, Scott HS, Mericq V (2011) CBG Santiago: a Novel CBG Mutation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab
External links
Fatty acid Hormone peptide hormone: Follistatin · Growth hormone binding protein · Insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP1, IGFBP2, IGFBP3, IGFBP4, IGFBP5, IGFBP6, IGFBP7) · Neurophysins (Neurophysin I, II)
steroid hormone: Sex hormone binding globulin/Androgen binding protein · Transcortin · Thyroxine-binding globulin · TransthyretinMetal/element calcium (Calcium-binding protein, Calmodulin-binding proteins) · copper (Ceruloplasmin) · iron (Iron-binding proteins, Transferrin receptor)Vitamin Other B proteins: BY STRUCTURE: membrane, globular (en, ca, an), fibrous Proteins: Globular proteins Serum globulins serpins: alpha-1 (Alpha 1-antichymotrypsin, Alpha 1-antitrypsin) · alpha-2 (Alpha 2-antiplasmin) · Antithrombin (Heparin cofactor II)
carrier proteins: alpha-1 (Transcortin) · alpha-2 (Ceruloplasmin) · Retinol binding protein
other: alpha-1 (Orosomucoid) · alpha-2 (alpha-2-Macroglobulin, Haptoglobin)carrier proteins: Sex hormone-binding globulin · Transferrin
other: Angiostatin · Hemopexin · Beta-2 microglobulin · Factor H · Plasminogen · ProperdinOtherOther globulins Albumins Othersee also disorders of globin and globulin proteins
B proteins: BY STRUCTURE: membrane, globular (en, ca, an), fibrousinhibitory Alpha 1-antichymotrypsin · Alpha 1-antitrypsin · Alpha 2-antiplasmin · Antithrombin · C1-inhibitor · Heparin cofactor II · Protein C inhibitor · Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 · Plasminogen activator inhibitor-2 · Protein Z-related protease inhibitor
SERPINA1 · SERPINA2 · SERPINA3 · SERPINA4 · SERPINA5 · SERPINA6 · SERPINA7 · SERPINA8 · SERPINA9 · SERPINA14
SERPINB1 · SERPINB2 · SERPINB3 · SERPINB4 · SERPINB5 · SERPINB6 · SERPINB7 · SERPINB8 · SERPINB9 · SERPINB13
SERPINC1 · SERPIND1 · SERPINE1 · SERPINE2 · SERPINE2 · SERPINF1 · SERPING1 · SERPINH1 · SERPINI1 · SERPINI2Cross class inhibitory noninhibitory Heat shock protein 47 · Maspin · Ovalbumin · SERPINF1 · Thyroxine-binding globulin · Transcortin · SERPINF1see also disorders of globin and globulin proteins Mucoproteins OtherProteoglycan Testican · PerlecanChondroitin sulfate proteoglycans: Aggrecan · Neurocan · Brevican · CD44 · CSPG4 · CSPG5 · Platelet factor 4 · Structural maintenance of chromosomes 3Fibromodulin · Lumican · KeratocanOther Activin and inhibin · ADAM · Alpha 1-antichymotrypsin · Apolipoprotein H · CD70 · Asialoglycoprotein · Avidin · B-cell activating factor · 4-1BB ligand · Cholesterylester transfer protein · Clusterin · Colony-stimulating factor · Hemopexin · Lactoferrin · Membrane glycoproteins · Myelin protein zero · Osteonectin · Protein C · Protein S · Serum amyloid P component · Sialoglycoprotein (CD43, Glycophorin, Glycophorin C) · Thrombopoietin · Thyroglobulin · Thyroxine-binding proteins · Transcortin · Tumor necrosis factor-alpha · Uteroglobin · Vitronectinbiochemical families: prot · nucl · carb (glpr, alco, glys) · lipd (fata/i, phld, strd, gllp, eico) · amac/i · ncbs/i · ttpy/i
This enzyme-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
